Context Clues
advertisement

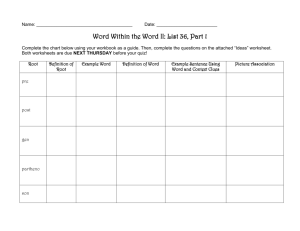
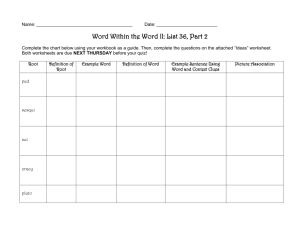
Cornell Notes Mini lesson What can good readers do when they read a word they don’t know? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Look for example clues Look for contrast/antonym clues Look for keyword clues Look for definition/explanation Look for restatement clues These clues are often referred to by Context Clues! Example Clues Examples of similar types can be excellent clues to the word’s meaning. Example: When our neighbors travel, they always look for comfortable accommodations, such as a beach cottage, hotel suite, or mountain cabin. Using clues we can conclude that the word accommodation means “a place to stay.” The word such as signal that the list of places to stay provide examples of accommodation. Contrast/ Antonyms Clues Look for words or phrases that are the opposite of a word’s meaning. Example: Knowledge is a remedy for many environmental problems, but knowledge without action cannot cure the ills. From the context, readers can conclude that remedy means “cure.” The word but signals that remedy contrast with the phrase “cannot cure.” Keyword Clues Look for words or phrases that modify or are related to the unfamiliar word. Example: The two characters in my story believe it is their destiny to be enemies. Their elders have taught them that this is meant to be. Using clues, readers can tell that destiny means “something that necessarily happens to a person.” the words meant to be signal the meaning of the word. Definition/ Explanation Clues A sentence may actually define or explain an unfamiliar word. Example: Alan will help the woman once she escapes and becomes a fugitive from her troubled country. From the context, readers can tell that fugitive means "runaway.” The words escapes signals the meaning of the word. Restatement clues Look for words and phrases that define an unfamiliar word. Example: The dried rose was fragile as a butterfly. In other words, its delicate petals can be damaged easily. The phrase in other words signals that the words easily damaged restate the meaning of the word fragile. These are often great clues to help readers. Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Good readers use clues when they read. Look for these clues when you come across a new word that you do not know. Look for example clues Look for contrast/antonym clues Look for keyword clues Look for definition/explanation Look for restatement clues Now try to use your new skill. Example: Another problem is that her eyes are luminous; they glow in the dark, so she stays hidden after twilight. What context clues can you use from the sentence to determine meaning? Use your context clues! Example: Star Trek: The Next Generation also gave key roles to aliens and androids. At first sight, Worf is a ghastly being, but fans love his frightful appearance. Use your context clues! Example They try very hard to avert disaster and save their planets. Use your context clues! Example No one likes to feel that his or her way of doing things has become old-fashioned, or obsolete, like a horsedrawn carriage. Use your context clues! Example Writers for TV must deliberate about what to include. Different age groups and time slots are among the consideration that must be carefully thought out. Summarize what you’ve learned! Write a summary to explain to someone who may have been absent today. What are context clues in your OWN words!