Cell Theory & Cell Organelles
advertisement

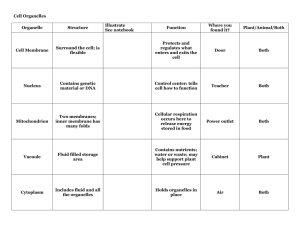
Cell Theory & Cell Organelles Sections 3.1 & 3.2 3.1 Cell Theory Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. More was learned about cells as microscopes improved Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. The Cell Theory: All organisms are made of cells. All cells come from other cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function in living things. http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-wackyhistory-of-cell-theory All cells share certain characteristics. Cells tend to be microscopic. All cells are enclosed by a membrane. All cells are filled with cytoplasm. All cells have ribosomes. All cells have genetic material (DNA – hereditary information) There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells & prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Have a nucleus Have membranebound organelles Prokaryotic cells Do not have a nucleus (still have DNA) Do not have membrane-bound organelles STOP & REVIEW The Cell theory has three parts. Fill in the missing word in each part. All organisms are made of _______. Cells All cells come from other _______. Cells The cell is the basic unit of ________ & _________ in living things. Structure & Function Name 4 parts of the cell that are common between all cells. 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell Membrane, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, and Genetic Material What are the 2 MAJOR differences between prokaryotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic cells? 1. 2. 1. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, 2. Prokaryotic Cells do not have organelles surrounded by a membrane. Eukaryotic Cells have both of these things. 3.2 Cell Organelles Key Concept: Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. Review from 3.1 All cells have: Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Genetic material Cell Membrane (aka Plasma Membrane) Function: the cell Made of: Controls what enters and leaves Phospholipids Proteins Carbohydrates Cholesterol Steroids IN ALL CELLS 1 1 1 Cytoplasm Function: holds organelles in place; location of various reactions in the cell Organelles: parts of the cell with specific jobs/functions 2 2 2 IN ALL CELLS Ribosomes Function: acids) protein synthesis (link amino Found in cytoplasm or on the Rough ER (Rough ER= eukaryotes only) IN ALL CELLS Cell Wall Function: protection and support for plant, fungal, and bacterial cells 5 5 NOT IN ANIMAL CELLS Nucleus Function: (“brain”) Control center of the cell Has its own membrane Nuclear envelope Stores 4 DNA (chromosomes) 3 4 3 Nucleolus Function: Makes rRNA (a nucleic acid) Found inside the nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) “Roadway” of the cell – a maze of enclosed spaces Rough ER Helps make, package, and transport proteins (headed to the Golgi) Ribosomes on surface make it look rough Proteins made include membrane & secretory proteins Smooth ER Helps break down toxins, poisons, and waste Helps process carbs & produce lipids Golgi Body/Apparatus Function: Process, sort, and packages products (proteins from the rough ER) for the cell to export UPS for the cell Transport of materials Vesicle: Small membrane-bound sacs that divide some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm and transport these materials within the cell. Proteins (such as secretory & membrane proteins) made by ribosomes on the rough ER are packaged in vesicles and sent to the cell membrane or Golgi Apparatus. The Golgi Body processes & sorts the proteins, then packages them into vesicles for storage, transport, or secretion from the cell membrane. STOP & REVIEW This cell part controls what enters and leaves a cell. ______ __________ Cell Membrane This is the watery part of the cell, found throughout the cell and where most chemical reactions take place? ______ Cytoplasm This is the part of the cell where proteins are made. _______ Ribosomes This is the brain of the cell which controls all cell functions. ______ Nucleus This is found in the nucleus and is where RNA is made. ________ Nucleolus This is the roadway of the cell, there are 2 kinds. Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum This is where proteins are packaged before being shipped to the ER. Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Function: Contain enzymes to digest materials for the cell Not found in plant cells Mitochondria Function: Where usable energy is made for the cell Have a double membrane Inner membrane (cristae) is folded – this increases surface area to allow more energy to be made at a time Other structures in the body are like this as well (small intestine, lungs, ER) Plastids Pigment-containing organelles found in plant & algae cells. Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis (makes food) 6 Chromoplast Make and store pigments in fruits, roots, etc. (red color in tomatoes) Vacuole Function: Stores water and food molecules Plant cells: large and singular Animal cells: small and numerous Cytoskeleton Function: helps cell maintain shape; helps cell move; helps move organelles around inside the cell (like railroad tracks) Centrioles Function: helps with cell division Only in animal cells PART OF CYTOSKELETON Cilia & Flagella Function: Help with cell movement PART OF CYTOSKELETON Review Eukaryotes Have nucleus (DNA) Have membrane-bound organelles (increase the efficiency of functions by confining them within smaller spaces within the huge cell, or with communication and movement within the cell.) Larger size because of organelles More complex Unicellular or multicellular Prokaryotes No nucleus (still have DNA) No membrane-bound organelles Smaller size because of lack of organelles Less complex Unicellular STOP & REVIEW Contain enzymes to digest and breakdown cell material. (trashcan). _______ Lysosomes This is the powerhouse of the cell where the energy (ATP) is made. __________ Mitochondria This organelle is pigmented and absorbs light energy to make and store food. ______ Plastid (chloroplast) This is like a pool, where water is stored. ______ Vacuole helps cell maintain shape; helps cell move; helps move organelles around inside the cell (like railroad tracks) _____________ Cytoskeleton helps with cell division. Only in animal cells _____ Centrioles Help with cell movement ______ and ________ Cilia and Flagella protection for plant, fungal, and bacterial cells ______ Cell Wall Cell rap: http://www.youtub e.com/watch?v=zafJKbMPA8