Metric Conversions Notes

Dimensional
Analysis Conversions
With Significant Digits!
1
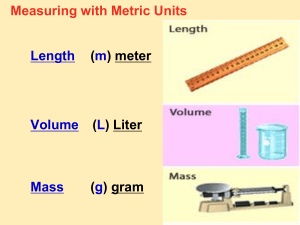
Metric Prefixes Review
MANY SMALLER PREFIX
Pico
Nano
Micro
Milli
ABBREVI
ATION p n
μ m
Centi c
Deci d
BASE UNIT m, g, L, etc.
Deka
Hecto
Kilo
Mega da h k
M
MEANS ONE LARGER
EQUALS
1 X 10 -12 1 gram =
1 X 10 -9 1 gram =
1 X 10 -6 1 gram =
1 X 10 -3 1 gram =
1 X 10 -2 1 gram =
1 X 10 -1 1 gram =
1
1,000,000,000,000 picograms
1,000,000,000 nanograms
1,000,000 micrograms
1,000 milligrams
100 centigrams
10 decigrams
1 X 10 1 1 dekagram = 10 grams
1 X 10 2 1 hectogram = 100 grams
1 X 10 3 1 kilogram = 1000 grams
1 X 10 6 1 megagram = 1,000,000 grams
2
Other Metric Mentionables
• For ALL substances: 1 mL = 1cm 3
• Water is special:
• 1 gram of has a volume of 1 ml or 1 cm 3
• 1 g water = 1mL water
• 1 g water =1 cm 3 water
3
Let’s Do It!!!
• Write the numbers 1-5 on your paper.
• Write which of these values is larger:
• 1. A microliter or a liter
• 2. A kilogram or a gram
• 3. A centiliter or a liter
• 4. A megasecond or a second
• 5. A decigram or a gram
4
Let’s Do It!!!
• Write the numbers 1-5 on your paper.
• Write which of these values is larger:
• 1. A microliter or a liter
• 2. A kilogram or a gram
• 3. A centiliter or a liter
• 4. A megasecond or a second
• 5. A decigram or a gram
5
Let’s Do It!!!
• Write the numbers 1-5 on your paper.
• How many ____________ are in a
____________:
• 1. micrograms in a gram
• 2. meters in a kilometer
• 3. centiliters in a liter
• 4. seconds in a megasecond
• 5. decigrams in a gram
6
Let’s Do It!!!
• Write the numbers 1-5 on your paper.
• How many ____________ are in a
____________:
• 1. micrograms in a gram 1,000,000 or 1X10 6
• 2. kilometers in a meter 1000 or 1X10 -3
• 3. centiliters in a liter 100 or 1X10 2
• 4. megaseconds in a second 1,000,000 or 1X10 -6
• 5. decigrams in a gram 10 or 1X10 1
7
Conversions
• How many kilometers are in 50 meters?
• This can get a little hairy!
• How many inches in a meter?
• Now we are trying to relate English units and metric units! Even more confusing!
• This is where we will use a technique called …….
(drum roll please)
• DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS!!!!!!!!
8
Dimensional Analysis
What is it?
• A problem solving method
• A series of multiplications and divisions
• Units are also multiplied and divided (units can cancel)
• We multiply by fractions called
“conversion factors”
• Conversion factor- a statement of fact expressed as a fraction equaling one that helps us convert from one unit to another
9
Conversion Factors
• All conversion factors are equal to 1
• Conversion factors can be made from
• English-English relationships
• 1 foot = 12 inches
• Metric-Metric relationships
• 1 km = 1x10 3 m
• English-Metric relationships
• 1.00 in = 2.54 cm
• Conversion factors can be made from information
10 given in a problem
Equal to 1???
