Campus/ District Data
advertisement
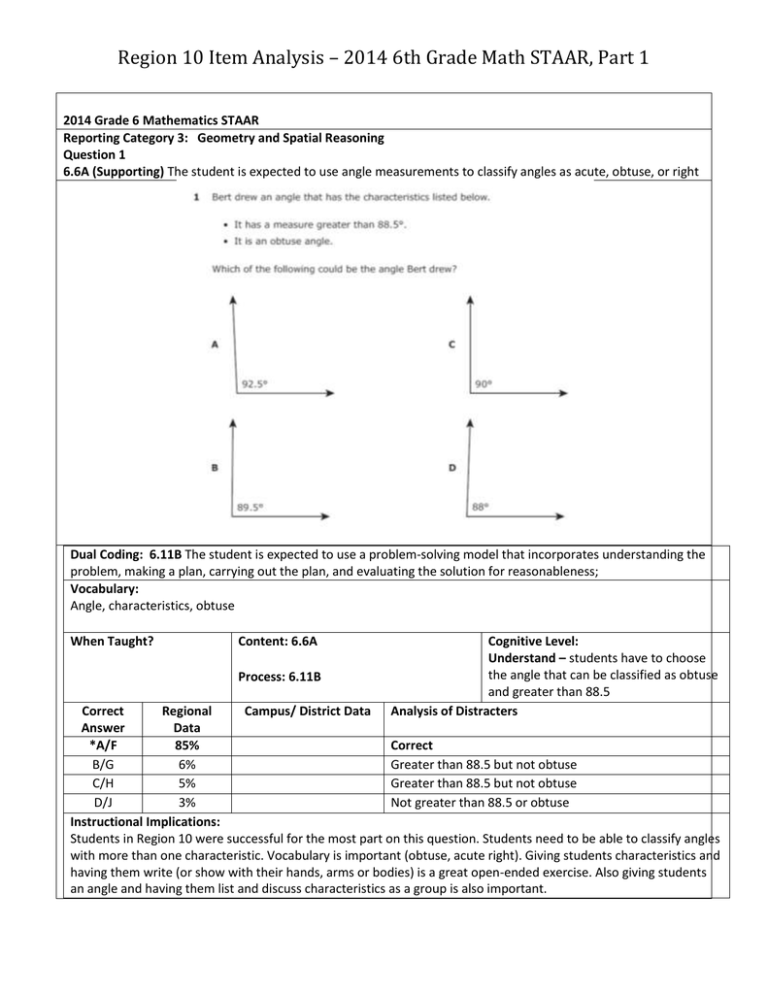
Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 3: Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Question 1 6.6A (Supporting) The student is expected to use angle measurements to classify angles as acute, obtuse, or right Dual Coding: 6.11B The student is expected to use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness; Vocabulary: Angle, characteristics, obtuse When Taught? Content: 6.6A Process: 6.11B Cognitive Level: Understand – students have to choose the angle that can be classified as obtuse and greater than 88.5 Analysis of Distracters Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Answer Data *A/F 85% Correct B/G 6% Greater than 88.5 but not obtuse C/H 5% Greater than 88.5 but not obtuse D/J 3% Not greater than 88.5 or obtuse Instructional Implications: Students in Region 10 were successful for the most part on this question. Students need to be able to classify angles with more than one characteristic. Vocabulary is important (obtuse, acute right). Giving students characteristics and having them write (or show with their hands, arms or bodies) is a great open-ended exercise. Also giving students an angle and having them list and discuss characteristics as a group is also important. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation and Quantitative Reasoning Question 2 6.1C (Supporting) The student is expected to use integers to represent real-life situations Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models; and Vocabulary: Represented, additional, shortens, divides When Taught? Content: 6.1C Process: 6.12A Correct Answer A/F B/G Regional Data 5% 11% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – Students must apply their knowledge of the addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers to real world scenarios Analysis of Distracters The multiplication of 14 would represent this situation. Dividing the players into teams would mean the original number would decrease so students might have confused division with subtraction. The addition of 14 would represent this situation. Correct answer C/H 8% *D/J 76% Instructional Implications: Ensure that all students understand the vocabulary in problems like these, by using the vocabulary in class and expecting students to use the vocabulary in their verbal and written responses. Use a word wall and provide students with strategies to work with unfamiliar terminology. Provide students an expression or part of an expression and have them to create multiple different scenarios to see and understand that many “key words” could be used. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 5: Probability and Statistics Question 3 6.9A (Supporting) The student is expected to construct sample spaces using lists and tree diagrams Dual Coding: 6.11C The student is expected to select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types, including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, acting it out, making a table, working a simpler problem, or working backwards to solve a problem Vocabulary: Possible outcomes When Taught? Content: 6.2C Process: 6.11C Correct Answer Regional Data Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – students must apply their understanding of sample space to construct a list or tree diagram Analysis of Distracters Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 A/F 11% B/G *C/H D/J 7% 80% 3% If the student found that there were 6 options, they might have chosen this option, but this option assumes Monday morning twice, and includes options that were not available (Tuesday afternoon and Wednesday evening) This option is missing Monday afternoon. Correct This option is missing Monday afternoon and Thursday evening. It also includes an option that was not available (Thursday afternoon) Instructional Implications: Students should have opportunities to experiment with different situations to construct sample spaces. Use real scenarios that students can relate to and have them create a sample space of all possibilities with lists and tree diagrams. Teach students how to create a list from their tree diagram. Expose students to different visual representations. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Numbers, Operations and Quantitative Reasoning Question 4 6.2C (Readiness) The student is expected to use multiplication and division of whole numbers to solve problems including situations involving equivalent ratios and rates Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Same number in each When Taught? Content: 6.2C Process: 6.11A Correct Answer *A/F B/G C/H Regional Data 85% 5% 4% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – Students must apply their understanding of multiplication, division, ratios and rates to a real world problem and solve it correctly. Analysis of Distracters Correct Subtracted 3 (the difference between 5 and 8) from 176 Didn’t carry the 1 when multiplying 22 (the unit rate slices per loaf) by 5 loaves Added 8 loaves and 5 loaves then subtracted from 176 D/J 6% Instructional Implications: Students in Region 10 were successful for the most part on this question. Students should be taught to label their rates, ratios and proportions with accompanying units. They should be asked to justify their set up. