The Growth of The New England Colonies
advertisement

The Growth of
The New England Colonies
Puritanism
Wanted to reform [purify] the Church of
England
Grew impatient with the slow progress of
Protestant Reformation in England
Separatists
Puritans who believe that only visible saints
should be admitted for church membership
Because the Church of England enrolled all the
king’s subjects, separatists felt they had to
share their church with the “damned”
Therefore, they believed in a “total break”
from the Church of England
Sources of Separatist Migration
Pilgrims
Ultimately left the Netherlands because they
didn’t think it was “pure” enough for them
Did not want to mix with the other religions
1620, a group of 100 people negotiated with
the Virginia Company to settle in their
jurisdiction
The Mayflower
Arrived far off course from
destination – Plymouth Bay
outside the domain of the
VA co.
Squatters without legal right
to land and authority to start
government
The May Flower Compact
November 11, 1620
The May Flower Compact
November 11, 1620
Written and signed before the passengers
disembarked from ship
Not a constitution, but an agreement to form to
a crude government and submit to majority
rule
Signed by 41 adult males
Led to meeting in assemblies to make laws
John Carver elected governor
That First year…
Winter of 1620-1621 extremely harsh (only 44
of the original 100 survived)
* weather
* starvation
* disease
None chose to leave in 1621 when the
Mayflower sailed back
The First Thanksgiving
Survival owed to Squanto and the Wampanaog
Indians
Native Americans were weak in the New England
area, epidemics had wiped out over ¾ pop
Chief Massasoit signed treaty with settlers in 1621
Colony survived with fur (especially beaver),
fish and lumber
Fall 1621 --- celebrated First Thanksgiving
Plymouth colony
William Bradford was chosen governor of
Plymouth over 30 times
Worried about non Puritan settlements
springing up nearby and corrupting Puritan
society ----- A Model of Christian Charity?
Plymouth stayed small and economically
unimportant
Merged with Massachusetts Bay colony
The First Seal of
the MA bay colony
Puritan Migration
The MA Bay Colony
The Great Migration of the 1630’s
Turmoil in England
Two main reasons for exodus?
Charles I inherits 1625 – tries to bring back Catholicism
Conflicts with Parliament
Avoid economic ruin
Avoid religious persecution
Royal Charter to form MA Bay Colony
Could govern colony as wished but could not violate
English law
The MA Bay colony
1630, approx. 1000 people established a colony with
Boston as its hub
These Puritans: Similar and different to Pilgrims
Escape attacks by conservatives in Church
Didn’t want to leave the church or cut all ties with England,
only its impurities, different economic statuses
John Winthrop – 1st Governor
Believed he had a calling from god to lead
“A City upon a Hill,” --- a model community
Back in Europe…
While Massachusetts Bay colony was beginning, a
Civil War erupted in England in 1642
PURITANS vs. ROYALISTS
(Roundheads) (Cavaliers)
Oliver Cromwell – Lord Protector
Puritans won, causing emigration to America to
virtually cease during the years of 1653-1658.
The New England Way
Winthrop’s colony was one guided by English law
and the Bible
Expected to work together for the common good
Voting rights granted to all freemen – those who
were church members and property owners
Freemen in each town then elected representatives to make
laws for the colony – General court
½ the men could vote
none of the women had right to vote
The New England Way
The symbol of this cooperation –
Meetinghouse
Used for both town meetings and church
Puritans extremely religious – not tolerant
Belief in Predestination – god had already
determined who would be saved, chosen ones
Basic unit of social life in colonial New
England -------- THE TOWN
The New England Way
Depended on educated people who could understand
the Bible
General Court’s Laws:
required parents to make sure that their children learned to
read
1636, Harvard College, Yale (1701) – ministry
training
1647, “the old deluder law
50 or more people = private tutor for kids
100 or more people = mandatory school built
Characteristics of Life
in New England settlements
•
•
•
Educated farmers, artisans
Orderly families
Patriarchy extremely important
•
•
•
Total obedience to fathers or husbands
Worked in fields during harvest
Made family essentials like, soap, candles, yarn,
clothes, butter, cheese
Characteristics….
Many large families
No food problem like Jamestown
Average 6 children
Average marriage age, women (22), men (27)
Diseases couldn’t survive in cold climate
Low mortality –
average life expectancy was 70 years old
In one town, 85% of all children lived to adult
Commerce
Very little need for indentured servants and
slaves
Large families, fathers, and sons provided the
labor needed
Cold winters and poor soil prevented farmers
from raising a large surplus of crops to sell
Business of New England: fishing and trade
Distilled rum, built ships
Sold fish, grain, lumber, meat, turpentine
Puritan Rebels
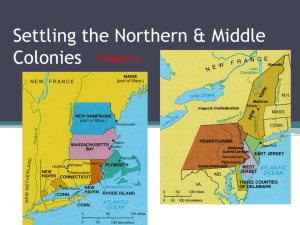
Connecticut
Founded by minister, Thomas Hooker 1636
Left Massachusetts bc of religious differences
with Puritans
Left for more farmland (towns too close)
1639, Fundamental Orders of CT adopted (1st
written constitution in the colonies)
Rhode Island
Founded by minister, Roger Williams, 1636
Banished from Massachusetts Bay colony bc
he questioned Puritan ways
Strict separation of church and state
Land should be purchased from Indians (which he
did from the Narraganset Indians in 1636)
Obtained a royal charter in 1644
Religious freedom to all its inhabitants
Seen as a “sewer” by the Puritans
Another challenger…
Anne Hutchinson “ a woman of ready wit”
Found refuge in Rhode Island after she was banished
from Massachusetts Bay colony
Refused to follow the New England Way
Arrested in 1637, charged with weakening the authority of
the church
Held religious meetings in her home
Claimed she received her religious insights directly from
god
Clergy feared rebellion and thus banished her in 1638
New Hampshire
Founded in 1638 by John Wheelright
Puritans in search of more land
Major City – Concord
Major Industries:
fishing
shipbuilding
Fear and Paranoia
Conflicts also existed within the MA bay colony.
The Salem Witch trials caused mass hysteria and
deaths. {Unsolved History: The Salem Witch Trials}
Possible Causes:
New England’s environment of fear/accusations
Puritan beliefs and New England Folklore
Economic and Political tension divided the community
Men’s fear of women gaining economic/social
independence, which would threaten the power structure
and social order