Conversion factors are made from equivalents
2 = 2
2
1
2
X = X x
1 x
4 - 2 = 1 + 1
4
1
2
1
1
1 foot = 12 inches
1 foot
12 inches
1
11
Equivalent
1 foot = 12 inches
1 km = 1 x 10 3 m
1 cm = 1 x 10 -2 m
Conversion Factor
1 foot
12 inches
1 2
1 inches foot
1 km
1 x 10
3 m
1 x 10
3 m
1 km
1 cm
1 x 10
2 m
1 x 10
-2 m
1 cm
12
Metric Conversions
• Fact: 1 kilometer = 1000 meters from our table
• This is a conversion factor and we can write it 2 ways: a. 1 km or b. 1000 m
1000 m 1 km
What do these mean? The exact same thing!
a. That there is 1 km PER 1000 m or 1 km = 1000m b. That there are 1000 m PER 1 km or 1000m = 1 km
Both the top and bottom are equal so the whole conversion factor is equal to one so we can use it without randomly changing values
13
Metric Conversions
• So…..
• How many kilometers ARE there in 50 meters?
• We can use a conversion factor that relates km to meters, but which one?
a. 1 km or b. 1000 m
1000 m 1 km
14
Question Mark Format-Reference
• We follow some steps and the UNITS WILL TELL
US WHAT TO DO.
• Follow this QUESTION MARK FORMAT , when doing dimensional analysis! Even if you can solve it in your head, these questions will get a LOT tougher!
• FOLLOW THE METHOD!!!!
• DID I SAY FOLLOW THE METHOD??????
15
Question Mark Format-Reference
• PSSSSTTTT. FOLLOW THE METHOD
• 1. Start every problem with the QUESTION MARK
FORMAT (the “?” means “how many?”)
• 2. Cancel the units
• 3. Insert fact
• 4. Do the math (multiply across and divide top by bottom just like fractions)
How many kilometers in 50 meters?
• ? km = 50 m
16
Metric Conversions
• PSSSSTTTT. FOLLOW THE METHOD
• 1. Start every problem with the QUESTION MARK
FORMAT (the “?” means “how many?”)
• 2. Cancel the units
• 3. Insert fact
• 4. Do the math (multiply across and divide top by bottom just like fractions)
How many kilometers in 50 meters?
• ? km = 50 m x ____km__ m
17
Metric Conversions
• PSSSSTTTT. FOLLOW THE METHOD
• 1. Start every problem with the QUESTION MARK
FORMAT (the “?” means “how many?”)
• 2. Cancel the units
• 3. Insert fact
• 4. Do the math (multiply across and divide top by bottom just like fractions)
How many kilometers in 50 meters?
• ? km = 50 m x _____ km__ m
18
Metric Conversions
• PSSSSTTTT. FOLLOW THE METHOD
• 1. Start every problem with the QUESTION MARK
FORMAT (the “?” means “how many?”)
• 2. Cancel the units
• 3. Insert fact
• 4. Do the math (multiply across and divide top by bottom just like fractions)
How many kilometers in 50 meters?
• ? km = 50 m x __1__km__
1000 m
19
Metric Conversions
• PSSSSTTTT. FOLLOW THE METHOD
• 1. Start every problem with the QUESTION MARK
FORMAT (the “?” means “how many?”)
• 2. Cancel the units
• 3. Insert fact
• 4. Do the math (multiply across and divide top by bottom just like fractions)
How many kilometers in 50 meters?
• ? km = 50 m x __1__km_ = 50 X 1 km = ?
1000 m 1000
20
Reference
• Convert 7.0 feet to inches
12
1
1 ft = 12 in in ft
1 ft
12 in
? in = 7.0
ft
*
12 in
1 ft
84 in
21
Reference
• Convert 2.89 hg to g
1hg=1*10 2 g
? g = 2.89
hg
*
1*10
2
1 hg g
289 g
22
Reference
• Convert 2.89 Mg to cg
1Mg=1*10 6 g
1cg=1*10 -2 g
? cg = 2.89
Mg
*
1*10
6
1 Mg g
*
1 cg
1*10
2 g
289, 000, 000 cg
23
Let’s Do It!!!!
• 1. How many kilograms are in a 350 grams?
• 2. I have 45 milliliters. How liters is this?