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 2: Patterns, Relationships and Algebraic Thinking Question 5 6.4B (Supporting) The student is expected to use tables of data to generate formulas representing relationships involving perimeter, area, volume of a rectangular prism, etc Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Rectangular Prism, volume, height, length, width, relationship, equation When Taught? Content: 6.4B Process: 6.12A Correct Answer A/F B/G *C/H D/J Regional Data 7% 18% 72% 2% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analyze – Students are expected to analyze the measurements in the table, use the formula for volume of a prism and generate a formula Analysis of Distracters Adding length and width instead of multiplying. Multiplying both sides by 2 Correct Adding 2 to both sides Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to work with the reference materials to create tables and graphs given dimensions of shapes. Assist them in understanding the context of the problem by providing visual representations or having students create visual representations. Students need to be able to manipulate the equation given length, width, height, volume or a combination. Students need to work both ways with rules and tables. Given a table, find the rule and given a rule, find a table. Provide opportunities for students to read and interpret information from tables. Provide opportunities for students to build input-output tables and explain the relationships in terms of input-output. Explaining the relationship in terms of input-output is crucial – have them use the words given in their explanation “the volume (128) divided by height (2) will equal length times width”. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Numbers, Operations and Quantitative Reasoning Question 6 6.2E (Readiness) The student is expected to use order of operations to simplify whole number expressions (without exponents) in problem solving situations Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics; Vocabulary: Borrowed, another, equal payments, the rest, repaid, expression When Taught? Content: 6.2E Process: 6.11A Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 8% *B/G C/H 86% 3% D/J 2% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – students are applying their understanding of order of operations to this situation Analysis of Distracters Did not do (12+16) first. Instead took 92-12 then added 16 and divided the sum by 4 Correct Divided 92 by 4 first, then subtracted the sum of 12 and 16 (which would be -5) Divided 92 by 4 first, then subtracted 12 then added 16 Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Students need to be exposed to all ways of representing multiplication and division. Always incorporate situations where subtraction comes before addition and division comes before multiplication (to address the common misconception that you always solve in the order PEMDAS). Also students need to see all types of “groups” – parenthesis, brackets, and in this case the expression 92-(12+16) above the division (fraction) symbol. Giving students a number as the solution, a set of numbers (to use in the expression), a set of parenthesis and instructing them to create a situation is a great problem solving activity for students to increase their conceptual understanding of the effect parenthesis have in different parts of the expression. 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 5: Probability and Statistics Question 7 6.10D (Readiness) The student is expected to solve problems by collecting, organizing, displaying, and interpreting data Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Graph, statement Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 When Taught? Content: 6.10D Process: 6.12A Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 18% B/G 11% C/H 11% *D/J 59% Instructional Implications: Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analyze – Students are expected to analyze the data presented in the graph and determine which statements are true or false. Analysis of Distracters The graph shows the dry cleaner to be open for 12.5 hours, but this answer would be 12 hours The graph shows the restaurant to be open for 10 hours, but this answer would be 9 hr and 45 min The graph shows the post office as open for 8.5 hours, but this answer would be 9 hrs Correct Provide students with information in graphs and tables and have them practice drawing conclusions. Have students justify their conclusions and evaluate other student conclusions. Provide students with words or sentence stems to use in their conclusions (such as twice, half, the sum of ____ and ____ is greater than _____), so they have practice with that vocabulary and practice with conclusions that are multi-step. Have students label information directly on the table. Use tables and graphs from print or electronic media using contexts students find interesting. Students have seen bar graphs since early elementary school, so always incorporate multiple steps to analyze the information in bar graphs particularly (As in this question where students have to turn number of hours into a start and end time). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 3: Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Question 8 6.6C(Readiness) The student is expected to describe the relationship between radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Drilled, circular, diameter, equation, radius When Taught? Content: 6.6C Process: 6.12A Cognitive Level: Apply – Students apply their understanding of the relationship between parts of a circle, to choose the appropriate equation Analysis of Distracters Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Answer Data A/F 24% Would solve for diameter (not r) *B/G 50% Correct C/H 9% Confuses elements of a circle D/J 17% Used the formula for circumference, given a radius Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to know and understand the relationships that exist between the radius, diameter and circumference. They should calculate: circumference with radius, circumference with diameter, diameter with circumference, radius with circumference, diameter with radius, and radius with diameter. Have students explain what the components of various equations mean in relationship to finding the diameter, radius or circumference. Provide opportunities for students to know and understand the formulas used for circumference, diameter, and radius and manipulate these formulas. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 4: Measurement Question 9 6.8D (Supporting) The student is expected to convert measures within the same measurement system (customary and metric) based on relationships between units Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: How many When Taught? Content: 6.8D Process: 6.11A Cognitive Level: Understand - Students understand the relationship between units, understand the use of the reference materials and are able to use multiplication and division to convert gallons to cups Analysis of Distracters Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Answer Data *A/F 72% Correct B/G 12% Converts to quarts C/H 3% Converts to ounces D/J 13% Converts to pints Instructional Implications: Provide student with plenty of opportunity to understand the measurement information on the reference materials and to use it as a tool to answer questions. Provide opportunities for students to think aloud and talk through the decisions they make and the steps they take to solve. Show students that this can be solved using a proportion and always have them label their units. Have real world examples displayed in your classroom to represent 1 gallon, 1 quart, 1 pint and 1 cup and reference them while teaching to build students’ conceptual understanding of the size and conversion of each. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 2: Patterns, Relationships and Algebraic Thinking Question 10 6.4A (Readiness) The student is expected to use tables and symbols to represent and describe proportional and other relationships such as those involving conversions, arithmetic sequences (with a constant rate of change), perimeter and area Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Value, determined, expression, represents, relationship When Taught? Content: 6.4A Process: 6.12A Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 16% *B/G C/H 55% 17% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Applying - Students must apply their understanding of additive patterns to create a table or find the matching table. Analysis of Distracters The difference between r values is 9/8 so the student might mistake that they should be looking for the relationship between g and r, the expression would be r – 1/8 Correct r + 9/8 Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 D/J 12% The difference between r values is 9/8 so the student might mistake that they should be looking for the relationship between g and r, the expression would be r + 1/8 Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to write an equation, test the equations validity and understand the context of the problem. Students need to work both ways with rules and tables. Given a table, find the rule and given a rule, find a table. Provide opportunities for students to read and interpret information from tables. Provide opportunities for students to build input-output tables and explain the relationships in terms of input-output. Explaining the relationship in terms of input-output is crucial – in this question a common misconception was that students found a relationship between r and r rather than what the question asked; the relationship between r and g. Students need to be exposed to fractions and decimals within the table and expression (not just integers). