31.4 Conflicts in the Middle East

Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Conflicts in the Middle East
Preview
• Faces of History: Golda Meir
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Conflicts in the Middle East
Preview, continued
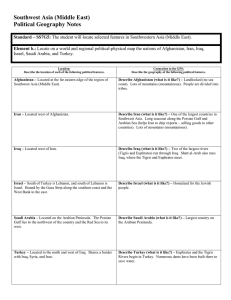
• Visual Study Guide / Quick Facts
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Conflicts in the Middle East
Main Idea
Regional issues in the Middle East have led to conflicts between
Israel and its neighbors and to conflicts in and between Iran and
Iraq.
Reading Focus
• How have regional issues contributed to conflicts in the Middle
East?
• What were some key events in the Arab-Israeli conflict?
• What caused a revolution in Iran?
• How have conflicts in Iraq affected that country?
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Regional Issues
Over the last few decades, major conflicts have erupted in the Middle
East. Issues that have contributed to the conflicts include the presence of huge oil reserves, the growth of Islamism, and the conflict between
Israel and its neighbors.
Oil in the Middle East
• About two-thirds of world’s known oil reserved located in Middle East
• Reserves have been great source of wealth for Saudi Arabia, Iran,
Iraq, Kuwait, other countries
• Most members of Organization of
Petroleum Exporting Countries
Oil Revenues
• OPEC attempts to regulate production of oil exports to maximize revenues
• Oil revenues allowed Middle East governments to modernize countries, promote industrialization, economic, social development
However, oil has also been a source of conflict.
Africa and the Middle East
Importance of Oil
Section 4
Oil as source of conflict in Middle East
• Some governments have used oil revenues to build up military, maintain power, threaten neighbors
• Oil wealth has caused internal clashes within countries, societies
• Region’s strategic importance as source of oil has led outside nations to become involved in Middle Eastern affairs, politics
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Growth of Islamism
Islamists
• Movement to reorder government, society according to Islamic laws
Conflicts, Violence
• Egypt, Iran, Iraq have seen growth of Islamism; has led to conflicts within society, government
• Islamists believe Muslim countries have strayed from true Islam, followed Western models of political, economic development
• Some extremists have used violence to bring about changes, have attacked regional governments, their allies, innocent civilians
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Conflicts with Israel
• 1948, Israel established; since then most Middle Eastern countries have refused to recognize its right to exist
• Some countries have repeatedly attacked Israel, funded militant groups that conduct raids, terrorist attacks against Israelis
Expansion of Israel
• Series of wars between Israel, neighbors has led to expansion of
Israel
• Israel controls more land now than in 1948 when created
• Result: many Palestinian Arabs live under Israeli control; another source of tension, conflict in region
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Summarize
What regional issues have led to conflicts in the Middle East?
Answer(s): use of oil revenues; growth of
Islamism; conflicts with Israel
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
The Arab-Israeli Conflict
The Arab-Israeli conflict that began in 1948 has continued through the years.
In 1967 and again in 1973, war erupted. Six years after the 1973 war, Egypt and Israel singed a peace agreement, but unrest among Palestinian Arabs in
Israel remained a major problem.
War in 1967, 1973
• 1967, Egypt demanded UN remove troops from
Gaza, Sinai
Peninsula
• Egyptian troops moved into Sinai to close off Gulf of
Aqaba, Israel’s route to Red Sea
Israeli Attacks
• Israel expected largescale Arab attack, decided to strike first
• Launched air strikes against Egypt, Syria,
Jordan; destroyed most of airplanes on ground
• Ground troops moved in, defeated Arabs
Six-Day War
• In Six-Day War Israel took control of Golan
Heights, Sinai
Peninsula, Gaza
Strip, West Bank,
East Jerusalem
• Took control of land in
West Bank, Gaza with large Palestinian population
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Egypt Strikes Back
Yom Kippur War
• Egypt, Syria determined to win territory back, launched Yom Kippur War , surprise attack against Israel in 1973
• Took name from Jewish holy day when attack began
U.S. Support
• At first Arab troops made gains in war; Israeli’s government, led by Golda
Meir , not fully prepared for attack; needed military support from U.S.
• With support, Israeli forces regrouped, pushed back Egyptian, Syrian armies
Oil Embargo
• Both sides agreed to cease-fire after weeks of fighting
• During war, Arab members of OPEC declared oil embargo against countries supporting Israel
• Price of oil around world rose dramatically as result of refusal to sell oil
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
A Peace Agreement
Until the late 1970s, no Arab nation had recognized Israel’s right to exist.
