Here are the Solutions

Mr. Maurer
AP Economics
Name:______________________
Unit 2 Test Review – Supply and Demand
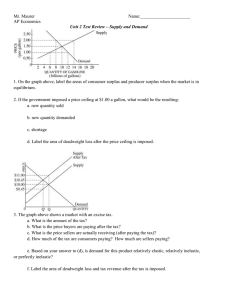
1. On the graph above, label the areas of consumer surplus and producer surplus when the market is in equilibrium. Consumer surplus would be the red shaded area above price, but below the demand curve.
It’s difficult to say whether it would extend all the way to the price axis, because, according to this demand curve, there is no demand at price higher than about $2.60. That’s why I stopped it where I did.
On a test, the area will be labeled and you will just have to identify it by letter. Producer surplus is the shaded blue area. See above for why I stopped it where I did.
2. If the government imposed a price ceiling at $1.00 a gallon, what would be the resulting: a. new quantity sold 6 billion gallons b. new quantity demanded 12 billion gallons c. shortage 6 billion gallons d. Label the area of deadweight loss after the price ceiling is imposed. triangle with the green outline, between the supply and demand curves.
Deadweight loss is the
3. The graph above shows a market with an excise tax. a. What is the amount of the tax? $1.00 b. What is the price buyers are paying after the tax? $10.45 c. What is the price sellers are actually receiving (after paying the tax)? $9.45 d. How much of the tax are consumers paying? How much are sellers paying?
Consumers: $0.45 Sellers: $0.55 e. Based on your answer to (d), is demand for this product relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, or perfectly inelastic? Demand is relatively elastic because sellers are paying more of the tax than buyers are.
Mr. Maurer
AP Economics
Name:______________________
Unit 2 Test Review – Supply and Demand f. Label the area of deadweight loss and tax revenue after the tax is imposed. Deadweight Loss is shaded pink. Tax revenue is shaded blue.
4. Circle the factors below that will shift the supply curve (change supply) price of the product demand for the product change in resource costs consumers’ incomes change in technology imposition of an excise tax. change in price of complementary goods (this one only if producers can shift production to these same goods, which is unlikely unless the test questions specifically says that).
5. Identify the resulting change in equilibrium price and quantity from each of the following
(assume that both changes happened together):
Demand
Increase
Supply
Increase
Price
?
Quantity
Up
Increase
Decrease
Decrease
Increase
Up
Down
?
?
Decrease Decrease ? Down
6. If sales of Toyotas increase by 5% when the price of Hondas goes up by 10%, calculate the cross elasticity of the two products. 5%/10% = .5
7. If the government imposed a $2.00 tax/gallon on gasoline, and the price of gasoline rose from
$3.00/gallon to $4.75/gallon, who is paying most of the burden of that tax? What does that tell you about the price elasticity of demand for gasoline? Consumers are paying most of the burden because price went up by $1.75, which is almost the whole tax. That tells me that demand for gasoline is highly inelastic.
8. In the example above (#7), if the price had risen all the way to $5.00 per gallon, what would you be able to say about the price elasticity of demand for gasoline?
Demand would be perfectly inelastic because consumers were burdened with the whole tax.
9. If the price of a good goes up, how will the substitution effect change consumers buying habits for that good and other goods? Quantity demanded of that good will go down. Demand for other products will go up.
10. Draw a graph of a market in equilibrium for a product with perfectly inelastic demand. What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when supply goes down? You draw the graph. Equilibrium price goes up. Quantity does not change because, when demand is perfectly inelastic, quantity does not change when price changes. (The demand curve is a vertical line.)
11. Draw two separate graphs of two markets in equilibrium, Product A and Product B. Product
A is a normal good and Product B is an inferior good. On your graphs, show what happens to demand, equilibrium price, and equilibrium quantity when consumers’ income goes up.
You draw the graphs, but they should show that demand shifts to the right for the normal good, so quantity and price both increase. For the inferior good, demand shifts to the left, so price and quantity both go down.
Mr. Maurer
AP Economics
Name:______________________
Unit 2 Test Review – Supply and Demand
12. In your own words define consumer surplus and producer surplus.
Consumer surplus is the amount that consumers would have paid that is over the price of the product. In other words it is the value they placed on the good in excess of its price
Producer surplus is the difference between what sellers were willing to sell the product for and the actual price. It is the amount they received that is in excess of what they would have been willing to accept. (Those are my own words – you may find the book definition easier to understand.)
13. What is the most likely short term effect of a price ceiling on a market in equilibrium.
14. On the diagram to the left, identify the elastic, unit elastic, and
P1 inelastic portions of the demand curve. Show that the midpoint of the demand curve is unit elastic. The left side is elastic, and the right side is inelastic.
15. If the market price for coffee is P1, show and shade the area of consumer surplus. See diagram.
16. What does the law of diminishing marginal utility say?
Look it up in the book.
17. Explain the utility-maximizing rule.
Look it up in the book.
18. What is the effect of a price reduction on quantity sold and total revenue when demand is elastic? Now ask yourself this question in all possible combinations of price increases, decreases, elastic, inelastic, perfectly inelastic, and unit elastic demand. Know it. Feel it.
Elastic demand, price reduction increases total revenue. Price increase decreases total revenue.
Inelastic demand, price reduction decreases total revenue. Price increase increases total revenue.
Unit elastic – no change in total revenue when price changes.
Perfectly inelastic – same result as inelastic because there is never any change in quantity.
19. When demand and supply are anything other than perfectly elastic or perfectly inelastic, what effect does an excise tax have on consumer surplus and producer surplus? Draw a graph if you have to.
Excise taxes always reduce both consumer and producer surplus.
20. If the government imposes a price ceiling at P3 on the market pictured at left, what will be the effect of price and quantity sold? Yes, it’s sort of trick question, but you need to know it.
No effect. It is an ineffective price ceiling because it is set higher than equilibrium price.
Mr. Maurer
AP Economics
Name:______________________
Unit 2 Test Review – Supply and Demand
21. And finally, just be darn sure you know the difference between change in quantity demanded and demand. Know the difference between quantity supplied and supply. What is the only factor that can cause a change in quantity supplied or quantity demanded?
Hey, it’s up to you to know it and feel it. Price is the only factor than can change quantity demanded or quantity supplied.