Simple Machines PowerPoint
advertisement
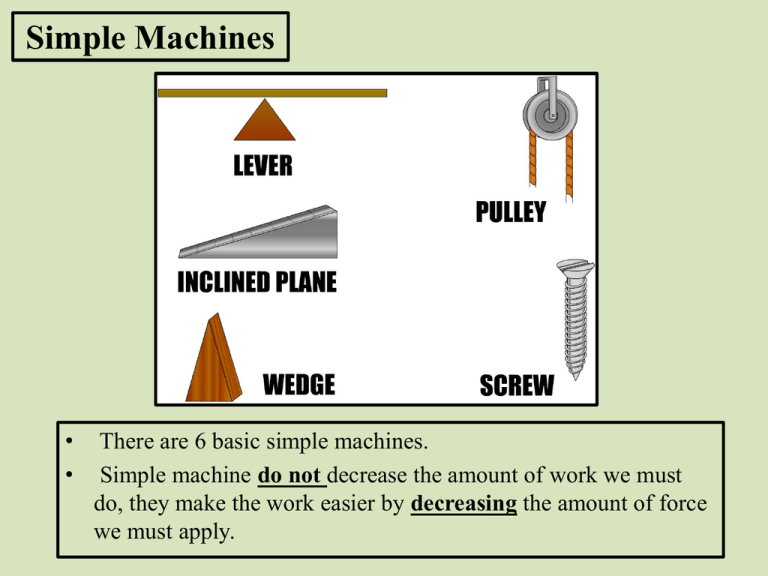
Simple Machines • • There are 6 basic simple machines. Simple machine do not decrease the amount of work we must do, they make the work easier by decreasing the amount of force we must apply. WInput = WOutput • Hence, Finput dinput = Foutput doutput • Notice that cos(θ) has been omitted since the direction of motion and force is 0. • Also, notice that all of these may have different names such as effort, load or resistance. d F Fd • Remember in all these cases the Winput = Woutput • Thus the man above applies a small force (FI) over a big distance (dI) while the rock moves upward with big force (FO) over a small distance (dO). Mechanical Advantage • Is the amount a machine amplifies an applied force. • Hence, a you would only need to apply 50 N of force to a machine with MA = 2 in order to lift 100 N. • Ideal mechanical advantage (IMA) is the advantage gained by a 100 % efficient machine (i.e. no friction). • MA can always be determined by dividing the Foutput by the Finput (however, certain simple machines have other ways of determining this value). Levers • 3 types: – Class 1 – Fulcrum is between the effort and the load (scissors, crowbar). – Class 2 – Load is between the fulcrum and the effort (wheelbarrow, bottle opener). – Class 3 – Effort is between the fulcrum and the load (tweezers, your arm). • Another way of determining the MA of a lever is to divide the effort length by the resistance length. Problem 1: (a) A lever used to lift a heavy box has an input arm of 4 meters and an output arm of 0.8 meters. What is the mechanical advantage of the lever? (b) If you pushed down with 20 N of force over a distance of 0.80 m how much work did you accomplish? (c) How high was the box raised? (d) What is the mass of the box? Problem 2: A broom with an input arm length of 0.4 meters has a mechanical advantage of 0.5. What is the length of the output arm? Pulley • Is really just a glorified lever! • MA is determined by counting the number of supporting strands (subtract one if the strand just changes the direction of the applied force). • Be careful with change of force direction strand! • In each of these pulley systems find: • the MA • the effort force • the amount of rope that must be pulled to raise the load 0.50 m Inclined Plane/Ramp • The output work of the load is the vertical distance traveled or mgh. • The MA can be determined by dividing the length of the ramp by its vertical height. Practice Problems • A 5 meter ramp lifts objects to a height of 0.75 meters. What is the mechanical advantage of the ramp? – How much work would be required to bring a 10 kg object to the top of this ramp? – What would be the input force required to use this ramp? • Gina wheels her wheelchair up a ramp using a force of 80 N. If the ramp has a mechanical advantage of 7, what is the output force? • A mover uses a ramp to pull a 1000 N cart up to the floor of his truck (0.8 m high). If it takes a force of 200 N to pull the cart, what is the length of the ramp? Image Sources 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. http://capocci.pbworks.com/w/page/22877939/Simple%20Machines http://www.science-class.net/Notes/Notes_simple_machines_7th.htm http://campus.murraystate.edu/academic/faculty/tderting/atlases2009/runyon/Whatle ver.html http://etc.usf.edu/clipart/35900/35944/lever_35944.htm http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/teachers/activities/27po_sle2phar.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/mechanics/lever.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mechanical_advantage_device http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/mechanics/lever.html http://www.schoolphysics.co.uk/age1114/Mechanics/Forces%20in%20motion/text/Pulleys_/index.html http://www.phy.ilstu.edu/pte/489.01content/simple_machines/simple_machines.html http://road-to-psle.blogspot.com/2008/10/simple-machines-incline-plane.html