• 3. Superchallenge!!! How many kilometers are in a millimeter? You have to use two conversion factors!
24
Metric Conversions
Metric
video 8 min
• One last important step:
• CHECK SIGNIFICANT DIGITS!
• Any fact that is found in a conversion factor is not a measurement and so is ignored when calculating the number of significant digits.
25
Reference
• Convert 4.756 dm to yd
1dm=1*10 -1 m
1.00m=39.4in
12in=1ft
3ft=1yd
? yd = 4.756
dm
*
1*10
1
1 dm m
*
39.4
in
1.00
m
*
1 ft
*
12 in
1 yd
3 ft measured
4 SD
.521
yd definition measured definition definition
NO SD 3 SD NO SD NO SD
26
How many pounds are in a gallon of water?
1 g water = 1 mL
? lb =
1.00
gal 4 qt
*
1 gal
*
946 mL
1.00
qt
1 g
*
1 mL
*
1.00
lb
454 g
8.33
lb
27
Dimensional Analysis with Multiple
Units- Reference
Strategy:
1. Convert each unit in the fraction separately
2. Make sure units cancel!
28
Reference
Example 1:
Convert 70.0 mi/hr to km/sec
1 mi = 5280 ft
1 ft = 12 in
39.4in = 1.00m
1x10 3 m = 1km
1hr = 60 min
1 min = 60 sec
? km/sec =
70.0
mi hr
*
5280
1 mi ft
*
12 in
1 ft
*
1.00
m
39.4
in
*
1 km x
3 m
*
1 hr
60 min
1min
*
60 sec
km
.0313
sec
29
Example 2:
• Convert 15.3 g/L to lb/gal
454g = 1.00lb
.946L = 1.00qt
4qt = 1gal
? lb/gal
=
15.3
L g
*
1.00
lb
454 g
.946
L
*
1.00
qt
4 qt
*
1 gal
.128
lb gal
30
Let’s Do It!!!!
• 1. How many Megagrams are in a pound?
• 2. I have 45 liters. How many cm 3 is this?
31
Review
Dimensional Analysis
video 9min
• Number your paper from 1-5 and answer the following questions.
• 1. Which of these has 3 significant digits?
• a. 0.000000312
• b. 3.5 X 10 4
• c. 0.4506
• d. 910
32
Review
• A
• 2. Which of these is a qualitative observation?
• a. the sky is dark
• b. his head is 45 cm in diameter
• c. she has 20 freckles
• d. the candle was 17 cm long
33
Review
• A
• 3. Which of these is a conversion factor?
• a. 3 cm
• b. 12 inches = 1 foot
• c. 3 ft
1 yard
34
Review
• C
• 4. What’s the first step in setting up a dimensional analysis problem?
• a. cancel the units
• b. write down all the conversion factors
• c. cry
• d. set up the question mark format
35
Review
• D
• 5. What does this conversion factor mean?
14 frizzles drizzle
• a. There are drizzles that are frizzles
• b. There are 14 frizzles per drizzle
• c. A frizzle and a drizzle are equal
• d. There are 14 drizzles per frizzle
36
Review
• B
What observations can you make about this picture?
37
Density
• Density = mass per (divided by) unit volume
• D = mass/volume
• D= m/V
• Common units of density: g/mL, g/cm 3
• Remember that 1 mL=1cm 3 !
• Suppose we have an object with a mass of 5.0 grams and a volume of
2.0 mL. What would be the density ?
• D = 5.0g/2.0mL = 2.5g/mL (2 sig figs)
38
Let’s Do It!!!
• 1. Given a mass of 12g and a volume of 3 mL, calculate the density.
39
Let’s Do It!!!
• 1. Given a mass of 12g and a volume of 3 mL, calculate the density.
• Need density
• D = m/V
• D = 12g/3mL
• D = 4m/mL (1 sig fig since following multiplication rules
40
Let’s Do It!!!
• 2. Given that the density of iron is 7.9m/cm 3 what would be the volume of a 15.8 g piece of iron?
