Local Governments
advertisement

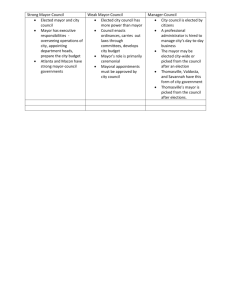
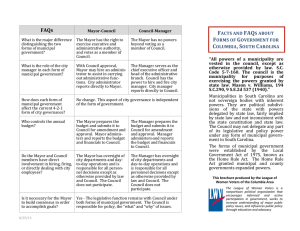
Local Governments Georgia Studies County Governments • Each county is represented in the General Assembly via districting • Each county has a probate court, magistrate court, and juvenile court • Some officials are elected at the county level – County commissioners – Clerk of superior court – Sheriff County Government Responsibilities • • • • • • Build and maintain roads Control licenses for cars and trucks Run Georgia’s welfare programs Voter registration & elections Land ownership records Marriage licenses Municipal Governments • Municipalities have charters (similar to constitutions) • Citizens can form a municipality by asking the state legislature to grant them a charter • Must hold regular elections, hold at least six meetings per year, & provide services (can vary) to citizens Three Main Forms of Municipal Government • In all forms of municipal government, citizens elect members to city council • City council is the legislative branch (makes laws) • Forms vary according to executive branch – Council-manager – Strong mayor-council – Weak mayor-council Council-manager • City council hires a city manager • City manager is head executive – Decides who is in charge of city services – Runs budget • City also has mayor – member of legislative branch – Can be chosen by council or elected by people Strong Mayor-council • Mayor is a powerful executive officer (elected by voters) – Can veto legislation – Can choose people to run city services – Power to run budget – Influence makeup of city committees Weak mayor-council • Mayor is elected by voters • Mayor is more for show than for function – No power to choose committee members – No power to veto – No power to run budget Special PurposeDistricts • Formed in order to meet the specific needs of the people • Administrative units which aim to accomplish a specific task – – – – Development Authorities Downtown Development Authorities Recreation & Park Authorities Housing Authorities