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Numbers, Operations and Quantitative Reasoning Question 11 6.2B (Readiness) The student is expected to use addition and subtraction to solve problems involving fractions and decimals Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Another, fraction When Taught? Content: 6.2B Process: 6.11A Cognitive Level: Apply – Students must determine the fraction of the pizza leftover. They must also apply their knowledge of converting percent to fraction to subtract. Analysis of Distracters Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Answer Data A/F 4% Convert 25% incorrectly, and subtract incorrectly *B/G 64% Correct C/H 13% Convert percent to fraction only 25% = ¼ D/J 19% This is the amount Ryan HAS eaten Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to work multi-step problems, especially with fractions, decimals and percent. Teach students to write number sentences or equations before performing the operation in a word problem. Have students use a problem solving strategy such as draw a picture, work a simpler problem (re-read it with simple numbers to better understand the context and write a number sentence), or act it out. Consider choosing a problem solving system as a campus to use across grade levels. Practice consistently with benchmark fractions (such as 25%, 20%, 50%, 10% etc) so that students can convert them quickly and easily when embedded in a word problem. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 2: Patterns, Relationships and Algebraic Thinking Question 12 6.5A (Readiness) The student is expected to formulate equations from problem situations described by linear relationships Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Weight, times, half, equation, combined When Taught? Content: 6.5A Process: 6.12A Correct Answer A/F B/G Regional Data 6% 22% *C/H D/J 68% 4% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Evaluate – Students must analyze and compare symbolic equations to a verbal description and then determine which equation is equivalent to the verbal description. Analysis of Distracters Adding w+8 instead of multiplying Added both 8 and ½ to w (weight) – students may have been distracted by the word “combined” Correct Confuses the value for food with the value for water Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: This question required students to write equations from a verbal description. In order to prepare students for problems like this one, expose students to multiple solution approaches. Teach students how to justify their thinking and communicate their reasoning. Encourage students to think of “another way” to solve problems. Have them practice evaluating one another’s approaches. Emphasize the meaning of given variables. To accommodate struggling or English language learners, have them annotate directly in the verbal description their “math translation” for instance above “8 times weight” students would annotate “8xw”. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 5: Probability and Statistics Question 13 6.10B (Supporting) The student is expected to identify mean (using concrete objects and pictorial models), median, mode, and range of a set of data Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Median When Taught? Content: 6.10B Process: 6.11A Correct Answer *A/F B/G Regional Data 74% 8% C/H 6% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Understand – Students must understand how to find the median given a set of numbers. Analysis of Distracters Correct Found the number in the middle of this set without ordering the set from least to greatest Incorrect addition and division of 2 middle numbers 15 and 19 This is the mode D/J 12% Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to communicate their thinking and specifically to put “median” in their own words, not just “the middle”. Students should given the opportunity to explain why you need to put the data in order to determine the median. Expose students to sets of data with an even number in the set. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 4: Measurement Question 14 6.8B (Readiness) The student is expected to select and use appropriate units, tools, or formulas to measure and to solve problems involving length (including perimeter), area, time, temperature, volume, and weight Dual Coding: 6.11D The student is expected to select tools such as real objects, manipulatives, paper/pencil, and technology or techniques such as mental math, estimation, and number sense to solve problems Vocabulary: Measure, closest, nearest, combined, area, figure, square centimeters When Taught? Content: 6.8B Process: 6.11D Correct Answer A/F B/G *C/H D/J Regional Data 10% 8% 62% 20% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – Students must apply their knowledge of the ruler to correctly measure the dimensions (length, width, base and height), they must apply their knowledge of area Analysis of Distracters Did not round to the nearest ¼ inch Did not divide by 2 for the area of the triangle Correct Combined perimeter Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide many opportunities for students to use the ruler on the reference materials to measure irregular and regular figures. Emphasize the correct height of the triangle and why. Have students communicate the measurements, dimensions of shapes, and use of the formulas. Provide students with creative problems or have them create problems for other students to solve. Post the problems and solutions and have students critique the problems and solutions provided. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning Question 15 6.2C (Readiness) The student is expected to use multiplication and division of whole numbers to solve problems including situations involving equivalent ratios and rates Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Total, intersection, how many When Taught? Content: 6.2C Process: 6.11A Cognitive Level: Applying – Students must read the problem, and apply their understanding of ratios and rates to solve for the missing value Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Analysis of Distracters Answer Data A/F 8% 36 divided by 16 *B/G 68% Correct C/H 8% 36 – 16 + 4 D/J 16% 36 + 16 divided by 4 Instructional Implications: Have students estimate before performing the operation to check for reasonableness. If using a proportion to solve, have students always label their units, explain their set-up and justify their reasoning. Provide many opportunities for students to work multi-step problems with proportions and rates. Provide students with many different verbal scenarios for practice. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 5: Probability and Statistics Question 16 6.10D (Readiness) The student is expected to solve problems by collecting, organizing, displaying, and interpreting data Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Collected, total, amounts, represented, line plot When Taught? Content: 6.10D Process: 6.12A Correct Answer *A/F B/G Regional Data 54% 46% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analysis – students must interpret the data presented in the line plot and problem solve given the information provided Analysis of Distracters 40, Correct Did not accurately interpret the data, did not use the appropriate operations to solve, or did not compute correctly. C/H 0% D/J 0% Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to read and interpret tables. Have students think aloud and talk though the decisions they make and the steps they may take to solve. Make sure that students are provided a verbal description as well as the data in tables and graphs working problems. Expose students to multi-step problems where students not only have to interpret the graph, but use the information to answer a question or solve a problem. Make sure students practice using the griddable (especially when the answer is a whole number). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 3: Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Question 17 6.6B (Supporting) The student is expected to identify relationships involving angles in triangles and quadrilaterals Dual Coding: Vocabulary: Polygon When Taught? Content: 6.6B Process: Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 10% B/G 12% C/H 6% *D/J 71% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Understand – Students must understand the relationship between angles in a quadrilateral Analysis of Distracters Used the sum of the angle measures in a triangle (180) rather than a quadrilateral to subtract the angle 164 -> 180-164=16 Used the sum of the angle measures in a triangle (180) rather than a quadrilateral to subtract the angle 147 -> 180-147=23 Used the sum of the angle measures in a triangle (180) rather than a quadrilateral to subtract the angle 147 and did not borrow when subtracting Correct Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide students opportunities to measure angles within quadrilaterals using a protractor. A great introduction through inquiry or discovery is to teach students to measure with a protractor, have them measure the angles and find the sum of the angles in multiple different quadrilaterals and then draw their own conclusions about the relationship with their peers (with triangles as well). Another activity to have students draw their own conclusions is to “challenge” them to draw a quadrilateral with 3 acute angles or 3 obtuse angles (which they will find is not possible). Have them justify in their own words why angles in a quadrilateral have a sum of 360. Use Always/ Sometimes/ Never statements to have students think critically about angle relationships in quadrilaterals (and triangles). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 2: Patterns, Relationships and Algebraic Thinking Question 18 6.3C (Readiness) The student is expected to use ratios to make predictions in proportional situations Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: (at this) Rate When Taught? Content: 6.3C Process: 6.11A Correct Answer A/F *B/G C/H Regional Data 17% 67% 13% D/J 3% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Understand – students understand how to use a rate to make a prediction in this proportional situation Analysis of Distracters Incorrectly divided 460 by 3 which is approximately 153 Correct Round or divide incorrectly to find the unit rate of 40 per hour 460/3 + 12 = 165 poor procedural understanding and conceptual understanding of proportions Instructional Implications: When students set up a proportion, teach them to always label their units and have students think aloud and talk through how they set up a proportion using rates and ratios. Have students estimate first to check for reasonableness (and eliminate unreasonable answers in multiple choice questions). Teach students that ratios have a part to whole relationship just like fractions and can therefore be treated just like fractions (can be simplified, can find equivalent ratios just like you would for equivalent fractions, etc). