Cardiovascular System - Fort Thomas Independent Schools

Cardiovascular System
Health
Mrs. Wagner
Cardiovascular System
• Pathway through which blood can carry materials throughout the body (NC)
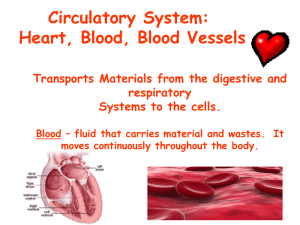
• Blood
- Brings oxygen, nutrients and other necessary materials to your body cells
- Carries waste products away
- regulates body temperature and water balance
Heart
• Muscular organ that pumps blood throughout your body (NC)
• Size of your fist
• Located near middle of chest
• Each minute – pumps 5qts. of blood through blood vessels
Structure of Heart
• Septum – thick wall that separates the left and right side (NC)
• Each side has 2 chambers
1. Atrium – receives blood entering heart (NC)
2. Ventricle – chamber that pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body (NC)
- blood flows from each atrium into ventricles
• Right Side
• Left Side
Blood to lungs
Rest of body
Circulation
• Pulmonary Circulation – pathway that blood follows from the heart to the lungs (NC)
• Systemic Circulation – route that blood travels from the heart to most of the body and then back to the heart (NC)
Right Side of Heart
• Blood from most of the body flows into
• Contains carbon dioxide – little oxygen
• Passes from right atrium into right ventricle pumps into lungs passes through lungs gains oxygen CO2 leaves blood passes into the air in lungs
From Lungs
• Oxygen rich blood returns to left side from lung
• Left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points of the body
• Oxygen passes from the blood to body tissues and CO2 moves from tissues to the blood
• Oxygen poor blood then returns to the right side of the heart
Blood Vessels
• Arteries – thick walled, elastic vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart (pulmonary circulation) (NC)
• Aorta – largest artery in the body (Systemic circulation ) (NC)
* Blood leaves the left ventricle through aorta branches into many smaller arteries brain, stomach, kidney, bones, muscles, etc.
• Coronary Arteries – carry blood to the heart muscles ( NC)
• Arterioles – smaller blood vessels that form in an organ or a tissue (NC)
• Capillaries – smallest blood vessels in your body – pass through single file (NC)
• Venules – small blood vessels that join together to form veins (NC)
• Veins – large, thin walled elastic vessels that carry blood TO THE heart – valves prevent from flowing backwards (NC)
Blood Pressure
• Force with which blood pushes against the walls of the blood vessels (NC)
- varies depending on activity
- average – teens – 120/80
• Systolic Pressure – force caused by the surge of blood that moves as a result of the contraction of the ventricles ( first & highest number (NC)
• Diastolic Pressure – force recorded when the ventricles are relaxed (NC)
Heartbeat
• Pacemaker – group of cells that help regulate the rate at which the heart beats and contracts ( NC)
• Artificial are added