CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
advertisement

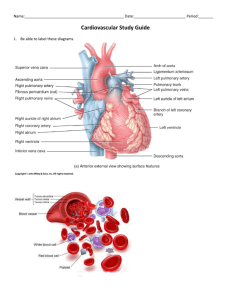
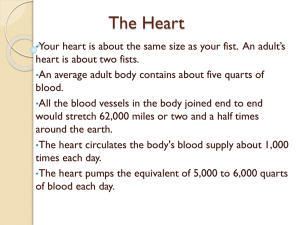
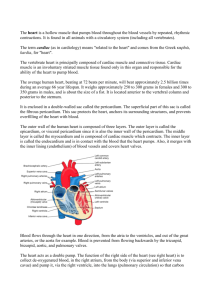
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANGIE FRANCO SARAH MCGARRY LILIANA MEDINA Period 2 FUNCTIONS AND GOAL • Pumps 7,000 liters of blood throughout the body every day • Goal = circulate blood so that the body gets enough oxygen and wastes don’t accumulate • Pulmonary Circuit: sends oxygen depleted blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and unload carbon dioxide • Systemic Circuit: send oxygen rich blood and nutrients to all body cells and removes wastes THE HEART CHAMBERS • Atria: upper chamber - Thin walls and receive blood returning to the heart - Auricles: small earlike projections, extend anteriorly from the atria, slightly increasing atrial volume • Ventricle: lower chamber - Force the blood out of the heart and into the arteries left - Interatrial septum separates the right from the atrium - Interventricular septum separates the two THE HEART VALVES • Tricuspid Valve (right atrioventricular valve) • Papillary muscle - chordae tendinea • blood move from right atrium to right ventricle • prevents blood from moving in the wrong direction • Pulmonary Valve (pulmonary semilunar valve) • opens when right ventricle contracts • prevents return flow into the right ventricle THE HEART VALVES • Mitral Valve (left atrioventricular valve or bicuspid valve) • prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium when ventricle contracts • Aortic Valve (aortic semilunar valve) • blood leaves left ventricle as it contracts • prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle COVERINGS • Pericardium: (pericardial sac) serous membrane, surrounds the heart • • Fibrous Pericardium: outer fibrous bag • Epicardium: (visceral pericardium) innermost layer of serous membrane Parietal Pericardium: inner lining of fibrous pericardium • Myocardium: muscle tissue of the heart • Endocardium: inner lining of the heart chambers BLOOD PATH Aorta RRight Coronary Artery y Posterior interventricular artery Walls of Right Atrium and Right Ventricle Left Coronary Artery Marginal artery Artery Circumflex Artery Ventricular Walls Walls of Left Atrium and Left Ventricle Cardiac Veins Coronary Sinus Right Atrium Anterior Interventricular Artery Ventricular Walls FLOW IN SYSTEM CIRCUIT VS. PULMONARY CIRCUIT BLOOD VESSELS • Layers: • Arteries: carry blood away from heart - Aorta - Pulmonary artery • Veins: carry blood towards the heart - Pulmonary vein - Coronary sinus - Superior vena cava - Inferior vena cava Capillaries: connects an arteriole and a venule 1.Tunica Interna 2.Tunica Media 3.Tunica Externa BLOOD PRESSURE • force the blood exerts against the inner walls of blood vessels • pressure in arteries by branches of the aorta • varies depending on activity, situation, disease states • Regulated by nervous and endocrine system • Hypotension and Hypertension • Filtration: force which pushes fluid into tissue spaces and out of vascular sites • glomerular filtration SYSTOLE VS. DIASTOLE • systolic pressure: the maximum pressure achieved during ventricular contraction • Systole: contraction of the heart especially of the ventricles, during which blood is forced into the aorta and pulmonary artery http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/st udent_view0/chapter22/animation__the_cardiac_cycl e__quiz_1_.html • diastolic pressure: the lowest pressure achieved during ventricular contraction • Diastole: the phase in which the heart relaxes between contractions PLASMA & PROTEINS • Plasma: clear, straw-colored, liquid portion of the blood in which the cells and platelets are suspended • Transports nutrients, gases and vitamins • Regulates fluid and electrolyte balance • Maintains favorable pH Proteins • Albumins • Globulins • Fibrinogen CARDIAC OUTPUT • Volume discharged from the ventricular per minute • Limited by the amount of blood returning to the ventricles • Cardiac output= stroke volume x heart rate • Stroke volume/ heart rate decreases = cardiac output decreases and blood pressure decreases HEARTBEAT & SOUNDS • indicate condition of the heart valves • vibrations produced as the blood flow is speeded or slowed • opening and closing of the valves • contraction and relaxation • Mitral valve: heard from the 5th intercostal space , left • Tricuspid valve: heard at the 5th intercostal space, right HEARTBEAT AND SOUNDS • (lubb) • (dupp) • Split: closure of the pulmonary and the aortic valves are long • Murmur: cusps not closed completely • Aortic sound: right • Pulmonic sound: left CONDUCTION • group of specialized cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the heart send signals to the heart muscle causing it to contract • location: myocardium • function: initiate and distribute cardiac impulses throughout the myocardium • http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_ view0/chapter22/animation__conducting_system_of_the_he art.html ○ Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle) ■ regulated by conduction control center of the ventricles, the AV node ■ located in upper portion of the interventricular septum ○ Bundle Branches ■ regulated by the AV node CELLS, FIBERS, ETC. ○ Purkinje fibers- (conduction myofibers) ■ regulated by both SA & AV nodes ○ cardiac muscle cells ■ autorhythmicity (automaticity) ○ some smooth cells - electrical synapse; gap junction; no neurotransmitter ■ autorhythmicity SA NODE V. AV NODE ● AV node (atrioventricular node) ○ location: inferior portion of septum that separates the atria and just beneath the endocardium ● SA node (sinoatrial node) ○ located in the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava Electrical System Work Cited • "Cardiac Conduction System." Nottingham.ac.uk. U of Nottingham, n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2015. <http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/nursing/practice/resources/cardiology/function/conduction.php>. • Chen, Michael A., Dr. "Cardiac Conduction System." nlm.nih.gov. A.D.A.M., n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2015. <http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/anatomyvideos/000021.htm>. • Shier, David, Jackie Butler, and Ricki Lewis. Hole’s Human Anatomy & Physiology. Eleventh ed. New York: Michelle Watnick, 2007. Print. 24 Feb. 2015. • "Your Heart's Electrical System." nhlbi.nih.gov. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2015. <http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/electrical>.