Powerpoint
advertisement

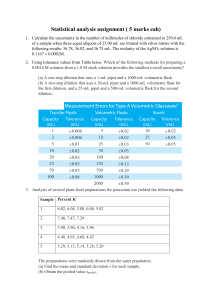
Chapter 0: The Analytical Process (Example) 1. Formulating the Question 2. Selecting Analytical Procedures 3. Sampling Random Heterogeneous Material Segregated Heterogeneous Material 4. Sample Preparation 5. Analysis 6. Reporting and Interpretation 7. Drawing Conclusions Terminology to Know From the Example representative sampling – random vs. segregated sample preparation extraction, centrifugation, filtering chromatography, stationary phase, adsorption aliquot calibration curve Chapter 2: Tools of the Trade Mechanical Balance Electronic Balance Buoyancy correction - a sample appears lighter than its actual mass by an amount equal to the mass of the air it displaces. da m 1 d w m da 1 d ' Example: Find the true mass of water (density = 1.00 g/mL) if the apparent mass is 100.00g Calibration of Volumetric Glassware True volume = mass H2O x correction factor Example p. 49: an empty weighing bottle had a mass of 10.283 g. After water was added from a 25-mL pipet, the mass was 35.225 g. The temperature was 23oC. Find the volume of water delivered by the pipet.