LS Outline of Part I
advertisement
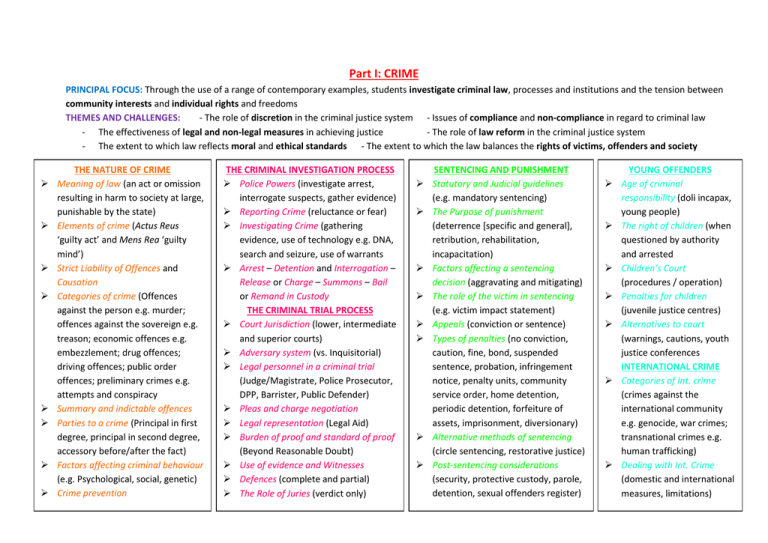
Part I: CRIME PRINCIPAL FOCUS: Through the use of a range of contemporary examples, students investigate criminal law, processes and institutions and the tension between community interests and individual rights and freedoms THEMES AND CHALLENGES: - The role of discretion in the criminal justice system - Issues of compliance and non-compliance in regard to criminal law - The effectiveness of legal and non-legal measures in achieving justice - The role of law reform in the criminal justice system - The extent to which law reflects moral and ethical standards - The extent to which the law balances the rights of victims, offenders and society THE NATURE OF CRIME Meaning of law (an act or omission resulting in harm to society at large, punishable by the state) Elements of crime (Actus Reus ‘guilty act’ and Mens Rea ‘guilty mind’) Strict Liability of Offences and Causation Categories of crime (Offences against the person e.g. murder; offences against the sovereign e.g. treason; economic offences e.g. embezzlement; drug offences; driving offences; public order offences; preliminary crimes e.g. attempts and conspiracy Summary and indictable offences Parties to a crime (Principal in first degree, principal in second degree, accessory before/after the fact) Factors affecting criminal behaviour (e.g. Psychological, social, genetic) Crime prevention THE CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION PROCESS Police Powers (investigate arrest, interrogate suspects, gather evidence) Reporting Crime (reluctance or fear) Investigating Crime (gathering evidence, use of technology e.g. DNA, search and seizure, use of warrants Arrest – Detention and Interrogation – Release or Charge – Summons – Bail or Remand in Custody THE CRIMINAL TRIAL PROCESS Court Jurisdiction (lower, intermediate and superior courts) Adversary system (vs. Inquisitorial) Legal personnel in a criminal trial (Judge/Magistrate, Police Prosecutor, DPP, Barrister, Public Defender) Pleas and charge negotiation Legal representation (Legal Aid) Burden of proof and standard of proof (Beyond Reasonable Doubt) Use of evidence and Witnesses Defences (complete and partial) The Role of Juries (verdict only) SENTENCING AND PUNISHMENT Statutory and Judicial guidelines (e.g. mandatory sentencing) The Purpose of punishment (deterrence [specific and general], retribution, rehabilitation, incapacitation) Factors affecting a sentencing decision (aggravating and mitigating) The role of the victim in sentencing (e.g. victim impact statement) Appeals (conviction or sentence) Types of penalties (no conviction, caution, fine, bond, suspended sentence, probation, infringement notice, penalty units, community service order, home detention, periodic detention, forfeiture of assets, imprisonment, diversionary) Alternative methods of sentencing (circle sentencing, restorative justice) Post-sentencing considerations (security, protective custody, parole, detention, sexual offenders register) YOUNG OFFENDERS Age of criminal responsibility (doli incapax, young people) The right of children (when questioned by authority and arrested Children’s Court (procedures / operation) Penalties for children (juvenile justice centres) Alternatives to court (warnings, cautions, youth justice conferences INTERNATIONAL CRIME Categories of Int. crime (crimes against the international community e.g. genocide, war crimes; transnational crimes e.g. human trafficking) Dealing with Int. Crime (domestic and international measures, limitations)