Bio J Genetics Test Study Guide * Test Friday, March 10
advertisement

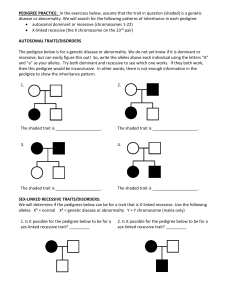
Bio H Genetics Study Guide Name Vocab Gene Allele Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Recessive Dominant Truebreeding Hybrid Gamete Zygote Polygenic Haploid Diploid Autosome Sex-linked Homologous Chromosomes Progeny Mendel: - Describe Mendel’s experiments. P F1 F2 - If given a characteristic, be able to work through the three generations. In your work, relate the following terms o True-breeding, hybrid, homozygous, heterozygous, carrier, dominance, recessive. - Using Mendel’s work, relate to the the o Law of Segregation o Law of Dominance o Law of Independent Assortment - With Law of Independent assortment, relate to what we know today about linked genes and crossing over. Are linked genes more/less likely to independently assort? How does relative position on the chromosome relate to likelihood of allele independent assortment? - How many different gamets can the following organisms produce? o AA o Aa o TtRr o TTRr Inheritance patterns There will be problems having you interpret these crosses and make predictions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Complete Dominance Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance Polygenic Multiple Alleles Sex-linked Di-hybrid Cross - know ratio! How does a polygenic trait differ from a trait that has multiple alleles? Which type of trait has a spectrum of possible phenotypes (think bell curve)? Punnett Squares What do the results of a punnett square represent? Is it what has to happen? We have done SOOOOOO many of these. They will be on the test, in copious amounts, in forms different than any we have ever done… Test Crosses: What is a test cross? What is the purpose of a test cross? Where would this have any practical application? Be able to work backwards through offspring genotypes to figure out the genotypes of the aprents. Pedigrees: What are the symbols used in a pedigree and what do they stand for? Be able to draw a pedigree given a verbal description of a family using genetic terms. Identify the pedigree as the following patterns. a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive c. X-linked recessive Examples discussed in class We have gone over certain genetic examples extensively in class. You are expected to know the following Blood types Colorblindness Cystic Fibrosis Hemophilia Tay Sachs Sickle Cell There will be word problems on the exam, like the quiz, where you need to pick out important parts and construct a punnett square.


![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)