Unit II Study Guide
advertisement
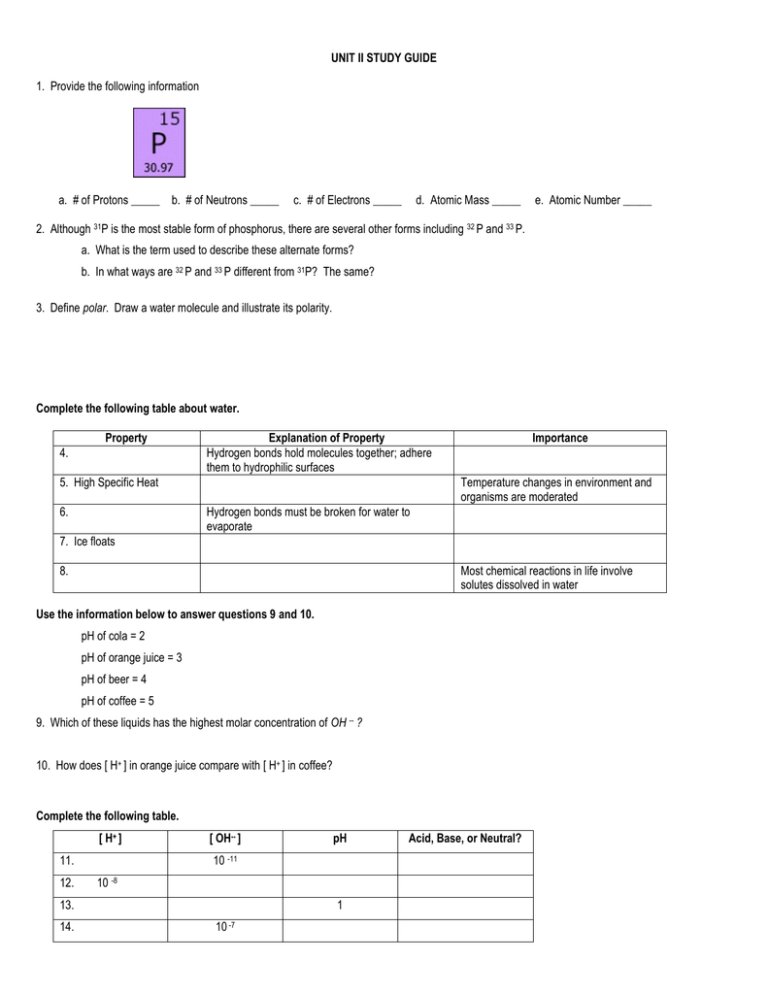
UNIT II STUDY GUIDE 1. Provide the following information a. # of Protons _____ b. # of Neutrons _____ c. # of Electrons _____ d. Atomic Mass _____ e. Atomic Number _____ 2. Although 31P is the most stable form of phosphorus, there are several other forms including 32 P and 33 P. a. What is the term used to describe these alternate forms? b. In what ways are 32 P and 33 P different from 31P? The same? 3. Define polar. Draw a water molecule and illustrate its polarity. Complete the following table about water. Property 4. Explanation of Property Hydrogen bonds hold molecules together; adhere them to hydrophilic surfaces 5. High Specific Heat 6. Importance Temperature changes in environment and organisms are moderated Hydrogen bonds must be broken for water to evaporate 7. Ice floats 8. Most chemical reactions in life involve solutes dissolved in water Use the information below to answer questions 9 and 10. pH of cola = 2 pH of orange juice = 3 pH of beer = 4 pH of coffee = 5 9. Which of these liquids has the highest molar concentration of OH -- ? 10. How does [ H+ ] in orange juice compare with [ H+ ] in coffee? Complete the following table. [ H+ ] 11. 12. [ OH-- ] 10 -11 10 -8 13. 14. pH 1 10 -7 Acid, Base, or Neutral? 15. The carbonic acid buffer system is very important in human blood. a. Write the equation that illustrates this buffer system. b. If the pH of blood is too high, in which direction will this reaction proceed? c. What is the normal pH of blood? Dehydration Synthesis or Hydrolysis? _____________________ 16 Produces water as a by-product. _____________________ 17 Breaks up polymers to form monomers. _____________________ 18. Joins amino acids to form a protein. _____________________ 19. Glycerol and fatty acids combine this way to form a fat. _____________________ 20. Occurs when polysaccharides are digested to form monosaccharides. _____________________ 21. –H and –OH forms water 22. Name two structural polysaccharides. Where are they found? 23. Name two energy storage polysaccharides. What are the monomers in each? Where they found? 24. Examine the following structural formula, C12 H22 O11. a. Identify a molecule with this formula. b. Specifically, what type of molecule is it? c. Name an isomer of the molecule identified in a. d. What are the monomers of the molecule you identified in a? e. What reaction took place to form this biomolecule? Identify any functional group(s) present in the following molecules by circling and naming them. Identify the following biomolecules as carbohydrate, lipid, or nucleic acid. In addition, a. if the molecule is a carbohydrate, indicate whether it is mono, di, or poly. b. if the molecule is a fat, indicate if it is saturated or unsaturated. 36. Enzymes a. Label the active site, enzyme, and substrate in the following diagram. b. If this enzyme is lactase, what is the substrate? c. What are the products? d. What reaction occurs to form the products? e. What is meant by “induced fit”? What is its importance? f. Explain the difference between a competitive inhibitor and non-competitive inhibitor. g. Describe allosteric regulation. Amino Acids & Proteins a. Circle and label the carboxyl, amino, and R groups in each amino acid shown. b. Identify each amino acid as non-polar, polar, acidic, or basic. c. Illustrate the formation of a dipeptide from two amino acids. Protein Structure – Identify each description as pertaining to 1˚, 2˚, 3˚, or 4˚ structure. 42. Results from hydrogen bonding between amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of another ________ 43. Results from interactions between two polypeptide chains ____________________________________________ 44. Sequence of amino acids ______________________________________________________________________ 45. Alpha helix _________________________________________________________________________________ 46. Results from interactions between R groups _______________________________________________________ 47. Beta pleated sheet ___________________________________________________________________________ 48. Nucleic Acids a. Label the components of the DNA molecule shown below. b. In addition to naming each nitrogen base, identify it as a purine or pyrimidine. c. How does RNA differ from DNA?