Lesson 6.2
advertisement

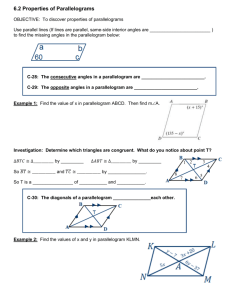
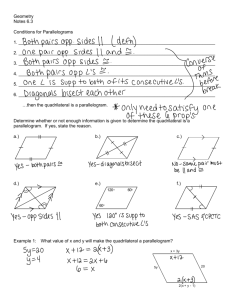
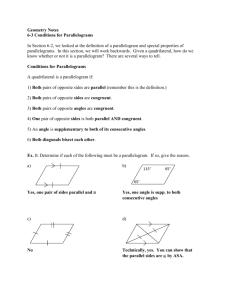
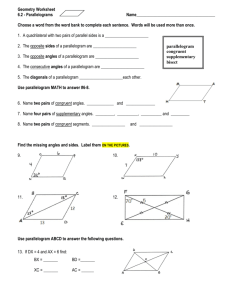
6.2 Parallelograms CCSS Content Standards G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. Mathematical Practices 4 Model with mathematics. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Then/Now You classified polygons with four sides as quadrilaterals. • Recognize and apply properties of the sides and angles of parallelograms. • Recognize and apply properties of the diagonals of parallelograms. Vocabulary • Parallelogram: a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel Theorem 6.3: Vocabulary Parallelogram Property #1 If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite sides are congruent. Theorem 6.4: Vocabulary Parallelogram Property #2 If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite angles are congruent. Theorem 6.5: Vocabulary Parallelogram Property #3 If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its consecutive angles are supplementary. Theorem 6.6: Vocabulary Parallelogram Property #4 If a parallelogram has one right angle, then it has four right angles. Vocabulary Parallelogram Diagonal Theorem 6.7: Property #1 If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its diagonals bisect each other. Vocabulary Parallelogram Diagonal Theorem 6.8: Property #2 If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then each diagonal separates the parallelogram into two congruent triangles. Parallelogram • Mark in all of the sides and angles Example 1A A. ABCD is a parallelogram. Find AB. A. 10 B. 20 C. 30 D. 50 Example 1B B. ABCD is a parallelogram. Find mC. A. 36 B. 54 C. 144 D. 154 Example 1C C. ABCD is a parallelogram. Find mD. A. 36 B. 54 C. 144 D. 154 Example 1A of Parallelograms Use Properties A. CONSTRUCTION In suppose mB = 32, CD = 80 inches, BC = 15 inches. Find AD. Example 1B of Parallelograms Use Properties B. CONSTRUCTION In suppose mB = 32, CD = 80 inches, BC = 15 inches. Find mC. Example 1C of Parallelograms Use Properties C. CONSTRUCTION In suppose mB = 32, CD = 80 inches, BC = 15 inches. Find mD. Example 2A Use Properties of Parallelograms and Algebra A. If WXYZ is a parallelogram, find the value of r. Example 2B Use Properties of Parallelograms and Algebra B. If WXYZ is a parallelogram, find the value of s. Example 2C Use Properties of Parallelograms and Algebra C. If WXYZ is a parallelogram, find the value of t. Example 2A A. If ABCD is a parallelogram, find the value of x. A. 2 B. 3 C. 5 D. 7 Example 2B B. If ABCD is a parallelogram, find the value of p. A. 4 B. 8 C. 10 D. 11 Example 2C C. If ABCD is a parallelogram, find the value of k. A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7 Example 3 Parallelograms and Coordinate Geometry What are the coordinates of the intersection of the diagonals of parallelogram MNPR, with vertices M(–3, 0), N(–1, 3), P(5, 4), and R(3, 1)? Example 3 Parallelograms and Coordinate Geometry What are the coordinates of the intersection of the diagonals of parallelogram LMNO, with vertices L(0, –3), M(–2, 1), N(1, 5), O(3, 1)?