Camp David
• 1977, Egyptian president
Anwar Sadat made momentous declaration: Egypt wanted peace with Israel
• U.S. president Jimmy Carter invited Sadat, Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin to
Camp David, presidential retreat in Maryland
Peace Treaty
• 1978, Sadat, Begin reached agreement known as Camp
David Accords
• Egypt recognized Israel; Israel returned Sinai Peninsula to
Egypt
• Treaty ended 30 years hostility between Egypt, Israel
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Palestinian Unrest
• Egypt, Israel made peace; Palestinian Arabs continued struggle for nationhood
• 1947 UN partition plan had called for two states in Palestine—a
Jewish state, an Arab state
• After 1948 Arab-Israeli war, land set aside for Arab state occupied by
Israel, Egypt, Jordan
Palestinian Nationalism
• 1964, Palestine Liberation
Organization (PLO) formed
• Pledged to destroy Israel, replace with Palestinian state
• 1969, Yasser Arafat became leader,
PLO launched guerilla attacks against Israel
Palestinian Resentment
• In effort to stop attacks, Israel invaded Lebanon, 1978 and 1982
• Tensions building also in West
Bank, Gaza where Israel had begun building settlements
• 1987, Palestinian resentment began rebellion called intifada
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Tenuous Peace
Intifada
• Palestinian youths battled Israeli troops in widespread street violence
• Israel responded with military, police resistance; fighting continued to 1990s
• 1993, Arafat, Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Rabin negotiated Oslo Accords
Oslo Accords
• Oslo Accords called for Palestinians to gradually gain control over governing
West Bank, Gaza
• Israel, PLO supposed to sign permanent peace agreement by 1998
Undermining Peace
• Extremists on both sides worked to undermine peace process
• Militant group Hamas launched suicide bombings in Israel
• 1995, Rabin assassinated; relations between Israeli, Palestinian leadership soured
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Continuing the Conflict
• 2000—second intifada began
• Palestinian youths joined by Palestinian security forces with guns
• Hamas sent suicide bombers into Israel to attack civilians
More Fighting
• Israelis countered by sending troops backed by tanks, fighter jets, helicopter gunships into cities in
West Bank, Gaza
• 2004, Arafat died, succeeded by
Mahmoud Abbas
Hamas in Control
• 2004, Israeli prime minister Ariel
Sharon withdrew Israel from Gaza, parts of West Bank
• 2005, Gaza turned over to
Palestinians
• 2006, militant Hamas won control of Palestinian parliament
Armed conflict also erupted when Israeli soldiers were kidnapped along borders with Gaza and Lebanon. Israel launched air strikes to secure its borders.
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Sequence
Describe the sequence of events in the
Arab-Israeli conflict.
Answer(s): 1967: Six-Day War; 1973: Yom Kippur
War; 1978: Camp David Accords; 1987: intifada;
1993: Oslo Accords; 2000: second intifada; 2005:
Israel withdraws from Gaza
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Revolution in Iran
Different Kind of Conflict
• Different kind of conflict erupted in Iran
• Revolution ousted shah,
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
Westernization of Iran
• Shah had close ties with
Western governments, oil companies
• Iran westernized, foreign influence grew
Society Changed
• By 1970s, Iran had changed from traditional rural society
• Had become more industrialized, urban society
Islamists Opposed Shah
• Many Iranians felt threatened by rapid change, others felt betrayed by corrupt government
• Islamists opposed shah because of ties to West
Africa and the Middle East
Rise of Khomeini
Section 4
1978, Iranians began to protest against shah’s rule
• Protests inspired by Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini , Shia religious leader
• 1979, unable to calm unrest, shah fled Iran
• Iran became Islamic republic with Khomeini as leader, during Iranian Revolution
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Khomeini’s Reign
Khomeini’s Reign American Hostages
• Under Khomeini, government suppressed political opposition, enforced strict social religious values
• Foreign policy strongly anti-
Western, especially after shah went to U.S. for medical treatment
• 1979, Iranian revolutionaries seized U.S. embassy in Tehran, took 66 Americans hostage
• Iranians demanded shah be returned to Iran, stand trial
• Shah left U.S., but Iranians held hostages until January, 1981
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Sequence
What was the sequence of events that led to the Iranian Revolution?
Answer(s): Protests began against the shah; the shah fled Iran in 1979; Iran became an Islamic republic with Khomeini as its leader
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Conflict in Iraq
As Iran’s new government was dealing with the hostage crisis, it found itself at war with its neighbor, Iraq.
Iran-Iraq War
• 1980, Iraq attacked Iran because of border disputes
• Also Iran called for revolution among Iraq’s Shiite population
• War long, costly; as many as
500,000 dead on both sides
• Iraq used chemical weapons
• 1988, both sides agreed to cease-fire
Persian Gulf War
• After cease-fire, Saddam
Hussein continued to build up
Iraq’s military; already had largest army in Arab world
• 1990, Iraq accused neighboring Kuwait of drilling into Iraqi oil field, stealing oil
• Hussein used this as excuse to invade Kuwait
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Sanctions
• In effort to end Iraqi occupation of Kuwait, UN passed economic sanctions against Iraq; sanctions failed
• Result: U.S.-led coalition launched Persian Gulf War
• Attacked Iraqi forces in Kuwait; Kuwait freed within weeks
Weapons
• After war, UN continued economic sanctions, insisted Iraq destroy chemical, biological weapons, agree not to develop nuclear weapons
• Inspectors had been sent to verify Iraq’s weapons had been destroyed
• Iraq failed to fully cooperate with UN weapons inspectors
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
The Iraq War
• After attacks of September 11, 2001, some U.S. leaders believed
Saddam Hussein posed a greater threat to America than before
• Hussein might have deadly weapons he could give to terrorists
Weapons Inspections
• UN weapons inspections did not find stockpiles of chemical, biological, nuclear weapons
• Iraq again did not fully cooperate
• Some U.S. officials convinced
Hussein hiding weapons
Growing Insurgency
• 2003, another U.S.-led coalition invaded Iraq, forcing Hussein out
• Efforts to restore peace thwarted
• Growing insurgency targeted coalition forces, Iraqi allies, innocent civilians
Insurgent attacks by different groups from both inside and outside Iraq caused a greater number of casualties.
Africa and the Middle East
Coalition Government
Section 4
Meanwhile, coalition worked to create new, democratic government in Iraq
• 2004, power transferred to Iraqis
• 2005, Iraqis voted in country’s first multiparty election in fifty years
– Later approved new constitution to make Iraq Islamic federal democracy
• Continued violence, potential for civil war made country’s future highly uncertain
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Infer
What are the main problems Iraq has faced in recent years?
Answer(s): wars, economic sanctions, insurgency, potential for civil war
Africa and the Middle East Section 4
Africa and the Middle East
Video
The Impact of Oil
Section 4
Click above to play the video.