Sara_WdRecog_07
advertisement

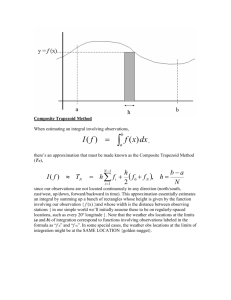
Word recognition in normal reading Sara C. Sereno Collaborators: Paddy O’Donnell Hartmut Leuthold RAs/PGs: Sébastien Miellet Graham Scott Christopher Hand Word Recognition • What factors affect word recognition? • How can word recognition processes be accurately measured? • How can effects be interpreted? What factors affect word recognition? • Orthography of language – English vs. Hebrew or Japanese • Intraword (sublexical) variables – – – – word-initial bi/tri-grams spelling-to-sound regularity neighborhood consistency morphemes • prefix vs. pseudo-prefix • compound vs. pseudo-compound clown vs. dwarf hint vs. pint made vs. gave remind vs. relish cowboy vs. carpet What factors affect word recognition? • Word (lexical) variables – – – – – – – – – word length word frequency AoA expert vocabulary syntactic class ambiguity concreteness/imageability animacy affective tone duke vs. fisherman student vs. steward rabbit vs. violin voxel open/closed-class; A,N,V bank (“money” “river”) tree vs. idea dog vs. cup love vs. farm vs. fire What factors affect word recognition? • Extraword (supralexical) variables – Contextual predictability Neutral He bought a large plant for his garden. Biasing Terry went to the new gardening centre. He bought a large plant for his garden. – Syntactic complexity Trans. Mary took the book VERB on the table. was good. the table. Mary knew the book on was good. the table. Intrans. Mary hoped the book on was good. What factors affect word recognition? • Extraword (supralexical) variables – Discourse factors Focus The dog chased the cat today. The cat was chased by the dog today. What the dog chased was the cat today. It was the cat that was chased by the dog today. Elaborative inferences & anaphora stabbed … The mugger assaulted her with his weapon… He threw the knife into the bushes and ran away. What factors affect word recognition? • Language skill – beginning (novice) vs. skilled (expert) readers – normal vs. dyslexic vs. neuropsychological patient How can word recognition processes be accurately measured? Measure Task Time Res. “electrical” imaging (EEG, MEG) single word presentation word-by-word reading ~80 – 500 ms (P1,N1,EPN,N400) Eye movements in normal reading fixation time, location & sequence of EM’s ~250 ms RT naming, lexical decision categorization tasks; ± priming, masking, lateralized presentation ~500 – 800 ms “blood flow” imaging single word presentation (PET, fMRI) seconds Word-by-word reading: 200 ms per word presentation reading-like sentence word rate. This fast by of at is a Word-by-word reading: 600 ms per word presentation sentence typically studies. word used ERP slow This rate by of at in is a Normal Reading * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. * This is an approximation of normal reading in real time. This is an approximation of normal reading * time. in real This is an approximation of normal reading in* real time. This is an approximation of normal reading * in real time. The importance of making eye movements in normal reading Cond1 Cond2 There was a box of… Cond1 Cond2 She saw a cat in the… There was an enormous box of… She saw a cup in the… Perception of text influences how EMs made. AND Location/duration of EMs affect perception. How can effects be interpreted? • Additive factors (1) Pick factors: stimulus quality, frequency, predictability (2) Independently manipulate 2 factors at once: Lo freq RT Hi freq – stim RT Lo freq RT + stim + – stim qual (3) Additive Interactive + sequential overlapping Hi freq + – context – context Context Stimulus Quality Frequency How can effects be interpreted? • Modelling (1) Pick factors: oculomotor-related factors launch distance to word location of fixation within word number of fixations on word word length word frequency contextual predictability language-related factors How can effects be interpreted? • Modelling (1) Pick factors: oculomotor-related factors launch distance to word location of fixation within word number of fixations on word word length word frequency contextual predictability language-related factors (2) Perform repeated measures multiple regression analysis to determine which factors account for most variance. Factors orthography bi-/tri-grams regularity neighborhood morphology length frequency jargon word class ambiguity imagability animacy emotionality predictability syntactic prefs. focus inference anaphora skill Measures ERPs + word-by-word (slow) presentation Eye movements + normal reading EM-ERP co-registration? Approach Additive factors Repeated measures multiple regression lexical humans Distributed hierarchical visual processing in primates higher-level semantics syntax meanings word forms letters features Conclusion Precisely delineating the time course of different components of word recognition allows us to: – determine when top-down effects modulate bottom-up processes; – inform neuroimaging localisation studies in order to construct a temporally realistic neural circuitry of normal reading. Measurement EMs = best on-line measure of visual word recognition in the context of normal reading ERPs = best real-time measure of brain activity associated with the perceptual and cognitive processing of words (Sereno & Rayner, Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2003) Sereno, Rayner, & Posner (1998). NeuroReport. Sereno, Brewer, & O’Donnell (2003). Psych. Sci. (Sereno & Rayner, Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2003)


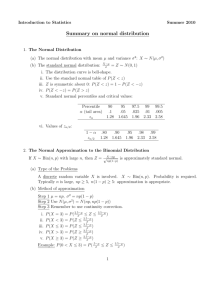

![1 = 0 in the interval [0, 1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007456042_1-4f61deeb1eb2835844ffc897b5e33f94-300x300.png)