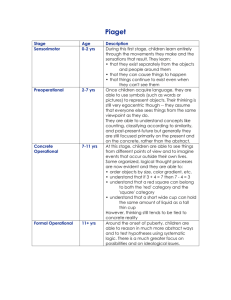
So far, we know that the Earth has experienced at least 8 ice ages
advertisement

Geography 1001: Climate & Vegetation Instructor: Andrés Holz Teaching Assistant: Eungul Lee Agenda for Lecture 13: Monday July 2 • Today’s lecture: – Historical development of the ecosphere • Biological processes that changed the atmosphere • Atmospheric changes – A bit of ourselves • How we have modified our environment at various scales • Traditional (& less traditional) modifications of our environment at local (& global) scales Agenda for Lecture 13: Monday July 2 • Today’s lecture: – A bit of ourselves • World Population Prospects • Population collapse predictions • Could these changes be relevant for our future? • Does earth experience natural changes? • If so, then what? Take-home message A bit of history here… 500 million years ago.. 400 million years ago.. 300 million years ago.. 200 million years ago.. 100 million years ago.. 50 million years ago.. 1 million year ago.. Less than a million year ago.. •So far, we know that the Earth has experienced at least 8 ice ages •Last one? Today •If we think of the earth life being a calendar year (i.e. from Jan 1 to Dec 31), when do you think we appeared? But how have the conditions for life changed over these 4 billion years? The solar system form 4.6 billion years ago. 4 billion years ago, the atmosphere was made off of volcanic emissions • TIME – 4 billion yrs ago • PROCESS – – – – Water vapor Ammonia (NH3) Methane (CH4) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) – Hydrogen gas (H2) – Carbon monoxide (CO) – **Very little O2 & N2 All water was held in the atmosphere as vapor because of high temperatures (water vapor in high clouds greenhouse effect). • TIME – 4 billion yrs ago – 3.1-3.5 billion yrs ago • PROCESS – Water vapor, CO, (N) dominant. – O2 begins to accumulate. How? – Water vapor clouds common in the lower atmosphere (albedo forcing clouds). – Cooling of the atmosphere causes precipitation and the development of the oceans. – Break of H2O by ultraviolet rays H2O O2 + H – First single cell algae & bacteria • TIME • PROCESS – 3.1-3.5 billion yrs ago – Anaerobic respiration • Single cells algae were able to – produce Energy without O2 – Take C-H20 (simple organic molecules food) & break down into CO2 + alcohols energy For ~800 millions of years, CO2 was released (as by-products of respiration) & built up in the atmosphere and oceans There was enough CO2 in the atmosphere to sustain life…. • PROCESS • TIME – Photosynthesis Single-cells (bluegreen algae have chlorophyll) – 2.3 billion yrs ago…. sunlight CO2 + H2O CH2O + O2 energy –Initially, the released O2 was lethal to the living organisms food built up • TIME – 1.9 billion yrs ago…. • PROCESS – Ozone (O3) layer is being built in the stratosphere Filters out the UV radiation making life possible on land development of O2 tolerant organisms Aerobic life on the land took longer to start because it could only occurred after the ozone layer was formed • TIME – 1.3 billion yrs ago…. CH2O + O2 • PROCESS – Aerobic respiration CO2 + H2O energy • TIME – 600 mill yrs ago…. • PROCESS – Life is widespread in the oceans • Single cells • Early fishes • Large algae • TIME – 420 mill yrs ago…. • PROCESS – Life is widespread on lands • Earliest plants • Invertebrates • Vertebrates • TIME – 350 mill yrs ago…. • PROCESS – Development of tropical rainforest • fossil fuel today’s oil • TIME – 200 mill yrs ago…. • PROCESS – Colonization of larger vertebrates One of those (smaller) vertebrates were our ancestors: a bit of ourselves.. Date of Separation according to Mitochondrial DNA Early Human Phylogeny Africa Asia Asia Europe eastern Africa Africa? southern Africa eastern Africa Europe & W Asia How we have modified our environment at various scales (remember the movie?) Broad Expansion of Human Habitat (we took over spatially!) Remember that 18,000 BP, the Earth looked like this map from Earth and Life Through Time Food Web-Land Animals (we also took over new niches) World Population Trend from 10,000 B.C. to 200 A.D. Traditional modification of our environment at local scale (Less) Traditional modification of our environment at global scale • http://www.mongabay.com/deforestation_r ate.htm UN, World Population Prospects:1992 A this rate, it was predicted that it would take only 774 years (for the 1994 population of 5.6 billion) to increase to the point where there were 10 human beings for each square meter of ice free land on the planet! • Is there any problem with that? Population collapse predictions • Malthus (~1800) – population would outrun food supply by 1930s • Technology & Market economy Yet, Malthus (& his opponent) didn’t see the current • Biodiversity loss – – – – Habitat fragmentation Species introduction (that are taking new niches) Over hunting Greenhouse gases • Could these changes be relevant for our future? • Does earth experience natural changes? 1-Let’s play with history: First civilization self-collapse..(local scale) • Eastern Island • Mayas Empire Does earth experience natural changes? Yes! Examples: – Sunspots (~11 cycle) – El Niño/ La Niña – Hugh Volcanic eruptions (random) – Meteorite impacts (very infrequent & very random) – Ice ages (~100,000 yrs cycle) – Massive Biodiversity loss If so, then what? Take-home message • Current rates and scales of these changes are unprecedented on earth • Natural changes increasingly influenced by “we”, may rapidly create new conditions at the planet scale – triggering erratic jumps that are hard to predict and understand – enhancing feedback loops that weaken these prediction efforts even further If so, then what? Evidence of Ice ages? • Swiss hunter in the Alps (1815) associated scratch marks on rocks with the P of ice Yosemite Cycles of Ice ages: Milanković cycles (Theory) Performed detailed calculations concerning the periodicity of the earth’s orbital parameters during the 1920-40s • Precession • Axial tilt • Eccentricity Eccentricity • During periods of high eccentricity higher differences between max & min distance from sun to earth more potential for extreme (cold & warm) climate Orbit eccentricity Tilt angle (or obliquity) Tilt angle (or obliquity) • The greater the angle of the tilt the greater the potential for extremes in seasonal climate (especially for polar regions) Precession (or wobble) Precession (or wobble) • It’s a ‘slowing down’ of the rotation of the earth tilt of the earth point to various directions (like the axe of a spinning top) • What about us? How do scientists track glaciation? • Stable-isotopes from zooplankton (tiny shells of calcite) • Come from seawater • Once dead built up on the ocean bottom as layers (~2.5 cm or 1” = 1,000 yrs) How do scientists track glaciation? Lighter Oxygen (16O) evaporates easier with water vapor (due to insolation) and then precipitates as either: a) rain and returns with rivers and groundwater to oceans seawater remains the ~same (interglacial) [e.g. now] Or b) snow and accumulates and does NOT return to oceans seawater change rate between 16O & 18O Comparison between O2 isotope record & Milanković theory