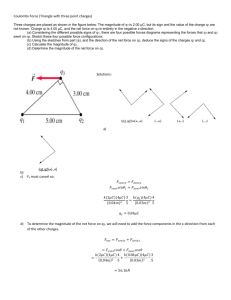
here
advertisement

Physics and Physical Measurement The Realm of physics Measurement and uncertainties Scale Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bz9D6xba 9Og&list=PL772556F1EFC4D01C&index=1&fea ture=plpp_video Why does that matter? • Must have a consistent set of units agreed upon. (SI system) – SI has 7 fundamental units w/ lots of combinations. • How far off were you? – Need an appreciation for the magnitude of things. (masses, time, distances, forces…) 1.1.2 State the ranges of magnitude of distances, masses and times that occur in the universe, from smallest to greatest. Distances • Sub-nuclear particles = 10-15m • Extent of the visible universe = 1025m • Distance from Earth to Moon = 3.84 x 105km • Radius of Earth = 6380km = 107m • Diameter of a nucleus = 10-15m 1.1.2 State the ranges of magnitude of distances, masses and times that occur in the universe, from smallest to greatest. Masses • Rest mass of and electron = 10-30kg • The universe = 1050kg • Mass of the Earth = 5.97 x 1024kg • Mass of the Moon = 7.35 x 1022kg • Mass of an electron = 9.11 x 1031kg 1.1.2 State the ranges of magnitude of distances, masses and times that occur in the universe, from smallest to greatest. Times • Passage of light across a nucleus = 10-23s • Age of the universe = 1018s • Light to travel from Sun to Earth = 8min = 102s • Period for one orbit of Earth = 365day = 107s • Time between vibrations of Cesium = 10-10s 1.1.2 State the ranges of magnitude of distances, masses and times that occur in the universe, from smallest to greatest. • Range of magnitudes of quantities in our universe: – Visible universe= 1026 m – The age of the universe= 1018 s – The total mass of the universe= 1050 kg • The atom: – The diameter of an atom = 10-10 m – The diameter of the nucleus = 10-15 m Upper and lower measurements • • • • Size of proton 10-17 m (lower) Speed of light in a vacuum 3 x108 m/s Age of universe 1017s If quarks are the fundamental unit then their mass would give us the lower limit, but they hide in protons and our best guess is 10-30 kg. This is also the approximate mass of an electron at rest. 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude • 10-10m/ 10-15 m= 105 • 105 is known as a difference of five orders of magnitude. The ratio of the diameter of the hydrogen atom to its nucleus is about 100000 times or 105 times, or a difference of 5 orders of magnitude. 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Example • The rest mass of a proton is about 1.67x10-27kg. The rest mass of an electron is about 9.1x1031kg. How many orders of magnitude bigger is the mass of the proton than that of the electron? 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Example • Solution 1x10-27kg and 10x10-31kg (1x10-30kg) -27- -30 = 3 orders of magnitude Realize that the proton is not 3 times more massive it is 103 times more massive or 1000 times more massive. 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Practice 2 • The length of a football pitch is about 100m. The distance from the earth to the moon is about 384x106m. How many orders of magnitude larger is the distance from earth to the moon than the length of a football pitch? 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Practice 2 solution • Football pitch = 102 • Earth to moon = 108 • 8-2 = 6 orders of mag Or 1,000,000 times larger 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Practice 3 • The mass of the Sun is 1.99 x 1030kg. The mass of the Earth is 5.98x1024kg. How many orders of magnitude more massive is the Sun than the Earth? 