41
Let’s Do It!!!
• 2. Given that the density of iron is 7.9g/cm 3 what would be the volume of a 15.8 g piece of iron?
• D = m and asking for volume so solve for V
V
• Multiply both sides by V: V x D = m x V
V
So V x D = m
• Divide both sides by D: V x D = m
So V = m = 15.8g
D 7.9g/cm 3
D D
= 2.00 cm 3 (3 sig figs)
42
Let’s Do It!!!
• 3. Find the density of a block with a length of
4.0cm, width of 3.0cm, and a height of 2.0cm and a mass of 36g
43
Let’s Do It!!!
• 3. Find the density of a block with a length of
4.0cm, width of 3.0cm, and a height of 2.0cm and a mass of 36g
• Need density
• D = m/V
• V = l x w x h = 4.0cm x 3.0cm x 2.0cm = 24cm 3
• D = 36g/24cm 3 or 1.5g/cm 3
44
Review
• Number your paper from 1-5 and answer the questions that follow
• 1. Which of these is correct?
• A. 1 gram = 1 x 10 -3 milligrams
• B. 1 gram = 1 x 10 6 kilograms
• C. 1 gram = 1 x 10 3 milligrams
• D. 1 gram = 1 x 10 -6 micrograms
45
Review
• C
• Round to the appropriate significant digit
• 2. If I dropped a toy car into a glass and the toy car displaced 20mL of water, what is the volume of the toy?
• A. 20cm
• B. 2mL
• C. 20mm
• D. 20cm 3
46
Review
• D
• 3. What is the mass of an object with a density of 4.0g/cm 3 that displaces 3.0 cm 3 of water?
• A. 7 g
• B. 12 g
• C. 0.75 g
• D. 1 g
47
Review
• B
• 4. What is the mass of 50mL of water?
48
Review
• 1 g = 1 mL = 1 cm 3 of water, so 50mL = 50g
• D = m/V not needed!
• 5. Super challenge! You have a piece of silver with a mass of 31.5 g. Silver has a density of
10.5g/cm 3 . What would be the new level of water if this piece of silver is placed into 15mL of water?
• A. 12.0mL
• B. 5.0mL
• C. 18.0mL
• D. 21.0 mL
49
Review
• C
• Solve D = m/V
• So V = m = 31.5g
D 10.5g/cm 3
= 3.00cm
3 = 3.00mL
So add 15.0 mL + 3.00mL = 18.0mL
50
Experimental and Percentage
Error
• ALL measurements are subject to some uncertainty because an estimate is involved
• Accuracy - the nearness of a measurement to its accepted value
• Accuracy can be expressed in either absolute or relative terms called experimental error or percentage error respectively.
51
Experimental and Percentage
Error-Reference
• Experimental error (absolute)=observed - accepted experimental error
• Percentage error (relative) = --------------------X 100 % accepted value
An accepted value is a standard or known value
1. 12 inches in a foot
2. Water freezes at 0 o C
52
Experimental and Percentage
Error-Reference
• Sample Problem:
• A student is asked to weigh out 5.00 grams of salt the balance.
When checked by the instructor, it is found that the student has weighed out 4.942 g. Calculate the student’s experimental error
(EE) and percentage error (PE).
• Experimental error = observed value - accepted value
• Experimental error = 4.942 g - 5.00 g = -.06 g (sig digits!) experimental error - .06 g
• % error = ------------------------ X 100 % = ------------ X 100 % = -1 % accepted value 5.00 g sig digits!!!
53
Experimental and Percentage
Error-Reference
• Reminders:
• Experimental Error
• 1.Always put the observed (student) value first
• 2.Answer can be positive or negative with same units as what you subtracted
• 3.Significant digits are done by place value because it’s addition
• Percentage Error
• 1.When calculating, do not use the % key on your calculator
• 2.Answer will have the same sign as experimental error and units will always be %
• 3.Significant digits are done by counting because it’s multiplication
54
Let’s Do It!!!!