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 4: Measurement Question 19 6.8A (Supporting) The student is expected to estimate measurements (including circumference) and evaluate reasonableness of results Dual Coding: 6.11B The student is expected to use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness Vocabulary: Cylindrical, diameter, best estimate, circumference When Taught? Content: 6.8A Process: 6.11B Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 20% B/G 18% *C/H 55% D/J 7% Instructional Implications: Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply –Students must the formula to estimate the circumference of the shape. They also must convert inches to ft. Analysis of Distracters Used the formula C=2(pi)r and misunderstood 20 as the radius instead of diameter Estimate diameter as 20 in. then converted to ft and round down to 2ft. (does not find circumference or use the formula) Correct 12in=1ft. Students need to see images of real world shapes. Students also need to understand which formula to use and how to calculate an estimate using 3 for pi. This can be accomplished by providing students with real world images and problem situations. Students should use a problem solving method, and especially when working with a shape and not given a picture, students should be taught to draw and label the picture. Provide opportunities for students to think aloud and explain the decisions they make and the steps they took to solve a problem with their peers. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 2: Patterns, Relationships and Algebraic Thinking Question 20 6.4A (Readiness) The student is expected to use tables and symbols to represent and describe proportional and other relationships such as those involving conversions, arithmetic sequences (with a constant rate of change), perimeter and area Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: Share equally, table, relationship When Taught? Content: 6.4A Process: 6.12A Correct Answer *A/F B/G Regional Data 69% 7% C/H 12% D/J 12% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Applying - Students must apply their understanding of multiplicative patterns to create a table or find the matching table. Analysis of Distracters Correct Takes 180 pieces minus the number of people, to get the number of pieces. P=180-n Takes 180 pieces times n, the number of people to get p the number of pieces. P=180n Takes 180 pieces divided by n, the number of people, minus 2 Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to write an equation, test the equation’s validity and understand the context of the problem. Students need to work both ways with rules and tables. Given a table, find the rule and given a rule, find a table. Provide opportunities for students to read and interpret information from tables. Provide opportunities for students to build input-output tables and explain the relationships in terms of input-output. Have students use a verbal description using the words given to describe the relationship to check for reasonableness. For instance “180 pieces of gum minus the number of people” is not a reasonable situation, but “180 pieces of gum divided by the number of people” is. Provide opportunities for students to justify why a given table is not appropriate for the given expression. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 5: Probability and Statistics Question 21 6.10C (Supporting) The student is expected to sketch circle graphs to display data Dual Coding: 6.12A The student is expected to communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Vocabulary: The rest, ratio, circle graph, best represents When Taught? Content: 6.10C Process: 6.12A Correct Answer *A/F B/G Regional Data 56% 11% C/H 28% D/J 5% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analyze – Students must analyze the circle graph to determine which one correctly represents the verbal description Analysis of Distracters Correct Confused the ratio 3 to 2 as tables to chairs instead of chairs to tables Has an equal number of tables and chairs instead of using the ratio 3 to 2 Assumes 20/80 benches and 10/80 desks Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Students need to work from verbal description to the circle graph and also from information given in a list or table to a circle graph. Emphasize the importance of finding the total since circle graphs show a part to whole relationship. Provide opportunities for student to think aloud and talk through the decisions they make and the steps they take to solve. With circle graphs, encourage them to communicate their reasoning with and without using specific percentages for parts of the graph – for instance “I knew there would be more chairs than tables because of the ratio 3 to 2” or “the part representing desks would have to be less than half the circle, because 20/80 is less than half of 80” to increase their problem solving and reasoning skills. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation and Quantitative Reasoning Question 22 6.1B (Readiness) The student is expected to generate equivalent forms of rational numbers including whole numbers, fractions, and decimals Dual Coding: Vocabulary: Length, fraction, equivalent When Taught? Content: 6.1B Process: Cognitive Level: Apply – Students apply their understanding of equivalent fractions, whole numbers, and decimals. Analysis of Distracters Correct Regional Campus/ District Data Answer Data A/F 15% 84/10 is not equivalent to eighty four hundredths B/G 3% 92/500 = 0.184 *C/H 52% Correct D/J 30% Instructional Implications: Provide opportunity for students to represent numbers in different ways but always understand that their values don’t change. Provide opportunities for students to correctly read and write numbers to help them learn place value. Emphasize and expect the formal vocabulary when naming numbers. Don’t say or allow students to say “one point eight four”, read “one and eighty four hundredths” – with fractions as well, don’t accept “92 over 500”, hold out for “92 hundredths”. Have a place value chart in your classroom to reference when asking students to selfcorrect using the formal vocabulary. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 4: Measurement Question 23 6.8B (Readiness) The student is expected to select and use appropriate units, tools, or formulas to measure and to solve problems involving length (including perimeter), area, time, temperature, volume, and weight Dual Coding: 6.11C The student is expected to select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types, including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, acting it out, making a table, working a simpler problem, or working backwards to solve a problem Vocabulary: Weighed, combined, ratio, closest Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 When Taught? Content: 6.8B Process: 6.11C Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 22% B/G 17% C/H 11% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – Students must apply their understanding of ratios to estimate the value of box A Analysis of Distracters Subtracted the numbers given in the ratio 3-1=2, then subtracted that from the combined weight 128-2=126 128 divided by 3 = 42 and 2/3 Both 128 and 3 are found in the problem Combined weight of the ratio 3:1 = 4, then 128 divided by 4 = 32 (did not multiply the 32 by 3) Correct *D/J 49% Instructional Implications: When students set up a proportion, teach them to always label their units and have students think aloud and talk through how they set up a proportion using rates and ratios. Have students estimate first to check for reasonableness (and eliminate unreasonable answers in multiple choice questions). Teach students to find the whole when given a ratio that is part to part and emphasize the importance of the whole. Provide students information embedded in images, and diagrams as well as graphs and table. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation and Quantitative Reasoning Question 24 6.2E (Readiness) The student is expected to use order of operations to simplify whole number expressions (without exponents) in problem solving situations Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Decreased, another, expression, determine When Taught? Content: 6.2E Process: 6.11A Correct Answer *A/F B/G C/H D/J Regional Data 65% 9% 16% 11% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply – students are applying their understanding of order of operations to this situation Analysis of Distracters Correct 90-2(60 / (10-4)) 90-2((60 / 10) - 4) Incorrect computation of the multiplication, division or subtraction Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Students need to be exposed to all ways of representing multiplication and division for example 2(6) and 4/5. Provide opportunities for students to work multi-step problems using order of operations. Have students communicate their thinking and explain why certain operations must be performed first. Giving students a number as the solution, a set of numbers (to use in the expression), a set of parenthesis and instructing them to create a situation is a great problem solving activity for students to increase their conceptual understanding of the effect parenthesis have in different parts of the expression. