Section 1 – 1
advertisement

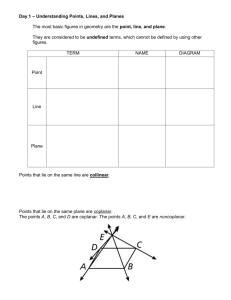
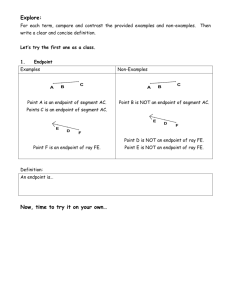
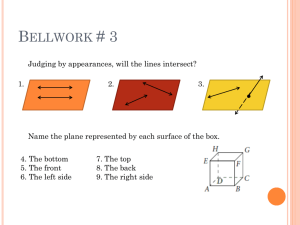
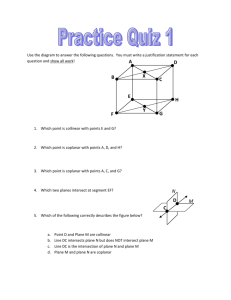
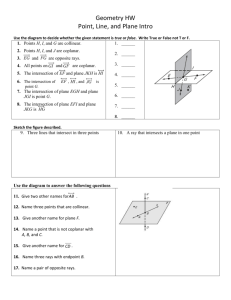
Section 1 – 1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Examples: Name a point on the line Points A, B or C ●A Point point A Non-examples: Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Has one dimension and is represented with two arrowheads and extends without end. Written like this: Line l, line AB, line BA Line Examples: Write the line 3 ways m D E Line m, line DE, line ED Non-examples: Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Has two dimensions and is represented by a shape that looks like a floor or Plane F, or Plane a wall and extends ABC without end. Plane Examples: Two other names for plane l Plane ABC Plane CAD etc. Non-examples: Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Points that lie on the same line. Points A, B, and C are all collinear Collinear points Examples: Non-examples: Name two collinear points Points A & D Points C & E are not collinear. Points A, B, E Points D, B, C Definition: Points that lie on the same plane Facts/Characteristics: Points A, B, and C are all coplanar Coplanar Examples: points Name 3 coplanar points Points G, E, O, B Points F, A, L, I, C Non-examples: Points G and F are not coplanar Points O and L are not coplanar Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Part of a line defined by two endpoints. Examples: Written as: AB or BA Segment What’s another name for CD DC Non-examples: Watch your symbols: CD is not CD Definition: Part of a line from a point in one direction without end. Facts/Characteristics: Written: ray AB Written: Ray Examples: Name rays with endpoint B Rays BA, BC BD, BE Non-examples: ray BA Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Two connected rays going in opposite directions. Opposite rays make a line. Examples: Opposite Rays Name 2 sets of opposite rays Rays BC and BD Rays BA and BE Rays CA and CB are opposite Non-examples: Definition: Facts/Characteristics: Two lines intersect Location where at a point. two geometric Two planes intersect figures have in a line. point(s) in common. Intersection Examples: Lines DC and AB intersect at point E Planes Q and P intersect at line AB Non-examples: Homework Section 1-1 Page 5 – 6 1 – 6, 8 – 12, 17, 18, 20, 25, 26 Vocabulary Point: Has no dimension and is represented by a dot. ●A point A Line: Has one dimension and is represented with two arrowheads and extends without end. l A B line l, line AB or BA Plane: Has two dimensions and is represented by a shape that looks like a floor or a wall and extends without end. A M C B plane M or plane ABC Collinear Points: Points that lie on the same line. Coplanar Points: Points that lie in the same plane. Segment: Part of a line defined by two endpoints. endpoint A endpoint B segment AB or BA Ray: Part of a line from a point in one direction without end. endpoint A B Ray AB endpoint A B Ray BA Opposite Rays: Two connected rays going in opposite directions. Opposite rays make a line. A C B Opposite Rays: CA and CB Intersection: Location where two geometric figures have point(s) in common. Two lines intersect at a point. Two planes intersect in a line. Example 1 a) Give two other names for BD. T D A DB and m. b) Give another name for plane T. E C B Plane ABE or ABC c) Name three points that are m collinear. A, B, C d) Name four points that are coplanar. A, B, C, E Example 2 P T Q R S c) Which of the rays from 2b a) Give another name for PR. are opposite rays? RP b) Name all rays with endpoint Q. QP and QR QT and QS QP, QR, QT, QS