File
advertisement

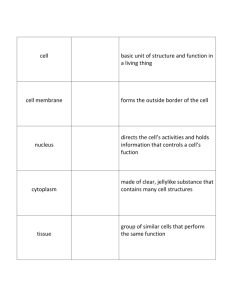
Chapter 14: Bones, Muscles and Skin Section 1: Body Organization and Homeostasis p. 468 – p.473 Body Organization • How the body systems work together to keep you alive Levels of Organization in the Body • The levels of organization in the human body consist of: – Cells – the basic unit of structure and function in living things – Tissues – a group of similar cells that work together to perform the same function – Organ – A structure in the body that processes materials necessary for the body to survive – Organ system – A group of organs that work together to perform a major function in the body – Organism – A complete, living thing homeostasis • Our internal environment stays the same in spite of changes on the outside • Keeping things in balance Homeostasis • The maintenance of stable internal condition in an organism even when the outside environment changes • Like body temperature • Sugar • Iron • Calcium Cell • The basic unit of structure and function in a living things. • A human being contains 100 trillion cells. Cell Membrane • The cell membrane forms the outside boundary of the cell. • It is picky about what it allows into and out of the cell. • One could say, “It is selectively permeable.” Nucleus • It is the control center of the cell. • It directs all the cell’s activities. • It contains the information that determines the cell’s form and function. Cytoplasm • The material within the cell apart from the nucleus. The clear, jellylike substance containing the cell’s structures and organelles. Tissue • A group of similar cells that perform the same function. The human body contains four basic types of tissue: – – – – Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue Connective Tissue Epithelial Tissue Muscle Tissue • Muscle tissue can contract or shorten. • By doing this, muscle tissue makes parts of your body move. Nervous Tissue • Nervous tissue carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and other parts of the body. • It controls the brain messages and responses from the brain. Connective Tissue • Connective tissue provides support for your body and connects all its parts. • Bone tissue and fat are connective tissues. Epithelial Tissue • The surfaces of your body, inside and out are covered by epithelial tissue. • Some epithelial tissue, such as your skin, protects the delicate structures that lie beneath it. • The lining of your digestive system consists of epithelial tissue that allows you to absorb the nutrients in your food. Organ • An organ is a structure that is composed of different kinds of tissue. • Your stomach, heart, brain and lungs are all organs. • An organ performs a specific job. Organ System • Each part of your body is part of an organ system. • An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function to sustain the body. • Check page 471 in your textbook Stress • The reaction of your body to potentially threatening, challenging, or disturbing events. Summary • What information was helpful to me? • Is there something interesting that I may look back at in this section?