Biology I
advertisement

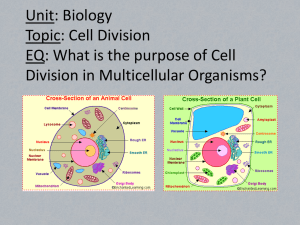
Biology I FINAL EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the goal of science? • To investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world and to use those explanations to make useful predictions. In an experiment, the variable that is changes is termed the…… • MANIPULATED VARIABLE Name 5 characteristics of all living things • • • • • • • • Respond to the environment Reproduce Grow and develop Maintain homeostasis Evolve as species over time Are made up of cells Obtain and use materials and energy Are based on a universal genetic code Define HOMEOSTASIS • The process in which organisms keep their internal conditions fairly constant The disproved idea that life could arise from nonliving matter is termed… • SPONTANEOUS GENERATION _______ are atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons • ISOTOPES Proteins that speed up chemical reactions are called… • ENZYMES Name the 4 main classes of organic compounds. • • • • CARBOHYDRATES LIPIDS PROTEINS NUCLEIC ACIDS Identify the purpose and set up of the pH scale. • Purpose is to show the relative concentration of Hydrogen ions and indicate whether a substance is an acid a base or neutral. 7 is neutral above that is a base and below is an acid the further away from seven the stronger of an acid/base it is. Each change in number is 10 times different. What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? • PROKARYOTIC = smaller, less complex, no nucleus • EUKARYOTIC = larger, more complex, has membrane bound organelles and a nucleus _______ is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. • OSMOSIS What (two-word) term refers to cells having different roles in an organism? • CELL SPECIALIZATION Put the following in order from most complex level to most simple level: tissue, organ, cell, organ system • ORGAN SYSTEM, ORGAN, TISSUE, CELL If the cell has to use energy to move substances in and out of the cell this type of transport is called • ACTIVE TRANSPORT The nuclei of eukaryotic cells is important because… • It contains coded information (DNA) that determines the structure and functioning of the organism. What are the three parts of the cell theory? • Cells are the basic units of life • All living things are made up of cells • Cells only come from pre-existing cells Photosynthesis takes place in this specialized organelle… • CHLOROPLASTS What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs? • Autotrophs make their own food while heterotrophs have to get energy by obtaining it from other organisms. What are four main things required for the process of photosynthesis? • • • • SUNLIGHT (UV LIGHT) CHLOROPHYLL WATER CARBON DIOXIDE One cause of muscle soreness is the production of __________ through fermentation in our muscle cells. • LACTIC ACID Cellular respiration occurs in…… • MITOCHONDRIA • ALL LIVING THINGS • EVEN PLANTS What are the products of cellular respiration? • CARBON DIOXIDE • WATER • STORED ENERGY IN OUR ATP The process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells is called… • CELL DIVISION What are the 4 phases of mitosis (IN ORDER)? • • • • PROPHASE METAPHASE ANAPHASE TELOPHASE The splitting of the cell’s cytoplasm is termed… • CYTOKINESIS What is the significance of stem cells? • They have not yet become specialized, so they have the potential to become different cells in the body. If we can figure out how (and if it is ethical to) to develop these that match our cells, how to deliver them to the target part of the body, and how to program them, we would be able to potentially cure many diseases, disorders or damage done to the body. What are two reasons cells remain quite small? • Keep the surface area to volume ratio low so that nutrients/wastes could effectively move in and out of the cell. • Not enough DNA to meet the needs of larger cells – DNA OVERLOAD Proteins that regulate the cell cycle are called… • CYCLINS __________ is a type of cell division that has the purpose of producing gametes. • MEIOSIS Chemical factors that determine traits are called… • GENES A Heterozygous brown rabbit is crossed with a white, homozygous recessive rabbit. The probability that the offspring will be white is…. • 25% Who is the scientist that laid the foundation of the field of genetics with his study of pea plants? • MENDEL What is the difference between phenotype and genotype? • Phenotype is the physical expression of a trait (what you see), while genotype refers to an organism’s alleles for a trait (their written genetic make-up). How is codominance different than incomplete dominance? • Codominance is where both alleles contribute to the genotype and are both distinctly and visibly expressed, whereas incomplete dominance is where neither allele is completely dominant so the expressed trait in a heterozygous individual is in between the two homozygous phenotypes. What are two differences between mitosis and meiosis? • Mitosis = one round of division, produces two identical diploid cells, used for growth/development and repair or replacement of body cells. • Meiosis = two rounds of division, produces 4 genetically different haploid cells, used for producing gametes What is a mutation? • Any change in the sequence of DNA that affect genetic information During transcription a DNA “gene” is converted into ... • MESSENGER RNA (mRNA). During the process of translation, messenger RNA is read by a ribosome to assemble a _________ by linking together individual ___________. • PROTEIN (POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN) • AMINO ACIDS DNA is double stranded and complimentary. During replication a strand that has the sequence AAGGGCATACAT would have ______ formed as its compliment. • TTCCCGTATGTA How is DNA different than RNA? • • • • Function or biological role Double stranded vs. single-stranded Different sugar – deoxyribose vs. ribose RNA has U (uracil) in place of T (thymine) A normal male chromosome make-up would be? Female? • 46, XY • 46, XX What does a pedigree chart show? • It shows the pattern of inheritance for traits through generations of offspring. What was the goal of the Human Genome Project? • Goal was to sequence the complete DNA for the human organism. Transgenic organisms are those that contain __________ from a different species. What are some purposes for creating • GENES • Increasing food supply, creating cells, organs for transplant, creating large amounts of biologically important molecules Gene Therapy is an effort to… • Replace or fix a faulty gene with a working one. Breeders can increase genetic variation by… • INDUCING MUTATION The hypothesis that species change over time by means of natural selection was proposed by… • CHARLES DARWIN Darwin’s exploration of the Galapagos Islands led him to see that each island…. • Had unique species of very similar type organisms as well as environmental differences. From reading Lyell and Hutton, Charles Darwin learned that the Earth… • Is very old • Is formed by processes that still operate to change the Earth today. Thomas Malthus proposed that… • The world’s population would one day outgrow (outpace) its supply of food resources. Artificial Selection is a process in which…. • Human beings, not nature chose which organisms to breed together based on desired characteristics. _______ is the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its specific environment. • FITNESS What are at least 3 areas of evidence supporting the theory of biological evolution? • • • • • • Fossil Record Observed microevolution events Geographic distribution of species Homologous structures Similarities in embryology Molecular evidence Scientists have discovered, identified and classified ________ of the planet’s living species. • Some, a part, less than ½… In a system called________ ________ each species is assigned a two-part universally accepted scientific name. • BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE Traditional classification efforts concentrated only on… • Similarities in appearance or structure. In biological classification, several different orders make up a ________ of organisms. • CLASS What is phylogeny? • The study of evolutionary relationships among organisms What characteristics differentiate the kingdom Animalia from the kingdom Plantae? • Animals are heterotrophic, do not have cell walls, and are motile.