Anatomy of Plants
advertisement

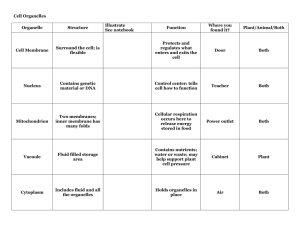
Anatomy of Plants Chapter 4 Prokaryotes • No membrane enclosed organelles • Considered primitive • Examples: Bacteria & Blue green algae Eukaryotes • Organelles bound with membranes • Organelles such as: nucleus, mitochondria, vacuoles etc. • Examples: plant & animal Cell Walls • • • • Made of hemicellulose Protects the organelles Give structure and support Secondary cell walls are made up of cellulose, pectic, suberin, cutin, and lignins Plasma Membrane • The lipid bilayer membrane surrounding the cytoplasm • Selective absorption Protoplast • Refers to the inside of the cell • Cytoplasm: – The fluid surrounded by plasma membrane – Made up of proteins – Suspends the organelles Organelles • Internal structures within the protoplast Chloroplasts • • • • • Responsible for photosynthesis Contains pigments Solar energy is harvested Made up of flattened discs called grana Double membranes plastids Mitochondria • • • • The manufacturing plant Site of respiration Involved in producing ATP Double membrane surrounding it Nucleus • Control center of the cell • Contains chromosomal DNA • Double membrane which is porous to allow material to pass in and out of the nucleus Vacuoles • 90% in mature cells • Storage devices • Water, Sugar, Salts, and toxic waste Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes Ribosomes • Decodes DNA • Contains RNA Golgi Apparatus (Body) • Membrane bound • Packages energy • Delivers packaged energy to different parts of the cell Tissues • Meristems – Apical – Subapical – Intercalary – Lateral/cambial Permanent Tissue • Epidermis • Parenchyma – Collenchyma, support function – Sclerenchyma, they make plant fibers or gritty cell like in pears Complex Permanent Tissue • Xylem • Phloem Structure of Primary Root Structure of Primary Stem Structure of leaves Cell Division Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase