Period 1 Highlight for Review
advertisement

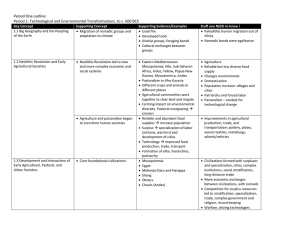
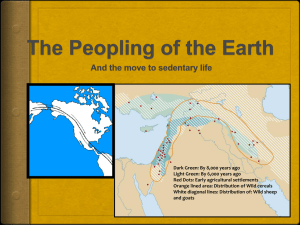
Period One-5% of Questions Period I – Technological and Environmental Transformations to 600 B.C.E Key Concept 1.1. Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth Key Concept 1.2. The Neolithic Revolution and Early Agricultural Societies Key Concept 1.3. The Development and Interactions of Early Agricultural, Pastoral and Urban Societies Big Geography • Global nature of world history • Human migration from Africa-EurasiaAustralia-Americas Paleolithic Age • • • • • Human adaptation and mobility Relatively egalitarian-small kinship groups Hunters, gatherers, traders Technologies-fire, tools Culture-cave art Transition: Paleolithic to Neolithic 1. After living for over 200,000 years as foragers… 2. 10,000 years ago, people gradually gave up a nomadic, hunting and gathering lifestyle and settled down. 3. Was it intentional? (sedentary trap) Changes occurred due to: The Great Thaw: Global Climate Change (warmer… food production easier) Population Growth (migration until no places left) Separate Farming Origins Origins of Farming • 11,000 ya Fertile Crescent and the Nile (wheat) • 8000 ya China (rice) and Papua New Guinea (taro and yams) • 5000 ya West Africa (millet and sorghum) • 4000 ya Mesoamerica (maize, squash) and Andes (potatoes) Positive Effects of Neolithic Revolution • Increased food production (until population catches up again) • More diverse foodstuffs possible • Textile production • Metallurgy (working of gold, copper, bronze, iron) • Secondary Products Revolution—innovations in agriculture and animal husbandry (milk, stirrups, plows, tools…) Downsides of Agriculture • Nutrition declined (H & G varied diet) • Starvation more likely (reliance on one crop and on nature, increased vulnerability) • More work (less leisure time) • More patriarchal (public vs private sphere) • People got shorter initially and more tooth decay • Increased infant mortality (more kids) • Higher disease rates (more dense pop) • Life expectancy declined • Increased class divisions Social Effects of Agriculture • Women probably first to realize plans grew from seeds and Control which plants grew where over time • Domestication of animals • Women build homes and farmed; men hunted further afield • Women involved in hearth, courtyard, and field—food production, informal education, child-rearing, arts, music and religious ritual. • Children became busier as they helped around the home • Surplus over time led to specialization in the community • Land ownership led to patriarchal societies and lower status for women • Status and power became more important Human Impact on Environment • Soil erosion • Deforestation • Contamination of water sources • Dependency on land and certain crops Nomadic groups continue • Conflict (wealth of agricultural surplus societies) • Peaceful exchange of technology, ideas, products and people Civilization • • • • • • • • • • Agricultural surplus Specialization of labor Cities Complex institutions Stratified social hierarchies Long distance trade Competition Religion Environmental challenges Violence • • • • • • • • • Monumental architecture Urban planning Arts and artisanship Systems of record keeping Legal codes Literature Social Hierarchies Patriarchy Technological advancements Period One Civilizations/Religions • Mesopotamia • Egypt • Indus Valley (MohenjoDaro and Harappa) • Shang • Olmec • Chavin • Pastoral people • Pastoral advancementsweapons and transportation • • • • • Polytheism Theocracies The Vedic Religion Hebrew Monotheism Zoroastrianism