glossary_3
advertisement

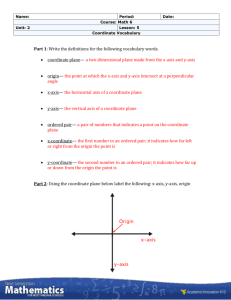
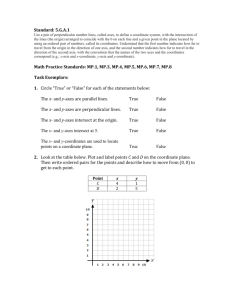
Introductory Algebra Glossary Chapter Three ordered pair A pair of numbers written within parentheses in which the order of the numbers is important. table of values An organized way of displaying ordered pairs. x-axis The horizontal number line in a rectangular coordinate system. y-axis The vertical number line in a rectangular coordinate system. rectangular coordinate system The x-axis and y-axis placed at a right angle at their zero points, also called the Cartesian coordinate system. quadrant One of the four regions in the plane determined by a rectangular coordinate system. origin The point at which the x-axis and yaxis of a rectangular coordinate system intersect. coordinate on a number line Each number on a number line is called the coordinate of the point that it labels. plot To locate an ordered pair on a rectangular coordinate system. graph of an equation The set of all points that correspond to all of the ordered pairs that satisfy an equation. The graph of a linear equation in two variables is a straight line. x-intercept The point where a graph intersects the x-axis. y-intercept The point where a graph intersects the y-axis. function A set of ordered pairs (relation) in which each value of the first component x corresponds to exactly one value of the second component y subscript notation A way of indicating two nonspecific ordered pairs, such as (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), that satisfy a particular equation relating x and y. slope The ratio of the change in y to the change in x along a line. rise The vertical change between two points on a line, the change in yvalues. run The horizontal change between two points on a line, the change in xvalues. parallel lines Two lines in the same plane that never intersect. perpendicular lines Two lines that intersect to form a right angle. Return to Introductory Algebra Created by James Q. Jacobs Superstition Mountain Campus Central Arizona College