1.1.3 Stating ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Practice 3 Solution • Sun = 1030 • Earth = 1025 • 30-25 = 5 orders of magnitude 1.1.4 Estimate approximate values of everyday quantities to one or two significant figures and/or to the nearest order of magnitude. – How high is a two storey house in meters? – What is the diameter of your pupil? – How many times does your heart beat in an hour when you are relaxed? – What is the weight of an apple in Newtons? – • • • • About 6m about 2-4mm / 4-8mm about 60-100 beats/min about 1N 1.1.4 Estimate approximate values of everyday quantities to one or two significant figures and/or to the nearest order of magnitude. Practice 7 • Estimate the thickness of a page in your book. Fundamental Units • • • • • • • Meter Kilogram Second Ampere Kelvin Mole Candela m kg s A K mol cd length mass time electric current temperature amount of matter intensity of light Mechanics and Derived Units • Mechanics is the study of matter, forces, and energy. With combinations of the first three base units (m, kg, and s), all other units for mechanics can be developed. • Name one not listed…. • Newton N force or weight kg m s-2 • Joule J energy or work kg m2 s-2 • Watt W power kg m2 s-3 • Pascal Pa pressure kg m-1 s-2 Derived Units Find the symbol, concept, and broken down base units for each of the following: • Hertz • Coulumb • Ohm • Tesla • Weber • Becquerel • • • • • • Hertz Coulomb C Ohm Ω Tesla T Weber Wb Becquerel Bq Hz frequency s-1 Electric charge As electrical resistance kg m2 s-3 A-2 magnetic flux Wb m-2 magnetic flux (T m2) or kg m-2 s-2 A radioactivity s-1 • • • • • • Hertz Coulomb C Ohm Ω Tesla T Weber Wb Becquerel Bq Hz frequency s-1 Electric charge As electrical resistance kg m2 s-3 A-2 magnetic flux Wb m-2 magnetic flux (T m2) or kg m-2 s-2 A radioactivity s-1 Problems 1. Give units for the following expressed as derived and base units: a. Force b. Kinetic energy 2. Check if these equations work by substituting units into them. a. Power= work/time or energy/time b. Power = force x velocity Answers 1. a. N or kg m s-2 b. J or kg m2 s-2 2. a. W: J s-1 or W: (kg m2 s-2 )s-1 or W: kg m2 s-3 b. W: N x (m s-1 ) or W: (kg m s-2 )x (m s-1 ) or W: kg m2 s-3 Problems 3. Which one of the following units is a unit of energy? a. eV b. W s-1 c. W m-1 d. N m s-1 4. Which on of the following lists a derived unit and a fundamental unit? A Ampere Second B Coulomb Kilogram C Coulomb Newton D Meter kilogram Answers 3. eV 4. B Other Units Name Symbol Concept Liter L volume Minute, hour, year, etc. Min, h, y, etc. Time Kilowatt-hour kWh Energy Electronvolt eV Energy Degrees celsius oC temperature Decibel dB Loudness Unified atomic mass unit U Mass of nucleon Problem 5. Convert these units to SI: a. Year b. 100 oC c. kWh d. eV Modifying SI Units • SI units can be modified by the use of prefixes. Prefix Abbreviation Value Tera T 1012 Giga G 109 Mega M 106 Kilo k 103 centi c 10-2 milli m 10-3 micro μ 10-6 nano n 10-9 pico p 10-12 femto f 10-15 Problems 6. Change 2360000J to scientific notation and MJ. 7. A popular radio station has a frequency of 1090000Hz. Change this to scientific notation and MHz. 8. The average wavelength of white light is 5.0x 10-7 m. What would this be in nanometers? 9. The time taken for light to cross a room is about 1 x10-8 s. Change this into microseconds. Answers 6. 7. 8. 9. 2.36 x 106 J or 2.36 MJ 1.09 x 106 Hz or 1.09 MHz 500 nm 0.01 μs 10.Estimate the speed with which human hair grows. 11.If all the people on earth were to hold hands in a straight line, how long would the line be? How many times would it wrap around the earth? 12.How many revolutions do the wheels of a car make before it is junked (wheel radius is 30cm,250,000km total) Answers • About 4 x 10-9 m/s • About 9 x 109m, about 200 times • About 108 Uncertainty and Error • There are two types of errors: • Random and systematic • Random errors can be reduced by repeating measurement many times. • Systematic errors can be reduced by repeating measurement using a different method or different apparatus and comparing the results.