Grade 7 Science: Cells & Life Structures Study Guide
advertisement

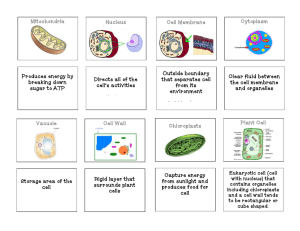
Grade 7 Science Cells: Life Structures Chapters 8 Study Guide Section 1: Living Things Six characteristics of all living things: 1. made of cells 2. grows and develops 3. interacts with environment- a stimulus (action) triggers a response (reaction) 4. maintains homeostasis 5. uses energy 6. reproduces Key terms: organism, cell, homeostasis Section 3: Cell Structure The microscope led to the development of the cell theory Who discovered the microscope? Who first discovered cells? Matthias Schleiden discovered that plants have cells and Theodore Schwann discovered that animals have cells What was Rudolph Virchow’s contribution to the cell theory? Three parts of the cell theory: 1. all living things are made of cells 2. the cell is the basic unit of life 3. all cells come from other cells Two groups of cells: 1. Prokaryotic- contains structures without membranes 2. Eukaryotic- contains organelles; plant and animal cells What cell parts do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common? Important cell parts/organelles: o Cell membrane o Cell wall o Nucleus o Endoplasmic reticulum o Ribosome o Chloroplasts o Mitochondrion o Golgi body Animals cells do NOT have cell walls or chloroplasts- only plant cells do Animal cells have lysosomes- plant cells have chloroplasts Animal cells have multiple, small vacuoles and plant cells have one, large vacuole What are the five levels of organization in all living things? Key terms: cell theory, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, organelle, mitochondrion, chloroplast, vacuole, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, golgi body, tissue, organ, organ system Grade 7 Science Cells: Life Structures The Microscope- NOT IN TEXTBOOK What are the only two parts of a microscope one should hold when carrying this instrument? There are three objective lenses: 1. Low – only use coarse adjustment knob 2. Medium- use fine adjustment knob 3. High- use fine adjustment knob Why should you put the cover slip over the slide at an angle? Possible short answer questions: 1. Cell theory 2. Eukaryotic cells