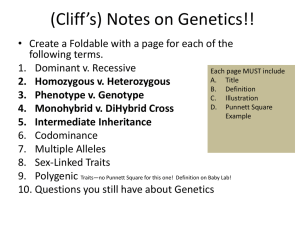
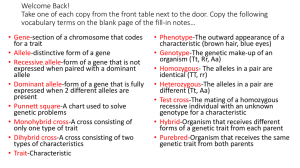
Human Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Trait
advertisement

Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Goal Determine if the dominant trait is the most prevalent trait •What is a trait? •What is a dominant trait? •What does it mean to be most prevalent? Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education What is a trait? • Genetically determined characteristic • What does ‘genetically determined’ mean? • Whatever was passed on to you from your parents • This determines how you will look. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education What is a trait? • More specifically, it is all the instructions your parents gave you so that you could actually make yourself! • Your Mom gives you ½ of the instructions, your Dad gives you the other ½. • How can you tell? Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education What is a trait? • “Your Mom gives you ½ of the instructions, your Dad gives you the other ½.” • In science jargon: Your Mom gives you one allele of that gene and your Dad gives you one allele of that gene and you put them together to make a chromosome. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Where does this happen? • The DNA or genes in the nucleus of the cell contains the building instructions • Those instructions are copied and carried outside the nucleus where they will act Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education • What instructions or genes you have from your parents are said to be your genotype • What people see on the outside is your phenotype • So your genotype determines your phenotype! Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education What are dominant traits? • When alleles get together, some alleles are “stronger” than other alleles. • We call these alleles dominant and then the trait that they express the dominant trait. • Both parents might give you instructions on how your ear lobes will look, but some looks are dominant (stronger) than others • Let’s try a simulation… Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Ear lobes • Free earlobes (dominant trait) hang below the point of attachment to the head. • Attached ear lobes (recessive trait) are attached directly to the side of the head. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Prevalent • The trait that we see mostly when we look around at people is the prevalent trait. • If more people have attached ear lobes then that is the most prevalent. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education The physical characteristics below are common genetic traits inherited from one generation to the next: Free vs. Attached Earlobes Straight vs. Curved Thumbs Bent vs. Straight Pinky With vs. Without White Forelock Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Thumbs • Straight thumbs (dominant trait) can be seen as nearly a straight line and may contain a slight arch when viewed from the side as in the illustrations. • Curved thumbs (recessive trait) can be seen as part of a circle. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Pinky Bent pinky (dominant trait) vs. Straight pinky (recessive trait): 1. Hold your hands together as if you are covering your face. 2. If the tips of the pinkies (or baby fingers) point away from one another, the pinkies are bent (recessive trait). Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education Forelock • A White Forelock (dominant trait) is a patch of white hair, usually located at the hairline just above the forehead. The photo to the left clearly shows an exaggerated white forelock. • No White Forelock is the recessive trait. Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education • For a given trait, which expression (dominant or recessive) would you expect to be most prevalent? • Is that true? • How can we really be sure? Copyright © 2007 Stevens Institute of Technology Center for Innovation in Engineering and Science Education