Data Collection & Sampling Techniques
advertisement

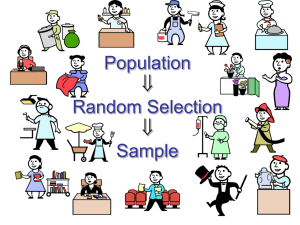
Section 1-3 Objectives Describe the process of a statistical study Identify various types of studies Learn the basic techniques for choosing a sample Introduction Usually a statistical study seeks to determine the value of an unknown parameter (numerical description of a population characteristic) The process of a statistical study is somewhat cyclic and begins with a question. Process of a Statistical Study Question Estimate Parameter Calculate Statistics Define Population/Variables Collect Data (Appropriately!!!) Process of a Statistical Study Step 1: Question Researcher must first determine a question that needs answering and determine the type of study* to conducted Examples: What is the favorite soft drinks of college students at GHC? What is the most popular eye color? What is the average income of CEOs of Fortune 500 companies? *Types of Statistical Studies Observational Study The researcher merely observes what is happening or what has happened in the past and tries to draw conclusions based on these observations No interaction with subjects, usually No manipulation is performed No cause and effect relationship can be determined Occur in natural settings, usually Can be expensive and time consuming Example: Surveys---telephone, mailed questionnaire, personal interview *Types of Statistical Studies Experimental Studies The researcher manipulates one of the variables and tries to determine how the manipulation influences other variables Interaction with subject occurs, usually Modifications on subject occurs May occur in unnatural settings (labs or classrooms) Example: Clinical trials of new medications ,treatments, etc. Examples Determine which type of study you would conduct: 1) Engineers wish to determine if a new laminating process for boat hulls is more susceptible to fractures at lower temperatures. 2) A car wash owner wants to determine the average age of his clientele 3) Researcher wants to determine if the color of the automobile driven is related to the driver running red lights 4) Scientists want to determine which one of four type special diets help to lower blood pressure. Process of a Statistical Study Step 2: Define Population and Variable The question usually defines the population and the variable(s) to be studied Often stated within the question itself DETAILS!!! DETAILS!!! DETAILS!!!! Examples 5) What is the favorite soft drinks of college students at GHC? 6) What is the most popular eye color? 7) What is the average income of CEOs of Fortune 500 companies? Process of a Statistical Study Step 3: Collect Data from a random sample* of the defined population Data can be collected in a variety of ways, BUT if the sample data is not collected in an appropriate way, the data may be so completely useless that no amount of statistical torturing can salvage them. Effective use of data requires that we know at least these three things: Context of the data (What, When, Where, Why) How the data was collected (Randomness is the key!) Population to which the sample will be inferred Selecting a Sample Sample must be representative (Representative sample) A representative sample: has the same relevant characteristics as the defined population and does not favor one group of the population over another. allows people to study a population without studying every single individual in that population. is a valuable research tool. Sampling Techniques Census Data is collected from the ENTIRE population Often impractical Too time-consuming Too expensive EVERYONE is included Sampling Techniques Random Sampling Selected by using chance or random numbers Each individual subject (human or otherwise) has an equal chance of being selected Examples: Drawing names from a hat Random Numbers Sampling Techniques Systematic Sampling Select a random starting point and then select every nth subject in the population Simple to use so it is used often (choose a random starting point and then choose every nth item Sampling Techniques Convenience Sampling Use subjects that are easily accessible Prone to creating non-representative sample (member all have a similar characteristic) Examples: Using family members or students in a classroom Mall shoppers Sampling Techniques Stratified Sampling Divide the population into at least two different groups (strata) with common characteristic(s), then draw SOME subjects from each group Results in a more representative sample Helps preserve certain characteristics of the population Basic Methods of Sampling Cluster Sampling Divide the population into groups (clusters), randomly select some of the groups, and then collect data from ALL members of the selected groups Used extensively by government and private research organizations Examples: Exit Polls Examples Identify the type of sampling used in each of the following cases: 8) In a large school district, all teachers from two buildings are interviewed to determine whether they believe the students have less homework to do now than in previous years 9) Every seventh customer entering a shopping mall is asked to select his or her favorite store. 10) Nursing supervisors are selected using random numbers in order to determine annual salaries 11) Mail carriers of a large city are divided into four groups according to gender and according to whether they walk or ride on their routes. Then, 10 are selected from each group and interviewed to determine whether they have been bitten by a dog in the last year Answers to Examples 1) Observational Study 2) Experiment 3) Observational Study 4) Experiment 5) Population: All GHC college students; Variable: Name of soft drink 6) Population: All living people in the world; Variable: Eye Color 7) Population: All CEOs of Fortune 500 companies; Variable: Income 8) Cluster 9) Systematic 10) Random 11) Stratified