Survey of A&P/Chapter 11 Cardiovascular
advertisement

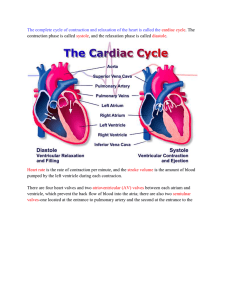
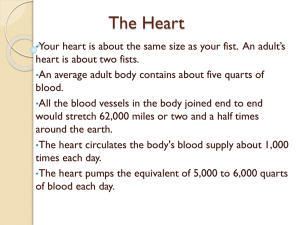
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Heart (Cardiac Muscle) • General – continuous, rhythmic beating – delivers: to cells thru blood • • • • oxygen nutrients hormones electrolytes – pump to lungs • exchange CO2 for O2 Heart • Anatomy of the Heart – lies in the mediastinum • medial cavity of the chest • big as fist 2nd rib and 5th rib – pericardium • sac around heart • film of serous fluid friction free • Pericarditis - inflammation – heart wall • epicardium - visceral pericardium • myocardium - thick cardiac muscle and connective tissue • endocardium – endothelial lining of heart chambers • Chambers of the Heart – right atrium • recieves blood “deoxygenated” • superior & inferior vena cava • tricuspid valve – right ventricle • pumps blood to lungs • pulmonary artery • semilunar valve “pulmonary” – left atrium • recieves blood “oxygenated” • pulmonary veins bicupsid(mitral) valve – left ventricle • pumps blood to body • aorta • semilunar valve “aortic” • Septum – divides chambers (wall) • Auricles – wrinkled flap like appendages on atria – musculi pectinati • muscle bundles in atria • Valves – prevent backflow – atrioventricular valves • tricupsid valve • mitral valve “bicuspid” • chordae tendinae – white cords anchor flaps of valves attached to papillary muscles – semilunar valves • pulmonary • aortic • Cardiac Circulation – coronary arteries - O2 and nutrients – arise from aorta – coronary veins take CO2 & wastes – coronary sinus ---> right atrium • General Cardiac Function – 70 beats/min – its own conduction system – contracts independently • Conduction – sinoatrial (SA) node “pacemaker” • in right atrium ---> depolarization • atrical contract – internodal fiber bundles • depolarization node to node – atrioventricular (AV) node • junction of atria & ventricle • ventricular contraction • Atrioventricular Bundle – purkinje fibers – rapid impulses • failed pacemakers – slow h.r. – bradycardia < 60 beats/min – rapid h.r. -tachycardia > 100 beats/min – fibrillation • rapid uncoordinated heart beat • Cardiac Cycle – initiated by the SA node – Cycle • Systole -contraction ventricles • Diastole -relaxed atria fill • Heart Sounds – auscultation – ‘lubb dubb’ • Lubb AV valves close • Dubb semilunar valves close – murmurs • abnormal heart sound • incompetent valve swishing sound • Stenosed- narrow valves • Cardiac Output – stroke volume • volume of blood pumped w/ each beat – cardiac output • 4900 ml/min ---> 4.9 l/min • SV x VR 70 ml/ beat x 70 beats/ min – exercise • increase SV increase venous return – cardiac reserve • ability of heart to increase cardiac output • Stroke Volume Regulation – healthy heart increase SV – Starling’s Law of the Heart • more cardiac muscle stretches greater stroke volume • Regulation of Heart Rate – autonomic nervous system • parasympathetic innervation –vagus nerve ---> ACH –slows h.r. • sympathetic innervation –speeds h.r. stimulate SA node –norepinephrine –AV cardiac muscle – hormones and ions • epinephrine speeds up h.r. • Ca++ levels down - h.r. down • thyroxine levels up -h.r. up – temperature, gender, exercise, & age • fetus 140 - 160 • heat h.r. goes up – congestive heart failure • hypertension • worn out and weak • age & coronary atherosclerosis • Electrocardiogram – three basic features of ECG • atria –P wave- depolarization of atriaatria contract • ventricle –QRS complex depolarization of ventricles –T wave repolarization of ventricles – shapes of the waves and the time intervals • Disturbances in Heart Rate & Rhythm – myocardial infarction- heart attack – Ischemia- lack of oxygen – Fibrillation- irregular heart beat – Atherosclerosis- narrowing of arteries – Artherosclerosis- scar tissue Ca build up Systemic & Pulmonary Circulation • Capillaries ----> cells ----> capillaries --->venuoles ---> veins ---> superior or inferior vena cava ---> right atrium --> tricuspid valve --> right ventricle --> pulmonary valve ---> pulmonary artery ---> lungs ---> pulmonary veins ---> left atrium ---> bicuspid valve --> left ventricle ---> aortic valve ---> aorta --->arteries ---> arterioles ---- • General Blood Vessels – closed system • blood in vessels – principal types of blood vessels – arteries • blood away from heart • arterioles – capillaries • exchange materials w/ cells • capillary beds – veins • venuoles • blood toward heart • Blood Vessel Wall – tunica interna ~ simple squamos – tunica media ~ smooth muscle – tunica adventitia ( externa) ~ connective • Major Arteries – aorta ~ largest artery • head and neck – carotid, brachiocephalic, subclavian • upper limbs and thorax – brachial, radial, ulnar • abdomen – hepatic • pelvis and lower limbs – renal - kidneys • Major Veins – superior vena cava • • • • head and neck jugular & subclavian upper limbs and thorax brachial & radial – inferior vena cava • • • • abdomen hepatic and mesentaric pelvis and lower limbs renal and femoral • saphenous (LONGEST VEIN) • Capillaries – wall only one layer thick – exchange between blood & tissues • nutrients, oxygen, CO2, & wastes • Special Circulation – brain • Circle of Willis • brain blood barrier – hepatic • digestive organs • liver – mesenteric • intestine Physiology of Circulation • Pulse – expansion and recoiling of artery – carotid, brachial, and radial • Blood Pressure – general • systolic / diastolic • pressure against walls of artery – Gradient auscultatory method • 120 mm Hg / 80 mm Hg brachial artery – Measuring Ventricular pressure • Systolic- contraction • Diastolic- relaxation • Factors Effecting Blood Pressure – resistance • • • • • • directly related to cardiac output vasoconstriction ~ sympathetic chemicals , temperature, diet Kidneys- blood volume autonomic nervous system Blood viscosity- > resistance – variations in pressure • hypotension – systolic < 100 mm Hg – diet • hypertension – > 140 / 90 sustained – myocardium enlarged Cardiovascular Disease • Developmental – con genital – heart defects • Aging – atherosclerosis ~ narrowing of veins – cholesterol “LDL’s” ~ form plaque – ischemic heart disease ~ lack of oxygen – angina pectoris ~ heart pains – myocardinal infarction ~ heart attack – varicose veins ~ venous valves weaken thrombophlebitis