File
Gilded Age Politics
Waving the “Bloody shirt” in the 1868 election
Scandals
Fisk and Gould-bribes
Credit Mobiler-bribes and unfair hiring practices
Grant’s secretary helped whiskey distillers escape
Foreign Policy
Alabama
Santo Domingo
Grantism
Tweed Ring
Stole from NYC
Grantism
Corruption
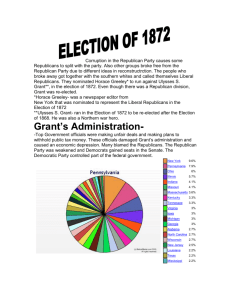
Election of 1872
Liberal Republicans (anti-
Grant) along with
Democrats nominated
Horace Greeley
Republicans nominated
Grant for 2nd term
Reform of Republican party was the true success of the liberal republicans
Causes:
Overproduction in both agriculture and industry
Jay Cooke and bank failure
Triggered 5-year depression
Debate hard v. soft money
Resumption Act of
1875
Panic of 1873
Reconstruction and the
Constitution
Ex parte Milligan
(1866)
Texas v. White
(1869)
Slaughterhouse cases (1873)
U.S. v. Reese (1876)
Reconstruction Abandoned
Democrats in the
South
Home rule
“Redemption”
Terrorism
Kansas fever
Plantation before and after the Civil War
Election of 1876 - And the
Winner is….
Hayes v. Tilden
Tilden won
Contested votes and fraud!
Compromise of 1877
(end of
Reconstruction)
Plessy v. Ferguson
(1896)
In reality, segregation and inequality were mainstays in
Southern society
Jim Crow Laws
Virginia Theaters: Every person...operating...any public hall, theatre, opera house, motion picture show or any place of public entertainment or public assemblage which is attended by both white and colored persons, shall separate the white race and the colored race and shall set apart and designate...certain seats therein to be occupied by white persons and a portion thereof , or certain seats therein, to be occupied by colored persons.
Virginia Railroads: The conductors or managers on all such railroads shall have power, and are hereby required, to assign to each white or colored passenger his or her respective car, coach or compartment. If the passenger fails to disclose his race, the conductor and managers, acting in good faith, shall be the sole judges of his race.
Class Conflicts
Railroad Strike
Agreement to cut wages
Strike with federal army brought in
Chinese
Primarily men
Economic hardship
Chinese Exclusion
Act (1882)
Garfield (not the cat!)
Garfield v. Hancock v.
Weaver (Greenback
Party) in 1880
Garfield won but was shot by deranged man
Arthur
Cracked down on Spoils system (Pendleton Act)
Led to “marriage of convenience” with corporations
Conflicting Views of Spoils
System
“The civil service law is the biggest fraud of the age. It is the curse of the nation. There can’t be no real patriotism while it lasts. How are you goin’ to interest our young men in their country if you have no offices to give them when they work for their party?...First, this great and glorious country was built up by political parties; second, parties can’t hold together if their workers don’t get the offices when they win; third, if the parties go to pieces, the government they built up must go to pieces, too; fourth, then there’ll be hell to pay.” –a political boss (George Washington Plunkitt)
“The men who are in office only for what they can make out of it are thoroughly unwholesome citizens, and their activity in politics is simply noxious…Decent private citizens must inevitably be driven out of politics if it is suffered to become a mere selfish scramble for plunder, where victory rests with the most greedy, the most cunning, the most brazen. The whole patronage system is inimical to American institutions; it forms one of the gravest problems with which democratic and republican government has to grapple. – Teddy Roosevelt
Mudwumps and Mudslingers
Republican Baine v.
Democrat Cleveland
(Election of 1884)
Personalities not principles debated throughout campaign
Cleveland the President
Spoils system
Tariff
Veteran Pensions
Election of 1888
The City v. Young
Tippecanoe
Harrison won
Used big business money
“voting cattle”
Billion-Dollar Congress
Republican Congress passed out money liberally
Major pensions
McKinley Tariff
Farmers respond with the vote
Election of 1892
Populist Party
Farmers
James B. Weaver as candidate
One of few third parties since Civil War to gain electoral votes (22)
Homestead Strike
Carnegie Steel
Pinkerton detectives
Troops eventually called in
Cleveland (Again!)
Won 1892 election
Panic of 1893
Depression
Gold Crisis with J.P.
Morgan to the rescue
Wilson Gorman
Tariff (1894)
Industry and Economics
Power of Industry
Vertical integration
Ex: Carnegie’s steel
Horizontal integration
Ex: Rockefeller’s Standard Oil
Interlocking directorates
Ex: Morgan’s banks
Transcontinental railroad
Union Pacific meets
Central Pacific
Vanderbilt
Positive Impact
Markets and industry
Mining and agriculture
Westward migration
Time zones
Problems
Credit Mobiler Scandal
Railroad “Kings”
Government intervened with the Wabash Case of
1886 and Interstate
Commerce Act of (1887)
Railroads
Railroads
Steel
Bessemer Process
Carnegie
J.P. Morgan and the
U.S. Steel Company
Rockefeller and the
Standard Oil
Company
Spies, manipulation and secrecy
Justification
Gospel of Wealth
Social Darwinism
Oil
Government Involvement
Commerce Act of 1887
Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890
Clayton Anti-Trust Act
Unions
Early Impact?
Major Unions
National Labor Union
Knights of Labor
Haymarket Square
American Federation of Labor
Samuel Gompers
New immigrants
Southern and eastern
Europe
Reasons for coming to
U.S.
Reactions
Bosses like Boss Tweed play role
Charity
Christian socialists
Hull House
Urban reformers
Nativism
Immigration
Education
Rise of public education and compulsory attendance
Black Rights
Booker T. Washington v.
W.E.B. DuBois
Colleges
Morrill Act of 1862
Novelists
(List the major writers in Chapter 25 for your notebook)
Newspapers
Sensationalism and yellow journalism
Magazines