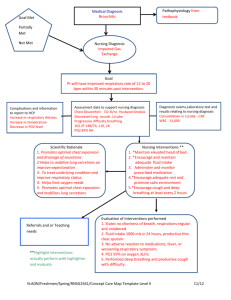
NURSING CARE PLAN Writing a nursing care plan involves multiple
advertisement

NURSING CARE PLAN Writing a nursing care plan involves multiple factors. Developing accurate assessment skills is a fundamental component of the nursing process required in order to systematically care for our patients. Understanding and application of the nursing process is also a key factor. The nursing process consists of five critical steps. 1. ASSESSMENT: an organized process involving 3 basic activities. a. systematically gathering data using the head to toe assessment, observational and communication skills. This includes subjective as well as objective data. b. Sorting and organizing the collected data. c. Documentation of the data. 2. DIAGNOSIS: analysis of the collected data in order to identify the patients needs or problems and coming up with a nursing diagnosis within NANDA guidelines. 3. PLANNING: simply put, this is your “plan of care” or goal. Then your nursing interventions are chosen. Your interventions are the actions that you as a nurse are going to do in order to “reach the selected goal.” 4. IMPLEMENTATION: This requires action. This is where you ACTUALLY put your planned interventions into action in order to meet your goal. 5. EVALUATION: this is where you “assess” your patients progress toward attaining the identified outcome or GOAL. The goal is either met or revised or the interventions may need to be revised. Here are some assessment areas that may assist the nurse in choosing a nursing diagnosis. The findings from these areas should be documented on your care plan under presenting signs and symptoms, notes and observations etc. The more “data” you have in this area, the easier it will be to come up with a nursing diagnosis. Some suggested assessment tools are: activity and rest, circulation, ego integrity(stress factors,feelings etc…)Elimination habits (incontinent,diarrhea etc…)food/fluid intake, hygiene, neurosensory (tingling,numbness etc…) pain/discomfort, respiration(SOB,dyspnea etc…) safety, social interactions and teaching/learning needs. These are a few suggestions to assist the nurse in developing a nursing care plan for the patient. By looking at these areas, the nurse will be able to come up with a plan of action in order to care for the patient. Remember…the more observations you make of your patient, the easier it will be to find an appropriate nursing diagnosis. Also remember to include subjective as well as objective data. Always put your care plan in your “OWN” words. Make use of all resources such as your Foundations of Nursing book, Adult Health, Nurses Pocket Guide and the internet. These are but a few suggestions to assist you in the development of your care plan. Keep it simple and make use of your developing assessment skills!!! This is but a beginning!!!! The nursing care plan that you are going to create has multiple components. The first area is your diagnosis. You will be forming your diagnosis from your assessment. The diagnosis must be NANDA approved and patient centered. After assessing your patient you will have a “list” of abnormal data that will help you with your diagnosis. You will be identifying a problem that you as a nurse can do something about, that is you can either make the problem better, or solve it or prevent it from worsening. The diagnosis will include certain information such as… what it is related to (why the pt. has the problem) and what it is evidenced by ( what you see that led you to believe the pt. has the problem) Next you will list objective data. Your objective data is what you “saw” that led you to the diagnosis or problem. Your objective data will come from your assessment findings and will also include the “evidence” of the problem. Next is the subjective data. This will be anything that the pt. states that relates to the problem. If the pt. does not contribute to this area, you may write “pt. did not contribute.” Now comes the “tricky” part. Your goal!!! The goal is going to be what you want accomplished regarding the diagnosis/problem. That is…what do you want to do about the diagnosis/problem. Your goal must be SMART!!! S=specific, M=measurable, A=attainable, R=realistic and T=timely. When coming up with your goal, you must consider all of these. The next area of your care plan is your interventions. Interventions are the things that you are going to do in order to meet your goal. You must have at least 4 interventions. Remember, your interventions are the actions that you are going to take to meet the goal. Along with your interventions are the rationales. These are the reasons why you are doing your interventions. Basically the rationales explain what the purpose of the interventions are. The final area of your care plan is the evaluation. Was the goal met or do you need more time. Do you need to reconsider the goal? Care plans are an integral part of what we do as nurses. The internet offers a vast amount of resources as do your books from school such as your Adult Health and Foundations of Nursing. Your pathophysiologies can help you with your care plans as well. Your pathophysiologies are a report about one of your pts. diagnosis where you will learn signs and symptoms, treatment and nursing interventions. Remember this while you are doing your care plans. In term 2 we are only introducing care plans. We want you to understand the basic concept of a care plan and how to begin to formulate it. Keep it simple at first until you have a better “grasp” on the whole idea. Remember…the instructors are here to help you . If you are having difficulty with this or anything else for the matter, PLEASE let us know!!! If you don’t know something…ASK!!!! The more you work on your care plans, the better understanding you will develop. The “light bulb will come on !!!!!”