• As the result of experimental work, a student finds the density of a liquid to be .145 g/mL. The known density of the liquid is .146 g/mL. Find the student’s experimental error (EE) and percentage error (PE).
55
Let’s Do It!!!!
• Experimental error = observed value - accepted value
• Experimental error = 0.145 g/mL – 0.146 g/mL = -0.010 g (sig digits!)
• Percentage error experimental error - .010 g
• % error = ------------------------ X100% = ------------ X100% = -.07 % accepted value 0.146g sig digits!!!
56
Temperature Scales-Reference
• There are 3 commonly used temperature scales in science.
• 1. Fahrenheit,
• 2. Celsius (or centigrade)
• 3. Kelvin (absolute) scale.
57
58
•
Temperature Scales-Reference
• Conversions between temperature scales:
• **Celsius to Kelvin conversion: T
K
= T
°C
+ 273
273 has no SD’s because it’s a known number
• Example: convert 25 °C to Kelvin
T
K
T
K
T
K
= T
°C
+ 273
= 25 + 273
= 298 K notice the unit is K not °K
59
Temperature Scales-Reference
• **Kelvin to Celsius conversion: T
°C
= T
K
• Example: convert 250 K to Celsius
T
T
T
°C
°C
°C
= T
K
- 273
= 250 - 273
- 273
= - 20 °C rounded to the tens place
60
•
Temperature Scales-Reference
• **Fahrenheit to o C conversion: T
°C
= (T
°F
- 32) ÷ 1.8
32 and 1.8 have no SD’s
• Example: convert 98.7 °F to Celsius
T
T
°C
°C
T
°C
T
°C
= (T
°F
- 32) ÷ 1.8
= (98.6 - 32) ÷ 1.8
= 66.7 ÷ 1.8
= 37.0 °C
61
Temperature Scales-Reference
• **Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion: T
°F
=(1.8 • T
°C
) +
32 1.8 and 32 have no SD’s
• Example: convert 36 °C to Fahrenheit
T
T
°F
°F
T
°F
T
°F
= (1.8 • T
°C
) + 32
= (1.8 • 36) + 32
= 65 + 32
= 97 °F
62
Let’s Do It!!!
• 1. Convert 25.0 °C to Kelvin
63
Let’s Do It!!!!
• T
K
• T
K
• T
K
= T
°C
+ 273
= 25.0 + 273
= 298.0 K the 273 does not affect SD’s because it is not measured
64
Let’s Do It!!!!
• 2. Convert 303 K to Celsius
65
Let’s Do It!!!!
• T
°C
• T
°C
• T
°C
= T
K
- 273
= 303 - 273
= 30 °C rounded to the ones place
66
Let’s Do It!!!!
• 3. Convert - 25 °F to Celsius
67
Let’s Do It!!!!
• T
°C
• T
°C
• T
°C
• T
°C
= (T
°F
- 32) ÷ 1.8
= (- 25 - 32) ÷ 1.8
= - 57 ÷ 1.8
= - 32 °C
68
Review
Temperature
video 5 min
• Number your paper from 1-5 and answer the following questions
• 1. How many sig figs should the product of 1.304 and 000.025 have?
• A. 1
• B. 2
• C. 3
• D. 4
69
Review
• B
• 2. Which of these is true?
• A. density = mass X time
• B. density = volume X mass
• C. density = volume X time
• D. density = mass/volume
70
Review
• D
• 3. What are the three systems of measuring temperature?
• A. Celsius, grams, liters
• B. Celsius, second, liter
• C. Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin
• D. Hot, Hotter, Hottest
71
Review
• C
• 4. You are in Paris and the weatherman says it’s going to be 35 o C today. What kind of clothes should you wear?
• A. A coat
• B. A light jacket
• C. A pair of shorts and a t-shirt
• D. A heavy coat and mittens and hat. That’s way too cold!
72
Review
• C
• 5. What is the temperature in Kelvin at which water freezes?
• A. 273.15 K
• B. 273.15 o K
• C. 0 K
• D. -170 K
73
Review
• A
74