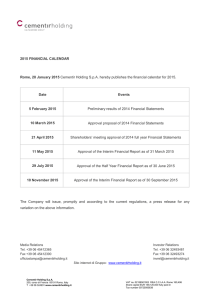
A Primer on U.S. Pension Systems
A Primer on
U.S. Pension Systems
S. Ghon Rhee, K. J. Luke Distinguished Professor of International Finance and Banking
University of Hawai’i
The 6 th International Financial Forum
April 27-28, 2005, Seoul, Korea
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
1
US Retirement Pension and
Security Systems: Three-Legged Stool
Retirees generally rely on three sources of income for retirement:
Retirement
Plans
19%
Social Security
38%
Personal
Savings
43%
Source: U.S. Social Security Administration, Facts and Figures about Social
Security (August 2004)
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
2
The U.S. Social Security System:
A “Pay-As-You Go” Basis
Social security taxes [or known as FICA (Federal
Insurance Contributions Act) taxes] are collected and divided among four Trust Funds:
The federal OASI (Old-Age and Survivors Insurance) Trust
Fund: 5.3% of FICA tax
The federal DI (Disability Insurance) Trust Fund:
0.9% of FICA tax
The federal HI (Hospital Insurance) Trust Fund:
1.45% of FICA tax
The federal SMI (Supplementary Medical Insurance) Trust
Fund: funded by general federal tax revenues and monthly premiums paid by enrollees
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
3
Sources and Uses of
Social Security Revenues in 2003
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
4
Distribution of Social Security
Tax Dollar (As of 2004 )
Medicare benefits
19 cents
41.7 million people
7.9 million people
Disability benefits
12 cents
Administrative costs
1 cents
39.7 million people
Retirement and survivor benefits
68 cents
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
5
Trust Funds Operations
(2004)
Unit: $ Billion
Assets (end of 2003)
Income in 2004
Expenditure in 2004
Increase in Assets
Assets (end of 2004)
OASI DI HI SMI
$1,355.30 $175.40 $256.00 $24.00
566.30
421.00
145.30
1,500.60
91.40
80.60
10.80
186.20
183.90
170.60
13.3
269.30
133.80
138.30
-4.50
19.40
Source: The 2005 Annual Social Security and Medicare Trust Fund Report
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
6
Short-Term Outlook for Trust
Funds:
OASI, DI, and HI Trust Fund Ratios
(Assets/Annual Expenditures)%
Source: The 2005 Annual Social Security and Medicare
Trust Fund Report
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii 7
Long-Term Outlook for Trust
Funds (I):
Social Security and Medicare Cost as a Percentage of GDP
Source: The 2005 Annual Social Security and Medicare
Trust Fund Report
8
Long-Term Outlook for Trust Funds (II)
Income and Cost Rates
(As Percentage of taxable payroll)
Source: The 2005 Annual Social Security and Medicare
Trust Fund Report
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
9
Life Expectancy at Birth
(1960, 1980, & 2002)
85
80
75
60
55
70
65
66.6
73.1
71.8
78.8
74.5
79.9
1960 1980 2002
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
Male
Female
10
Life Expectancy at 65
(1960, 1980, & 2002)
25
20
15.8
18.3
16.6
19.5
14.1
15
12.8
10
5
0
1960 1980 2002
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
Male
Female
11
Average Retirement Age
(1950-55, 1970-1975, & 1995-2000)
64
63
62
61
60
59
69
68
67
66
65
68.5
67.9
62.9
62.9
62.6
62.6
Men
Women
1950-55 1970-75 1995-2000
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
12
Long-Term Deficits of Four
Trust Funds (Percent of GDP)
Source: The 2005 Annual Social Security and Medicare Trust Fund Report
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
13
U.S. Retirement Market Assets
(2003)
Mutual funds
Pension funds,
Insurance companies, banks and
Brokerage
$9.3 Trillion
$2.7 Trillion
IRA 1.29 Trillion
Employer sponsored accounts
1.4 Trillion
Total 12.0 trillion
The $2.7 trillion in mutual fund retirement assets accounted for
1/3 of all mutual fund assets
Source: Investment Company Institute, 2004 Fact Book
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
14
U.S. Retirement Assets by Types of Accounts
The $12 trillion in U.S. retirement market assets are divided between IRA ($2.98 trillion) and
Employer Sponsored Accounts ($9.0 trillion)
IRA
$2.98 Trillion
Employer
Sponsored
Accounts
$9.0 Trillion
Source: Investment Company Institute, 2004 Fact
Book
Total 12.0 trillion
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
15
Who Manages IRA Assets?
3000 Unit: $ Billion
2,979
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
255 268
69
315
1 2
346
1,292
3
386
1,104 1,056
1994
2003
1.Bank and thrift Institutions
2. Life Insurers
3. Mutual funds
4. Securities Companies
4 Total
Source: Investment Company Institute, 2004 Fact Book
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
16
Mutual Fund-Managed Retirement
Assets (2003)
Other
Retirement
Plans
$237 Billion
403(b) plans
$260 Billion
$898 Billion
$1,292 Billion
401(k) plans
IRAs
Total $2,687 Billion
Source: Investment Company Institute, 2004 Fact Book
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
17
Mutual Fund Retirement Assets by Types of Funds (2003)
Unit: $ Billion
Source: ICI, 2004 Fact Book
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
18
Employer-Sponsored
Retirement Assets (2003)
Federal
Government
Defined
Benefit Plans
Annuity
Reserves
$1Trillion
$1.3 Trillion
Private
Defined
Benefit
Pension
Plans
$1.9 Trillion
Total $9.00 trillion
$2.5 Trillion
State & Local
Government
Employee
Retirement
Plans
$2.3 Trillion
Private
Defined
Contribution
Pension Plans
Source: ICI, 2004 Fact Book
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
19
401(k) Plan
401(k) plans: Named after the section number of of the Internal Revenue Code; Most important component of profit sharing program
Similar salary-deferral retirement plans are authorized in the tax code for:
457 plans: Public-sector employees
403(b) plans: Nonprofit-sector employees
401(K) plan assets: $1.9 trillion (2003)
Number of Participants:
44 million workers
EBRI/ICI Joint Database
15.0 million 401(k) plan participants
45,152 employer-sponsored 401(k) plans
$776.0 billion in assets .
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
20
Asset Allocation by 401(k)
Plan (2003)
60
51
50
44
45
40
1996
2000
30
20
8 8
9
19 19
16 16
11
13
7
5
10
10
5
4
5
0
Equity Funds Balanced funds
Company stock
Bond Funds Money Funds GICs and other stable value Funds
Source: EBRI/ICI (2004)
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
2003
21
Employee Stock Ownership Plans
An ESOP is a defined contribution plan that allows employees to become owners of stock in the company they work for.
Equity based deferred compensation plan.
Only ESOP is required by law to invest primarily in the securities of the sponsoring employer.
401(k) plan may be used for employee ownership; a company can match employee contributions with its own stock.
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
22
Growth of ESOP Assets
(Estimates)
Year Assets
1990
1994
1995
1998
$133 billion
$184 billion
$226 billion
$350 billion
2001
2005
$400 billion
$500 billion
As of 2005: 10 Million People Participating in 11,500 plans
Source: National Center for Employee Ownership
Asia-Pacific Financial Markets Research Center, University of Hawaii
23
Mahalo for You Attention!
24