eye development-001
advertisement

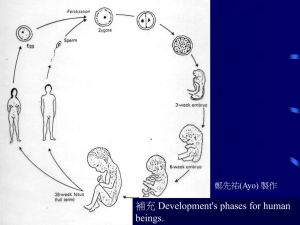
補充 Development's phases for human Life Science 2000 beings. 2 3- 4 days Fig. 16.8 (a) Life Science 2000 3 Fig. 15.10 The sperm have reached the egg and have surrounded it. However, only one sperm will enter into Life Science 2000 fertilization. 4 Table 16-1 Early stages of development 1. Fertilization (受精) 2. Cleavge (卵割) 3. Morula (桑椹胚) 3. Blastula (囊胚) 3. Gastrulation (原腸胚形成) 4. Neurulation (神經管形成) Life Science 2000 5 卵割 桑椹胚 囊胚期 Migration of cells Life Science 2000 6 卵割階段 Fig. 16.3 The gradual development of a grog embryo from the first cleavage toward the morula stage. Life Science 2000 7 Frog Chicken Human Science 2000 Fig. 16-4a A comparison of Life the development of three vertebrates. 8 Frog Chicken Human Science 2000 Fig. 16-4b A comparison of Life the development of three vertebrates. 9 5-6 days Fig. 16-8b Life Science 2000 10 Blustrula stage Gratrulation stage Fig. 16-5 a hen's egg. Life Science 2000 11 Table 16.2 Structures Produced by the three germ layers Ectoderm All nervous tissue; epidermis of skin, parts of eyes and ears, hair, pituitary gland, adrenal medulla Endoderm most linings of digestive system, of respiratory system Mesoderm muscle, cartilage, bone, blood, Kidneys and gonads Life Science 2000 Fig. 16.1 Neurulation. 12 Fig. 16-6 The basic tubewithin-a tube structure of most invertebrates and vertebrates. Life Science 2000 13 Life Science 2000 Fig. 16-6 The basic tubewithin-a tube structure of most invertebrates and 14 vertebrates. 羊膜 尿囊膜 絨毛膜 卵黃囊 Fig. 16-7 later development of membranes in the chick embryo Life Science 2000 15 Fig. 16-7 later development of membranes in the chick embryo Life Science 2000 16 補充 Late stage of development of the Life Science 2000 allantois in a chick embryo. 17 Amnion chorion allantois Yolk sac Extraembryonic coelom 補充 Early stage of development of the allantois Science 2000 in a four-day-oldLifechick embryo. 18 補充 Embryo of placental mammal. Life Science 2000 19 Science 2000 Fig. 16-4a A comparison of Life the development of three vertebrates. 20 Frog Chick Human Science 2000 Fig. 16-4a A comparison of Life the development of three vertebrates. 21 補充 various vertebrates embryos at the organogenesis stage of development illustrating similarity of gross structure. Life Science 2000 22 Fig. 16-2 Lens induction in the vertebrate eye. Life Science 2000 23 Fig. Schematic of the Saunders-Zwilling hypothesis for the mutual interactions of the apical extodermal ridge (AER) and mesoderm. The AER stimulates mesodermal outgrowth, while an apical ecotodermal maintenance factor (AEMF) from mesoderm promotes the health and well being of the AER. The zone of polarizing activity Life Science 2000 24 (ZPA) may influence anterior-posterior determination. Fig. Experimental procedures (a, b) and results (a', b') of grafting additional putative zones of polarizing activity (ZPA) to different sites on25 Life Science 2000 Fig. In the normal limb (A), the zone of polarizing activity is presumed to be the source of morphogen, which would theoretically diffuse across Science 2000 26 the limb to form a concetration Life curve, as seen in B. Life Science 2000 27 Human development Life Science 2000 28 ← At the beginning of the 2nd week, the embryo has developed extensive membranes that lie in close contact with the mother's tissues. → Well into the 3rd week, the chorionic membrane has continued to penetrate the mother's endometrium. The balloonlike structure The embryo at the 4th week↑. The dark lies protected in its amniotic sac. The dark eye is is the yolk sac. prominent and the enormous brain lies trucked Science 2000 against theLifeembryonic heart. 29 ↑The human embryo is shown at 42 days with the surrounding membrane removed . It is about 16 mm long. Life Science 2000 30 At 6 weeks, with the amnion removed, the fingers are apparent and the bulbous brain still dominates the embryo. Notice the tail trucked under the abdomen. The tiny pit above the arm will become the ear. Life Science 2000 31 At about 7 weeks, the embryo afloat in its amniotic fluid, is clearly anchored to its placenta by the twisted umbilical cord through which great blood vessels pass. The abdomen is swollen due to the rapid growth of the liver, the main bloodforming organ at this time. Life Science 2000 32 The 8-week embryo is shown here is front view. The organs are now more or less complete. The skeletal system is among the last to form, but bones are now evident in the arms and legs. Life Science 2000 33 At 9 week lids have begun to grow down over the eyes, and the outer ear begins to from. The fetus may begin to move, wave its arms and legs, and may even suck its thumb. It is now beginning to fill its amniotic space and will assume the typical upsidedown fetal posture. Life Science 2000 34 At 10 weeks the skeleton is well along in its development. Life Science 2000 35 At 14 weeks the fetus is e fist-sized. Ribs and blood vessels are visible through the translucent skin. The vigorous movements of the fetus can now be felt by the mother. Refinements such as fingerprints and fingernails have not yet developed. Life Science 2000 36 By the end of 5 months the fetus is covered with fine-downy hair and its head may have already started to grow its own crop. The heart is beating now at a rate of Life Science 2000 120 to 160 times per minute. 37 Fig. 16-9 The development of the human embryo showing relative size at different ages. Note that at 4 weeks, every few features are clearly distinguishable. The major organs have begun to form. The embryo at this time is strangely vulnerable to a variety of dangers from drugs to radiation. Life Science 2000 38 Would you give a cigarette to your unborn child? You do every time you smoke! Life Science 2000 Fig. 16-11 A plea from a concerned 39 citizen. Essay 16.1 Can humans regenerate missing parts? 這隻手曾被鱷魚咬斷,再重新接 回來,並用這些裝置固定住。 幾年前,有位年青的男孩,不小 心切斷小手指頭。於醫院,通常 會將斷掉的部份,再重新接回來。 但由於醫療人員的疏失,包紮後, 忘了進行接縫的手術。過了幾天, 當這個疏失被發覺後,醫生急忙 來看情況。令他們吃驚的是,這 個手指有自行再生回來的趨勢。 目前,對小孩而言,醫院普遍採 用此再生的方法來處理相同的案 例。 Life Science 2000 40 Essay 16.2 Wound healing. Flesh wounds are dangerous. The protective covering around the body has been broken, leaving an opportunity for invasion, by dangerous organisms. The body acts quickly by first sealing blood vessels in a process called clotting (凝血). Platelets (血小板) rush to the site, where they interact with a blood protein called fibrinogen to form the clot. Some of the platelets releasing a substance called serotonin, which constricts the blood vessels in the area. Once the blood flow has stopped, the body begins to respond to other chemicals (pyrogens) that have been released in response to the trauma. 這可以促進地區的 血液循環,引入更多的白血球。 Life Science 2000 41 An ethical concern • 試管嬰兒,抽取夫妻的精子和卵子進行 體外受精。 • Some couples found out that the eggs and sperm used were not theirs at all. • Would you want to know if your baby bore your genes? • What would you do if the baby didn't? • Would your feelings for the baby change? Life Science 2000 42 問題與討論 請提出問題! Life Science 2000 43