Chapter 3 Test Review
advertisement
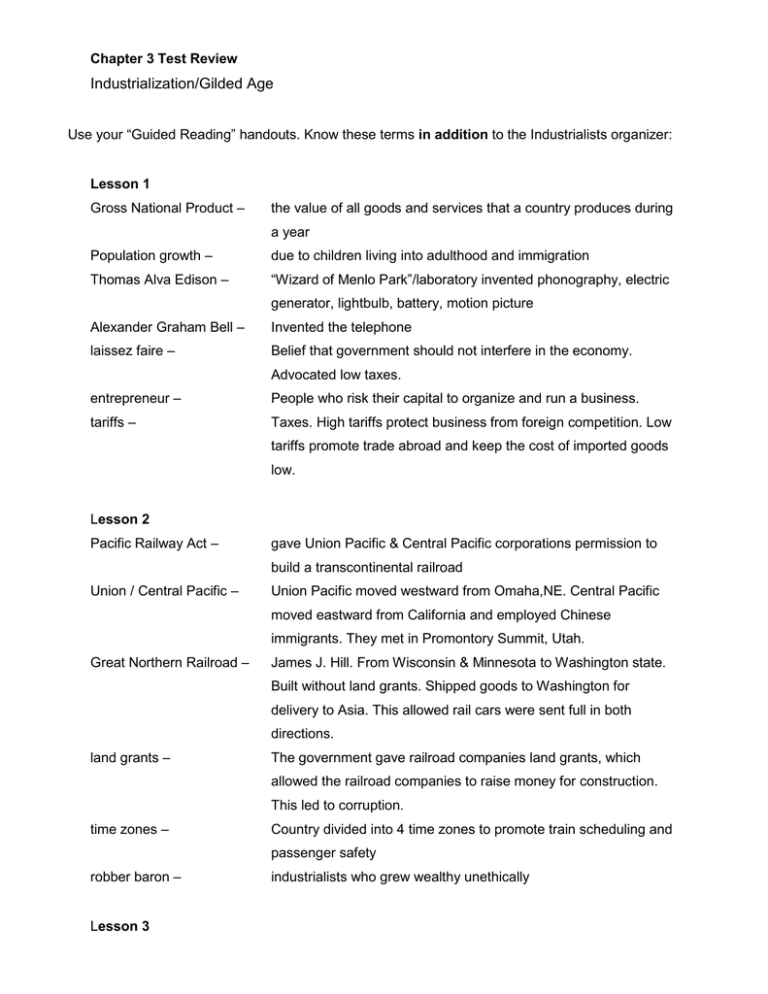
Chapter 3 Test Review Industrialization/Gilded Age Use your “Guided Reading” handouts. Know these terms in addition to the Industrialists organizer: Lesson 1 Gross National Product – the value of all goods and services that a country produces during a year Population growth – due to children living into adulthood and immigration Thomas Alva Edison – “Wizard of Menlo Park”/laboratory invented phonography, electric generator, lightbulb, battery, motion picture Alexander Graham Bell – Invented the telephone laissez faire – Belief that government should not interfere in the economy. Advocated low taxes. entrepreneur – People who risk their capital to organize and run a business. tariffs – Taxes. High tariffs protect business from foreign competition. Low tariffs promote trade abroad and keep the cost of imported goods low. Lesson 2 Pacific Railway Act – gave Union Pacific & Central Pacific corporations permission to build a transcontinental railroad Union / Central Pacific – Union Pacific moved westward from Omaha,NE. Central Pacific moved eastward from California and employed Chinese immigrants. They met in Promontory Summit, Utah. Great Northern Railroad – James J. Hill. From Wisconsin & Minnesota to Washington state. Built without land grants. Shipped goods to Washington for delivery to Asia. This allowed rail cars were sent full in both directions. land grants – The government gave railroad companies land grants, which allowed the railroad companies to raise money for construction. This led to corruption. time zones – Country divided into 4 time zones to promote train scheduling and passenger safety robber baron – Lesson 3 industrialists who grew wealthy unethically stocks – way to raise money and spread financial risk fixed costs – costs a company pays even if it is not operating (mortgage, taxes, loans) economies of scale – cost of manufacturing is decreased by producing goods quickly and in large quantities trusts – Rockefeller’s Standard Oil was the first. A legal agreement allowing one person (trustee) to manage another person’s property. holding companies – A company that does not produce anything itself but owns stock in companies that produce goods. Vertical Integration – Used by Andrew Carnegie – when a company grows by buying different steps in the production/distribution process Horizontal Integration – Used by John D. Rockefeller, Standard Oil, – when a company grows by buying its competitors Lesson 4 Unions Why were unions formed? Better wages, safer working conditions What tactics did they use? Strikes, Boycotts, Arbitration, Closed shops What challenges did they face? Contracts, Detectives looking for “troublemakers”, Blacklists, Lockouts, Strikebreakers. Violence during strikes undermined their goal. Injunction – a court order arbitration – settling a dispute by agreeing to accept the decision of an impartial outsider