Cell Structure and Functions Presentation

Cell Structure and Functions
Cell Theory
There are three parts to the cell theory
1. all living things are made of one or more cells
2. cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms.
3. All Cells arise from pre-existing cells
Cell
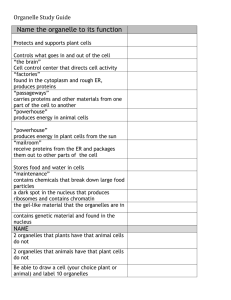
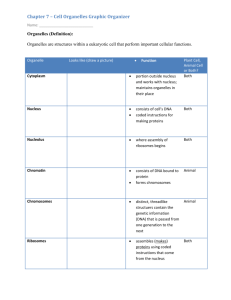
Organelles
• What are organelles?
• internal compartments that carry out specific cell functions
• How are organelles beneficial to a cell?
• They allow the cell to grow larger and become more specialized
• Nucleus : control center; houses DNA; directs activities of the cell
• Nucleolus: producing ribosomes
• Nuclear envelope : encloses the nucleus and its contents
• Nuclear pore : pore in nucleus; can allow substances (RNA) to leave
Mitochondria
• Powerhouse of the cell
• Energy production for cells (ATP)
• Sites of aerobic respiration
• “mitochondria makes me mighty”
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
• Synthesizes steroids
• Detoxifies poisons
(alcohol)
• Transports substances
• Regulates calcium levels for muscle contraction
• Transports proteins
Ribosomes
• Make proteins
Golgi Apparatus
• membrane-bound structure
• organelle modifies molecules and packages them into small membrane bound sacs called vesicles
Vesicle
• Membrane-sac that transports materials
Lysosomes
• digests waste materials and food within the cell
• breaks down molecules into their base components with strong digestive enzymes
Plant Cell
• Plant cells have different structures
• Contains:
– Cell wall
– Chloroplast
– Vacuole (large central, takes up most part of cell)
Cell membrane
• Regulates substances in and out of the cell.
• Protection
Cell wall
centrioles
Assist with cell division : helps to move chromosomes
• Hereditary informer
• Material consisting of
DNA and proteins only visible during cell division.
Different levels of DNA condensation. (1) DNA strand. (2) Chromatin strand
(DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4)
Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are now present) (5) Chromosome during metaphase.
• Part of cytoskeleton
• Assist in cell division
• Can combine with other proteins to form complex structures like cilia and flagella
Cilia
Flagella
• Cellular movement