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation and Quantitative Reasoning Question 25 6.1B (Readiness) The student is expected to generate equivalent forms of rational numbers including whole numbers, fractions, and decimals Dual Coding: 6.13A The student is expected to make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and nonexamples Vocabulary: Sets, statement, equivalent, each When Taught? Content: 6.1B Process: 6.13A Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 39% *B/G C/H 38% 16% D/J 6% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analysis – Students must apply their understanding of equivalent forms of rational numbers to compare the sets and analyze the statements provided for accuracy. Analysis of Distracters Able to accurately solve for equivalence when given a mixed number, but not with the improper fractions. Correct Mistakes seven tenths in the fraction form for seven hundredths in decimal form and incorrectly converts improper fractions Mistakes seven tenths in the fraction form for seven hundredths in decimal form Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide opportunity for students to represent numbers in different ways but always understand that their values don’t change. Provide opportunities for students to correctly read and write numbers to help them learn place value. Emphasize and expect the formal vocabulary when naming numbers. Don’t say or allow students to say “eight point seven”, read “eight and seven tenths” – with fractions as well, don’t accept “92 over 500”, hold out for “92 hundredths”. Have a place value chart in your classroom to reference when asking students to self-correct using the formal vocabulary. 6.13A The student is expected to make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and nonexamples Students need to be exposed to this process skill with more than just equivalent fractions. They should be able to group types of numbers and identify non-examples. Provide opportunities for this and for students to think aloud and talk through the decisions they make. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 3: Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Question 26 6.6C (Readiness) The student is expected to describe the relationship between radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle Dual Coding: 6.11D The student is expected to select tools such as real objects, manipulatives, paper/pencil, and technology or techniques such as mental math, estimation, and number sense to solve problems Vocabulary: Line segment, passes through, center, circle, coordinate grid, equation, circumference When Taught? Content: 6.6C Process: 6.11D Correct Answer *A/F B/G Regional Data 65% 26% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Apply - Students must use the information provided in the coordinate grid and apply the formula for circumference of a circle Analysis of Distracters Correct Uses the formula for circumference given the radius, but incorrectly inputs the value for diameter (60). Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 C/H 5% 60x2=120, and uses the formula that would solve for radius, not circumference 60/2 would solve for radius, not circumference D/J 4% Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to know and understand the relationships that exist between the radius, diameter and circumference. They should calculate: circumference with radius, circumference with diameter, diameter with circumference, radius with circumference, diameter with radius, and radius with diameter. Have students explain what the components of various equations mean in relationship to finding the diameter, radius or circumference. Provide opportunities for students to know and understand the formulas used for circumference and manipulate these formulas. When using coordinate grids, have students find the distance between two points. Use a variety of increments so they have the experience and exposure working with various values in coordinate grids. Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 2014 Grade 6 Mathematics STAAR Reporting Category 1: Number, Operation and Quantitative Reasoning Question 27 6.2B (Readiness) The student is expected to use addition and subtraction to solve problems involving fractions and decimals Dual Coding: 6.11A The student is expected to identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Vocabulary: Spent, preparing, conducting, the rest, statement, more than, same amount When Taught? Content: 6.2B Process: 6.11A Correct Answer A/F Regional Data 15% B/G C/H 14% 17% *D/J 54% Campus/ District Data Cognitive Level: Analysis – Students must use addition and subtraction of fractions (including regrouping) to solve this multistep problem and determine which statement is accurate. Analysis of Distracters Cannot be correct because 2 1/3 – (5/6 + ¾) is less than 1 ½ Cannot be correct because 2/3 < ¾ Cannot be correct because 5/6 + 5/6 + ¾ is 2 5/12 not 2 1/3 Correct Region 10 Item Analysis – 2014 6th Grade Math STAAR, Part 1 Instructional Implications: Provide opportunities for students to work multi-step problems, especially with fractions, decimals and percent. Teach students to write number sentences or equations before performing the operation in a word problem. Have students use a problem solving strategy such as draw a picture, work a simpler problem (re-read it with simple numbers to better understand the context and write a number sentence), or act it out. Students need to be comfortable with reading long questions, identifying multiple informational elements within the question, plan and carry out a solution. Consider choosing a problem solving system as a campus to use across grade levels. Have students communicate their thinking.