Force & Motion Unit
advertisement

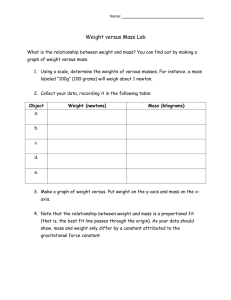
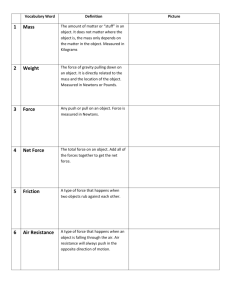
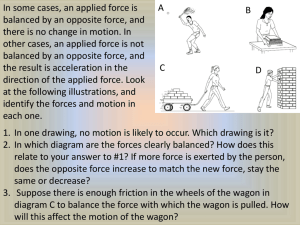
FORCE & MOTION Energy-the ability to do work or cause change Kinetic-energy of motion (like inertia, the more mass and speed means more kinetic energy) Potential-stored energy of position 1. Gravitational-the higher up, the more energy 2. Elastic-the more stretched or squeezed, the more energy Gravity-the force or pull one object has on another (objects with more mass have more of a pull) Earth is 6 times the mass of the moon, so Earth has 6 times the gravitational pull So, if you weigh 120 pounds on Earth, you would weigh 1/6th (20 pounds) on the moon In space, far away from any planet, you weigh nothing because no planet is pulling on you What’s the difference between weight and mass? Mass is a measure of how much matter an object has (this does not change) Weight is mass times the gravity acting on an object (this changes based upon the mass of the planet or moon you are near) Speed = Distance ÷ Time Example: What is the average speed of a car that travels 400 km in 5 hours? S = 400 ÷ 5 = 80 km/hr Velocity is the speed and direction of an object Acceleration is a change in velocity (speed or direction) Acceleration = (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time Example: Find the acceleration of a ball rolling down a ramp whose speed increases from 0.5 m/s to 1.7 m/s in 10 seconds. A = (1.7 – 0.5) ÷ 10 = 1.2 ÷ 10 = 0.12 m/s² This means that every second, the ball travels 0.12 m/s faster than the previous second. Newton’s 1st Law of Motion-an object remains at rest or in motion unless acted on by a force Inertia-the tendency of an object to resist changes in motion *The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has *The more speed , the more inertia Momentum-when an object is in motion, it has momentum *The greater the mass, the greater the momentum. *The faster an object is moving, the greater the momentum. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion Force = Mass x Acceleration Example: How much force does it take to accelerate a 7 kg wagon at 3m/s²? F = M x A, F = 7 x 3 = 21 Newtons (N) Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion-For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples: 1. A fish pushes its fins against water and the water pushes back, so the fish moves forward 2. A water hose moves backward as water goes out of hose 3. A bullet comes out of a gun and the gun kicks back Balanced Forces-act against each other (no movement) Unbalanced Forces-cause an object to move Net Force-the total force acting on an object **If Jane pushes a wagon East with a force of 70 Newtons and Dave pushes it West with a force of 50 Newtons, what is the net force? 70 – 50 = 20 Newtons East (the forces are unbalanced) *Thermal energy (HEAT) always travels from warmer objects to cooler objects *Thermal energy lost by a warm object equals the energy gained by the cool object it is in contact with Thermal equilibrium-when 2 objects are in contact, they will eventually be the same temperature HOW DOES HEAT TRANSFER (MOVE)? Convection-transfer of heat through a moving fluid, warm air rises because it is less dense (liquids or gases) Conduction-transfer of heat through a substance (metals are good conductors) Radiation-transfer of heat through rays or waves (sun’s rays) Electric Force-between 2 objects with charges(+ or -) An atom has 3 parts: 1. Proton-positively charged (+) 2. Electron-negatively charged (-) 3. Neutron-no charge (0) An atom with a charge is called an ion. If an atom loses an electron, it will have more protons than electrons and will have a (+) charge, and vice versa. If # electrons = # protons, the charge is neutral (0) Like charges repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. (+) and (+) = repel (-) and (-) = repel (+) and (-) = attract Conductor-allows electrons to flow through it freely, metals are good conductors Insulator-Do not allow; rubber, wood, glass **The closer 2 charge are, the greater the electric force between them. (Similar to gravity) Magnetic Force-Magnets are attracted to iron and have a North or South charge. N repels N S repels S N attracts S Magnetic force decreases with distance. Electromagnetism-magnetism from electric charges in motion. So, electricity can make magnetism. AND........ Magnetism can make electricity!! *Thermal Energy is the sum of Kinetic & Potential Energy of all atoms in an object *Temperature is a measure of average Kinetic Energy of an object’s particles SI units-metric units used by scientists everywhere (m, g, L) Law of Universal Gravitation-any 2 objects that have mass are attracted to each other