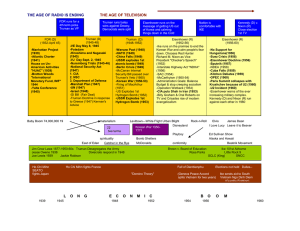
Cold War - ESC-20
advertisement
Graphic Organizer Soviet Views World Affairs American Views The Cold War 1945 - 1960 The Yalta Conference, Feb, 1945 Purpose: To plan post war Europe The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Concerns Soviet Security Concerns American Economic Concerns Keep Germany and the countries between them weak Promote economic growth by increasing world trade Capitalist countries would try to destroy communism Promote democracy and free trade The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Declaration of Liberated Europe Purpose: The right of all people to choose the type of government under which they will live The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Dividing Germany Divided into four zones between the United States, Britain, Russia and France, Berlin was also divided into four zones The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Stalin’s Next Move Pressured the King of Romania into a Communist government The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Potsdam Soviets wanted reparations United States wanted the economy and industry to be revived The Cold War 1945 - 1960 The Iron Curtain Political and military barrier that isolated Soviet-controlled countries of Eastern Europe after WWII The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Definitions Satellite Nations: countries not under direct Soviet control, but had to remain Communist and friendly to the Soviet Union Containment: the policy or process of preventing the spread of a hostile power The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Crisis in Iran Soviets had soldier in Northern Iran and The U.S. had soldiers. Instead of withdrawing as promise, Stalin remained in Iran The Truman Doctrine The Truman Doctrine Mar 12, 1947 Truman ask Congress for 400 million dollars to fight Communist aggression in Greece and Turkey The Marshall Plan The Cold War 1945 - 1960 The Marshall Plan In June 1947, Secretary of State George C. Marshall proposed the European Recovery Plan Give European nations American aid to rebuild their economies The Marshall Plan The United States offered up to $20 billion for relief, but only if the European nations could get together and draw up a rational plan on how to organize the recovery. The Marshall Plan The Marshall Plan, it should be noted, benefited the American economy as well. The money would be used to buy goods from The United States, and They had to be shipped across the Atlantic on American merchant vessels, but it worked. By 1953 the United States had pumped in $13 billion, and Europe was standing on its own. The Cold War 1945 - 1960 The Berlin Crises What led to the Berlin Crises? The Soviet Union believed that they would not receive reparation The Cold War 1945 - 1960 The Berlin Airlift, June 1948 Soviets cut off all traffic into West Berlin Why? In June 1948, Truman orders the Berlin Airlift to begin What type of military alliance did the Berlin Crisis put into motion? The Cold War 1945 - 1960 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), April 1949 Organization Purpose: NATO members agreed to come to the aid of any member who was being attacked How did the Soviet Leaders respond? The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Review Explain the Truman Doctrine Explain the Marshall Plan How did Truman feel about the Marshall Plan? The Cold War 1945 - 1960 Continuation of today’s lecture Divide into 5 groups U.S. & Truman, Marshall, Soviet Union & Stalin, Newspaper Reporters Congress, and the U.S. Citizens, NATO