dynamicppt_genetics
advertisement

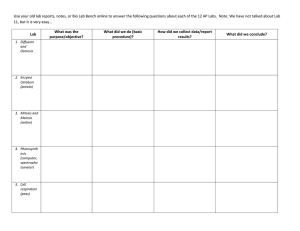
Introductory Psychology Concepts Genetics Instructor name Class Title, Term/Semester, Year Institution © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Chromosomal Abnormalities, a few examples: Down Syndrome: A cause of mental retardation resulting from the presence of an extra chromosome. Klinefelter’s Syndrome, or XXY syndrome: Males inherit an extra X chromosome. Associated with taller than average stature and impaired language skills. Turner Syndrome: Females have a missing X chromosome resulting in short stature and impaired spatial intelligence. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Genetics: Dominant If a gene in the pair received by mother and father is dominant, the characteristic that it controls will be displayed. Recessive If a gene received from one parent is recessive, the characteristic will not show up unless the partner gene from the other parent is also recessive. Polygenic Effects When a number of gene pairs combine their influences to create a single phenotypic trait, this is known as polygenic transmission. Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Behavior Genetics Heredity The transfer of characteristics from parent to offspring through their genes. Interaction of Nature Considering an individual’s innate qualities (nature) in determining individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. Nurture Considering environmental causes and personal experiences in the determination of physical and behavioral traits. Includes the influence of parents, siblings, family, friends, schooling, nutrition, and all other experiences to which a child is exposed Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Twin Studies Understanding behavior based on the amount of shared genetic material Two kinds of twins. Identical (monozygotic) twins come from a single egg and sperm as a result of a division of the zygote. They have all of their genes in common. Sperm Egg One sperm and one egg Zygote divides Two zygotes with identical chromosomes Identical twins (1 in 250 births) Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Twin Studies Understanding behavior based on the the amount of shared genetic material Two kinds of twins. Fraternal (dizygotic) twins result from two eggs fertilized by two sperm. They share only half of their genes. Two eggs and two sperm Two zygotes with different chromosomes Fraternal twins (1 in 150 births) Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Genetics Heritability: Estimating the impact of genetic influence Heritability Estimates for Various Human Characteristics Trait Heritability Estimate Height Weight Intelligence School Achievement .80 .60 .70 .40 Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Genetics Heritability: Estimating the impact of genetic influence Heritability Estimates for Various Human Characteristics Personality Extraversion Conscientiousness Agreeableness Neuroticism Heritability Estimate .36 .28 .28 .31 Introductory Psychology Concepts: Genetics Genetics Heritability: Estimating the impact of genetic influence Heritability Estimates for Various Human Characteristics Temperament Emotional reactivity Activity level Sociability Impulsivity Heritability Estimate .40 .25 .25 .45