English curriculum Spelling Y4
advertisement

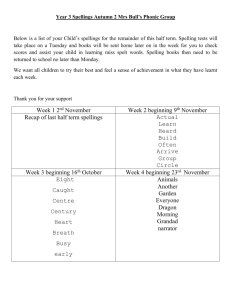
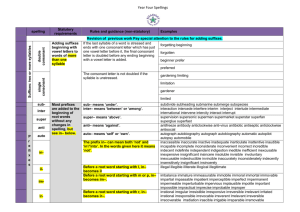
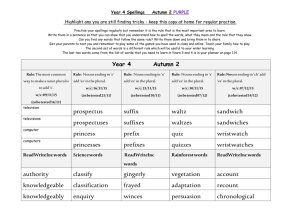
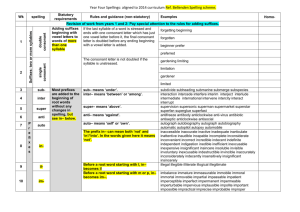
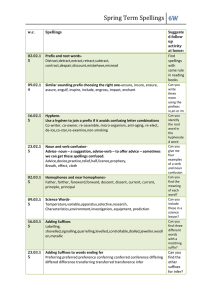
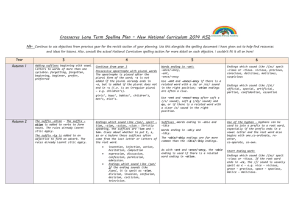
Spelling Year 4 Spelling for Grammar Year 4 investigations Spellings Nouns can be made by adding a suffix e.g. add –ness Adjectives can be made from nouns and verbs using suffixes e.g. add –ful, add – less add - ous (see below) Adverbs can be made by adding a suffix to adjectives -ly Rules/guidance Nouns can be made from adjectives by adding suffixes such as –ness Spellings are modified when the root word ends in y Root words can be modified to create word families by changing suffixes and prefixes. Spellings are modified when the root word ends in y Ful is not spelled with two ‘l’s Not all adverbs end –ly but Adjectives can be turned into adverbs by adding this suffix Spellings are modified when the root word ends in y Examples Happy – happiness Cheerful – cheerfulness Cold – coldness Cruel – cruelness Tidy - tidiness Weak - weakness Soft – softness Open - openness Aware - awareness Mild - mildness Nervous - nervousness Forgetful - forgetfulness Tired - tiredness Beauty – beautiful Help – helpful Harm – harmful Peace – peaceful Play – playful Success – successful Care – careful Pain - painful Sleeve – sleeveless Hope – hopeless Rest – restless End – endless Breath – breathless Point – pointless Price - priceless Angry – angrily Bad – badly Brave – bravely Cruel – cruelly Easy – easily Happy – happily Greedy – greedily Sad – sadly Safe – safely Foolish – foolishly Loud – loudly Quiet - quietly Spelling Year 4 New Spellings for Year 4 Spellings Rules/guidance Examples Adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters to words of more than one syllable If the last syllable of a word is stressed and ends with one consonant letter which has just one vowel letter before it, the final consonant letter is doubled before any ending beginning with a vowel letter is added. The consonant letter is not doubled if the syllable is unstressed. The prefix in– can mean both ‘not’ and ‘in’/‘into’. In the words given here it means ‘not’. Before a root word starting with l, in– becomes il. Before a root word starting with m or p, in– becomes im–. Before a root word starting with r, in– becomes ir–. sub– means ‘under’. forgetting, forgotten, beginning, beginner, prefer, preferred prefixes inter– means ‘between’ or ‘among’. super– means ‘above’. anti– means ‘against’. auto– means ‘self’ or ‘own’. The suffix –ation The suffix –ation is added to verbs to form nouns. The rules already learnt still apply. Words with endings sounding like /ʒə/ or /tʃə/ The ending sounding like /ʒə/ is always spelt –sure. The ending sounding like /tʃə/ is often spelt –ture, but check that the word is not a root word ending in (t)ch with an er ending – e.g. teacher, catcher, richer, stretcher. If the ending sounds like /ʒən/, it is spelt as –sion. Sometimes the root word is obvious and the usual rules apply for adding suffixes beginning with vowel letters. Sometimes there is no obvious root word. –our is changed to –or before –ous is added. A final ‘e’ of the root word must be kept if the /dʒ/ sound of ‘g’ is to be kept. If there is an /i:/ sound before the –ous ending, it is usually spelt as i, but a few words have e. Endings which sound like /ʒən/ The suffix –ous gardening, gardener, limiting, limited, limitation in–: inactive, incorrect illegal, illegible immature, immortal, imperfect impossible, impatient, irregular, irrelevant, irresponsible sub–: subdivide, subheading, submarine, submerge inter–: interact, intercity, international, interrelated (inter + related) super–: supermarket, superman, superstar anti–: antiseptic, anticlockwise, antisocial auto–: autobiography, autograph information, adoration, sensation, preparation, admiration measure, treasure, pleasure, enclosure creature, furniture, picture, nature, adventure division, invasion, confusion, decision, collision, television poisonous, dangerous, mountainous, famous, various tremendous, enormous, jealous humorous, glamorous, vigorous courageous, outrageous serious, obvious, curious hideous, spontaneous, courteous Spelling Year 4 New Spellings for Year 4 continued… Spellings Rules/guidance Endings which sound like /ʃən/, spelt –tion, –sion, – ssion, –cian Strictly speaking, the suffixes are –ion and –ian. Clues about whether to put t, s, ss or c before these suffixes often come from the last letter or letters of the root word. –tion is the most common spelling. It is used if the root word ends in t or te. –ssion is used if the root word ends in ss or –mit. –sion is used if the root word ends in d or se. Exceptions: attend – attention, intend – intention. –cian is used if the root word ends in c or cs. Words with the /k/ sound spelt ch Words with the /ʃ/ sound spelt ch Words ending with the /g/ sound spelt –gue and the /k/ sound spelt –que Words with the /s/ sound spelt sc Possessive apostrophe with plural words Homophones and nearhomophones revision Homophones and nearhomophones Word list (Greek in origin) (mostly French in origin) (French in origin) Examples invention, injection, action, hesitation, completion expression, discussion, confession, permission, admission expansion, extension, comprehension, tension musician, electrician, magician, politician, mathematician scheme, chorus, chemist, echo, character chef, chalet, machine, brochure league, tongue, antique, unique (Latin in origin) In the Latin words from science, scene, discipline, which these words come, the Romans fascinate, crescent probably pronounced the c and the k as two sounds rather than one – /s/ /k/. The apostrophe is placed after the plural girls’, boys’, babies’, form of the word; –s is not added if the children’s, men’s, mice’s plural already ends in (Note: singular proper nouns –s, but is added if the plural does not end in ending in an s use the ’s suffix –s (i.e. is an irregular plural – e.g. e.g. Cyprus’s population) children’s). there/their/they’re, here/hear, quite/quiet, see/sea, bare/bear, one/won, sun/son, to/too/two, be/bee, blue/blew, night/knight accept/except, affect/effect, fair/fare, grate/great, groan/grown, main/mane, medal/meddle, peace/piece, rain/rein/reign, scene/seen, weather/whether, whose/who’s accident(ally) difficult knowledge position actual(ly) disappear learn possess(ion) breath enough library possible breathe exercise material pressure build experience medicine probably busy/business extreme mention purpose calendar famous natural question centre favourite naughty recent century grammar notice separate certain guard occasion(ally) special complete guide opposite straight consider height ordinary strength continue imagine particular suppose decide increase peculiar therefore describe important perhaps though/although different interest