Grade 3 Structures of Life Unit 1 class notes
advertisement

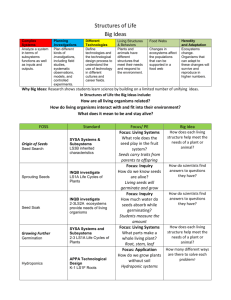
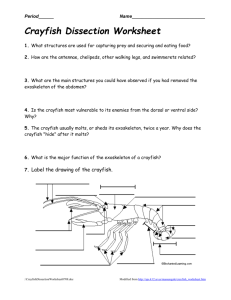
F.Q. Where do seeds come from? Where are seeds found on plants? Can a seed grow without soil? What effect does water have on seeds? How much water can a seed soak up? 1.Seeds develop in the part of the plant called a fruit. Seeds hold food for the plant. Seeds are alive, but dormant (resting and inactive stage). 2.Different kinds of seeds have different kinds and number of seeds. Seeds have a variety of property: shape, size, texture, color etc. 3.Seeds undergo changes when water is added to them, they become bigger and heavier. They also begin to grow and develop when placed in water. 4.A seed is an organism, a living thing. A seed contains the embryo (baby plant that has tiny leaves and roots), and stored food and water (cotyledon) for the plant. The seed coat is the layer covering the seed. 5.Mold is the slimy or cotton like growth that develops on moist material. 6.A fruit is the structure of a flowering plant where the seeds are found. F.Q. What effect does water have on the seeds in the minisprouter? How do the plants change over time? How can we grow plants without soil? What conditions do plants need in order to grow? What is the sequence of the bean plant's life cycle? 1.When a seed begins to develop or grow, after it is dormant (at rest), it is called germination. 2.Growth is when an organism gets bigger and more complex. 3.All living things are organism, including plants and animals. 4.Plants need water, light, and nutrients. Plants need soil for support, and nutrients. Support and nutrients can be provided in other ways, like through hydroponics (growing plants in water and nutrients). 5.Nutrients are essential (important) chemicals healthy plants need. F.Q. What are the structures of a crayfish? What do we need to think about in order to build a suitable habitat for the crayfish in the classroom? What do the crayfish do when something happens to them? Does each crayfish have its own house that it always goes to? How can we keep track of crayfish movements over many days? 1.Crayfish have different structures (body parts) that we can observe. 2.Crayfish have particular requirements for life, including clean, cool water; food; and shelter. 3.Habitat is where an animal lives. Behavior is what an animal does. 4.A territory is the part of an animal's habitat that it defends against others of its own kind. Some animals claim a territory that they protect from other animals. 5.Crustaceans are a class of mostly aquatic animals that have hard, flexible shells, jointed legs, and two pairs of antennae. 6.Elodea is a kind of aquatic plant that crayfish eat. 7.Molting is when an animal shed its skin as it grows when its hard shell becomes too small for its body. Crayfish are soft and its shell will feel rubbery during molting, which can be dangerous if it is attacked. F.Q. What structures do land snails have? What does a snail need in its habitat? What functions (jobs) do land snail's structures (body parts) serve? How are the structures of the land snail and crayfish alike and how are they different? 1.Land snails have a coiled shell, a large foot on which they glide, and a body with a variety of structures. 2.Land snails need water, vegetables or fruit, air and space to survive. 3.An organism's structures have functions (jobs) that help it survive in its habitat. 4.The structures found on different kinds of organisms can show similarities and differences. F.Q. What structures do bess beetles have? What does a bess beetle need in its habitat? How are the structures of the beetle and crayfish alike and how do they differ? 1.Bess beetles are insects. They have six legs, three body parts, two antennae, two jaws, and a horn. 2.Bess beetles need water, food (wood), space, and air in their habitat. 3.Organisms have some similar structures and some differences. 4.An organism's structures (body parts) have functions (jobs) that help it survive (stay alive) in its habitat (home).