OFF-SITE CONSTRUCTION
advertisement

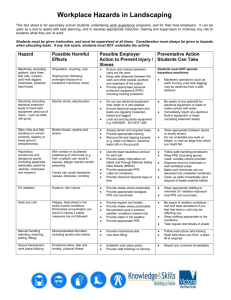
OFF-SITE CONSTRUCTION - - WORKPLACE COMMUNICATIONS - - - - PPE - (Personal Protective Equipment) What is personal protective equipment (PPE) and what are some of the types? PPE is defined as all equipment, including clothing, which is intended to be worn or held by a person at work and which protects him against one or more risks to his health and safety. Some of the types of PPE which are used throughout the workplace include: Hearing protection Head protection Eye protection Foot protection Hand &arm protection Body protection Respitory protection Hearing Protection Earmuffs/defenders, which completely cover the ear Earplugs, which are inserted into the ear canal Semi-inserts (also called canal-caps), which cover the entrance to the ear canal Head Protection Industrial safety helmets (hard hats), which are designed to protect against materials falling from height and swinging objects Industrial scalp protectors (bump caps), which are designed to protect from knocking against stationary objects Caps/hair nets, which protect against entanglement Hazards- Impact from falling or flying objects, risk of head bumping, hair entanglement Eye Protection Safety spectacles. These are similar to regular glasses but have a tougher lens. They can include side shields for additional protection Eye shields. A frame-less one piece moulded lens, often worn over normal prescription glasses Safety goggles. These are made with flexible plastic frames and an elastic headband Face shields. Heavier and bulkier than other type of eye protector. Face shields protect the face, but do not fully enclose the eyes so do not protect against dusts, mists or gases Hazards- chemical or metal splash, dust, projectiles, gas and vapor. Foot Protection Safety boots or shoes. Normally with steel toe-caps. Can also have other safety features (e.g. steel mid-soles, slip resistant soles, insulation against heat and cold) Wellington boots, which can be supplied with steel toe-caps Anti-static and conductive footwear. Designed to protect against the build up of static electricity. Hazards- Wet, electrostatic build up, slipping, falling objects Hand & Arm Protection Gloves and gauntlets (leather, nitrile, latex, plastic coated, chain mail etc.) Wrist cuffs and armlets, e.g. used in glass cutting and handling Barrier cream may sometime be used, where gloves cannot practicably be used Hazards- Abrasions, temperature extremes, cuts and punctures, impact, chemicals, electric shock, skin infection, disease or contamination. Body Protection Overalls, aprons and coveralls. Protection against hazardous substances Clothing for cold, heat & bad weather Clothing to protect against machinery, e.g. chainsaws High visibility clothing (e.g. jackets, vests) Harnesses Back supports Hazards- Chemical or metal splash, spray from pressure leaks or spray guns, impact or penetration, contaminated dust, excessive wear or entanglement of clothing Respiratory Protection Respirators that filter contaminated air or clean it as it is breathed in Respirators that supply clean air from an independent source Face masks cartridge filters Basic Dust mask (3M 8822) Hazards- Dust, vapor, gas, oxygen deficient atmospheres. SR 100 * SR 90-2 * SR 75 Half Mask Use – If equipped with a suitable filter, the mask provides protection against the inhalation of harmful gasses/vapors and/or particles. The choice of filter determines the degree of protection provided by the mask in a given situation Filters – Particle Filter Filter Class P3 (includes P2 & P1) Provides protection against all types of particles, both solid and liquid Gas Filters Type A Provides protection against organic gasses and vapors, I.e solvents whose boiling point exceeds +65 degrees Celsius Type AX Provides protection against organic substances with boiling points of up to +65 degrees Celsius Type B Provides protection against inorganic gasses and vapors. I.e Chlorine, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen cyanide Type E Provide protection against acid gasses and vapors. I.e Sulphur dioxide and hydrogen fluoride Type K Provides protection against ammonia and some amines. I.e Ethylendiamine Type HG Provides protection against mercury vapor. Maximum usage time is 50 hours Description 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Mask Body Filter Attachment Head Harness Membrane Seat Exhalation Membrane Protective Cap Inhalation Membrane Filter/Combination Filter Pre-Filter Pre-Filter Holder (Pre-Filter prevents premature Clogging of the main filter & Also prevents damage to the main filter) Description How do I know if the PPE is designed to provide adequate protection against the hazards at my workplace? Designers, manufacturers or suppliers of PPE can give advice on the specifications and appropriate use of their products. This is important as seen in the following example: Clearly, no one type of glove provides adequate protection against all chemicals. A respirator designed to be effective against medium air levels of one particular chemical, may not be effective against high levels of the same chemical, or lower levels of a different chemical. For this reason it is highly important to contact the suppliers and read any enclosed information regarding the uses and protections of the particular PPE employed. How do I determine whether or not to use personal protective equipment (PPE) in the workplace? Initially the employer must determine if there is a hazard and assess the risk associated with the hazard. An employer must then eliminate any reasonably foreseeable risk to the health and safety of any person within his/her workplace. If it is not possible to eliminate the risk, an employer must control the risk. PPE may assist in reducing this possible risk of harm. However, it should be noted that legal requirements state that all workplaces should specifically follow the outlined PPE and OH&S practices, and any workplace which does not have these regulations in place should be brought to the attention of head office, or in extreme cases, Work Cover and/or Industrial Relations Maintenance of PPE There are two main points to maintaining safe PPE equipment, these include: the PPE is well looked after and properly stored when it is not being used, for example in a dry clean cupboard or in the case of smaller items, such as eye protection, in a case or box. The PPE is kept clean and in good repair. Repairs and maintenance can be done by a set schedule which is organized and checked by a person put in charge of that specific area in the workplace. Key points to remember PPE is provided It offers adequate protection for its intended use Those using it are trained in some way Its properly maintained and that any defects are reported It is returned to its proper storage after use Assessing PPE is it appropriate for the risks involved and the conditions at the place where exposure to the risk may occur? E.g. eye protection will not provide adequate face protection for someone using a grinder. does it prevent or satisfactorily control the risks involved without increasing the overall level of risk. Can it be adjusted to fit the wearer properly? has the state of health of those who will be wearing it been taken into account? what are the needs of the job and the demands it places on the wearer? For E.g. the length of time the PPE needs to be worn, the physical effort required to do the job and the requirement for visibility and communication. If more then one item of PPE is being worn, are they compatible? For E.g. does a particular respirator (mask) make it difficult to wear eye protection properly? Suppliers 3M Australia PTY LTD 2-74 Dunheved Circuit , St Marys NSW 2760 Ph: 1800 024 464 HYMARK TRADING PTY LTD P.O. BOX 134 RED HILL SOUTH VICTORIA 3937 Ph: 03 5989 3033 SafetyEquipment.net.au PO Box 373 Concord West NSW 2138 Ph: 1300 73 22 74 All Purpose Abrasives 25 Lincoln Street Minto NSW 2566 (Earplugs, masks, goggles) West Hoxton Awevare (Shoes) Protector Safety Pty Ltd Guilford, Sydney NSW Australia 2161 Protector Allsafe (Shoes)