Unit 8
advertisement

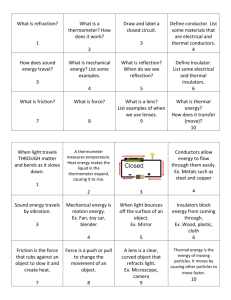
Unit 8: Heat and Heat Transfer 1. Temperature is the measure_____ of the _average___ kinetic___ energy_______ of the particles in an object a. If 2 substances have the same temperature, then they have the same _average kinetic energy_. b. Temperature is determined by how _fast____ the atoms or molecules of a substance are __moving______. c. How do we measure temperature? i. ____Fahrenheit________--based on the freezing and boiling points of water. 1. 32 °F= freezing point 2. 212 °F=boiling point ii. ___Celsius____________-- also based on the freezing and boiling points of water. This is what is used in the metric system, so this is the temperature scale they use in Canada, Europe, Asia. 1. 0 °C=freezing point 2. 100 °C=boiling point iii. _Kelvin_____________--the SI scale for temperature, based on ______________ ________. 1. 0 K= absolute zero (no _kinetic energy_____) 2. 273 K= freezing point of water 3. 373 K= boiling point of water 2. Thermometers work by using _thermal expansion____-- the increase in volume of a substance due to an increase in temperature. a. Examples of thermal expansion: 3. Thermal energy is the _total_ amount of kinetic energy. a. It is different than temperature because it depends on the _mass___ of the object. b. Which has more thermal energy? A mountain or a hill? Why? Mountain it has more masss c. Which has more thermal energy? Hot chocolate or the Atlantic Ocean? Why? 4. Heat Transfer-- ____3___ types a. Radiation—the transfer of energy through _matter___ or __space_____ as ___electromagnetic______ __waves_____. i. Examples: b. Conduction—the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another through __direct____ contact____. i. Examples: 1. Conductors—materials that _easily____ transfer thermal energy. a. Examples of good conductors: b. Examples of bad conductors: 2. Insulators—materials that _resists____ the transfer of thermal energy. a. Examples of good insulators: c. Convection—the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a __liquid____ or a __gas__. i. Examples: