Body Organization & Homeostasis
advertisement

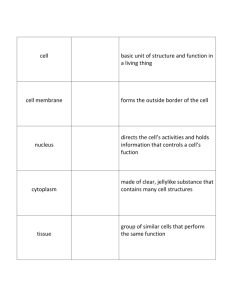
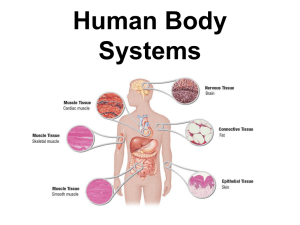
BODY ORGANIZATION & HOMEOSTASIS Chapter 1 Section 1 Pages: 6 - 11 Objectives: Order the levels of organization in the body. Describe the basic components of a body system & explain how they work together to function as a system. The levels of organization in the human body consist of… 1. Cell: the basic unit of structure & function in a living thing. Cell Membrane: outside boundary of the cell Nucleus: control center; directs cell activities & contains cell information Cytoplasm: material in a cell; clear, jellylike substance containing cell structures. Cell Functions: Carry on processes that keep the organism alive – Release energy, grow, get rid of waste, & reproduce. 2. Tissues: A group of similar cells that perform the same function. The body contains 4 basic types… *Muscle Tissue: can contract (shorten) *Nervous Tissue: directs and controls body processes- they carry electrical messages between the brain and other body parts. *Connective Tissue: provides support for your body and connects all its parts. (bone, blood, and fat for example. *Epithelial Tissue: covers the surfaces of your body, inside & out. Skin and the lining of your digestive system are examples. 3. Organs: A structure that is composed of different kinds of tissue. An organ performs a complex, specific job. Examples are: Heart, Brain, Kidneys, etc. 4. Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perform a major function. Examples are: circulatory system, skeletal system, etc. Homeostasis: The body’s tendency to keep an internal balance. *Homeostasis is the process by which an organism’s internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment. Stress: the reaction of your body and mind to potentially threatening, challenging, or disturbing events. Adrenaline: Gives you a burst of energy and prepares your body to take action. Fight or Flight Response: Reaction from adrenaline. It prepares you to either fight the stressor OR run away from the stressor. Long-Term Stress: Stressor that continue for a long time Examples: Short-Term Stress: Examples: Dealing with Stress: Examples: