Animal-Like Protists
advertisement
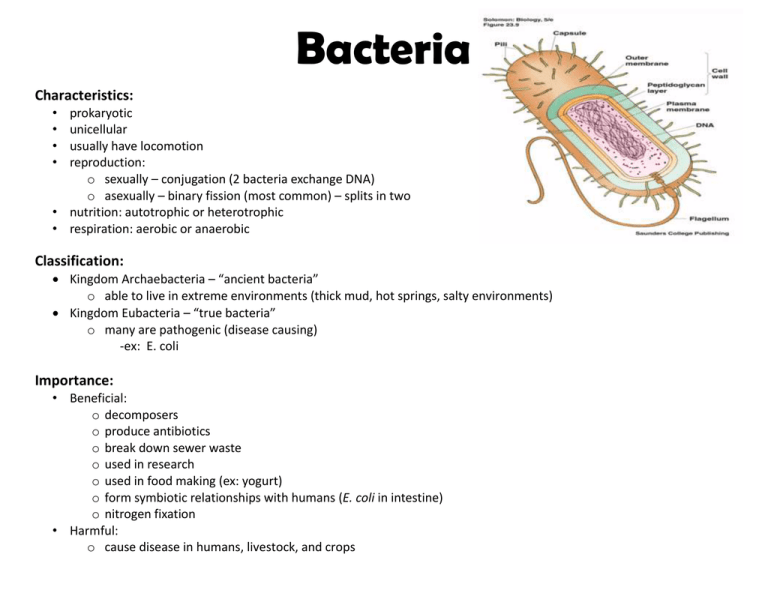
Bacteria Characteristics: • • • • prokaryotic unicellular usually have locomotion reproduction: o sexually – conjugation (2 bacteria exchange DNA) o asexually – binary fission (most common) – splits in two • nutrition: autotrophic or heterotrophic • respiration: aerobic or anaerobic Classification: Kingdom Archaebacteria – “ancient bacteria” o able to live in extreme environments (thick mud, hot springs, salty environments) Kingdom Eubacteria – “true bacteria” o many are pathogenic (disease causing) -ex: E. coli Importance: • Beneficial: o decomposers o produce antibiotics o break down sewer waste o used in research o used in food making (ex: yogurt) o form symbiotic relationships with humans (E. coli in intestine) o nitrogen fixation • Harmful: o cause disease in humans, livestock, and crops Protists Characteristics: • eukaryotic • mostly unicellular • may be plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like in mode of nutrition (how they get food) Animal-Like Protists: • • • • known as protozoans – “first animals” heterotrophic classified by locomotive structures (how they move) Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium, Plasmodium (causes malaria), Trypanosoma (causes African sleeping sickness) Plant-Like Protists: • • • • known as algae autotrophic by photosynthesis contain chlorophyll Examples: diatoms, dinoflagellates (cause red tide), kelp Fungus-Like Protists: • heterotrophic • decomposers • absorb food • Examples: Physarum (plasmodial slime molds), Dictyostelium (cellular slime molds) Importance: • Beneficial: o decomposers o major food source in aquatic food chains o used as abrasives in toothpaste o food source o used in many foods • Harmful: o cause disease (malaria, African sleeping sickness) o cause red tide o kill crops Fungi Characteristics: • eukaryotic • multicellular (except yeasts) • heterotrophic by absorption o contain hyphae – rootlike structures for absorbing nutrients • reproduce sexually & asexually • no locomotion • cell walls made of chitin • decomposers Examples: • • • • Rhizopus (black bread mold) Yeast Mushrooms, puffballs Cup fungus Importance: • Beneficial: o make antibiotics (penicillin) o used in cheese-making (bleu cheese) o used in baking industry (yeast) o used in alcohol industry (yeast) o used as a food source o decomposers • Harmful: o cause disease in humans and in crops o cause allergies o spoil food • Ringworm fungus • Athlete’s foot fungus • Truffles, morels