Thermochemistry (Chapter 17) and States of Matter
advertisement

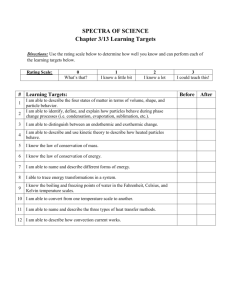
Thermochemistry (Chapter 17) and States of Matter (Chapter 13) At this point in time, I could… Learning Targets Link to Textbook NOT partially completely & accurately …answer the question/do the task! 1. Describe the role of energy in chemical and physical processes. Sections 3.2, 13.1, 17.1 & 17.2 1. What is the difference between heat and temperature? (be able to address definitions, instruments used, and appropriate SI units) Read pp 77-79, 388, 505, 507 2. What is the definition of the following terms associated with energy and chemical reactions: thermochemistry, system, surroundings, exothermic, endothermic? What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic processes? (address energy absorbed or emitted, where heat appears in a written equation, the sign of H, the overall shape and components of an energy diagram) Read pp 505-507 Do PP 1& 2 on p. 507 3. 2. Calculate the heat involved in a chemical reaction. a) b) c) d) What is the formula for calculating the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction and identify each component (m, T, C)? Given data, calculate the heat evolved from a burning candle (or other substance) and transferred to water in a calorimeter (H=mTc); Given data about the heat source, calculate heat per gram (J/g) Given data – and specific heat capacity values – calculate the heat transferred to or from a substance other than water (H=mTC) 3. Describe the 5 states of matter on an observable and particle level. a) b) c) How are the three primary states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) similar and different in terms of their physical characteristics and what is happening on a particle level? How does kinetic theory describe what is happening on a particle level in each of the primary states of matter (motion of particles)? b) c) d) e) Sections 17.1 & 17.2 Read pp 507-509 Read pp 507-513 And PP 12 & 13 on p. 513 Read pp 507-513 Do PP 3 & 4 on p. 510 Sections 13.1, 13.4, 17.3 For gases Read pp. 385-389 For liquids Read pp.390-393 For solids Read pp. 396 What are plasma and Bose-Einstein condensates? 4. 4. Describe the role that energy plays in phase changes. a) Read pp. 506 and 514516 What are the terms associated with specific phase changes? (evaporation, boiling, condensation, melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition) How is energy involved in phase changes? What happens to the motion of molecules as energy is added –or removed – from a system? What information can be obtained from a phase diagram? (i.e. triple point) What happens to the temperature of a substance (like ice) as it is heated? (What would a graph of this process look like? Why does the graph have flat regions? Given data (heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, mass of substance undergoing phase change), calculate the heat involved in a phase change. Date of Self-Assessments Sections 13.1, 13.2, 13.3, 13.4, 17.3 For evaporation & boiling Read pp. 391-394 For sublimation, Read pp. 401-403 Read pp. 402-403 Read pp. 520-524 See graph on p. 523 Read pp. 520-524 Do PP 21 & 22 on p. 521 Do PP 23 & 24 on p. 524 Check 1: __________ Check 2: __________ Check 3: _________ Check 4: _________ Thermochemistry (Chapter 17) and States of Matter (Chapter 13) At this point in time, I could… Learning Targets Link to Textbook NOT partially completely & accurately …answer the question/do the task! 1. Describe the role of energy in chemical and physical processes. a) What is the difference between heat and temperature? (be able to address definitions, instruments used, and appropriate SI units) b) c) What is the definition of the following terms associated with energy and chemical reactions: thermochemistry, system, surroundings, exothermic, endothermic? What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic processes? (address energy absorbed or emitted, where heat appears in a written equation, the sign of H, the overall shape and components of an energy diagram) 2. Calculate the heat involved in a chemical reaction. a) b) c) d) What is the formula for calculating the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction and identify each component (m, T, C)? Given data, calculate the heat evolved from a burning candle (or other substance) and transferred to water in a calorimeter (H=mTc); Given data about the heat source, calculate heat per gram (J/g) Given data – and specific heat capacity values – calculate the heat transferred to or from a substance other than water (H=mTC) 3. Describe the 5 states of matter on an observable and particle level. a) b) c) How are the three primary states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) similar and different in terms of their physical characteristics and what is happening on a particle level? How does kinetic theory describe what is happening on a particle level in each of the primary states of matter (motion of particles)? b) c) d) e) Read pp 77-79, 388, 505, 507 Read pp 505-507 Do PP 1& 2 on p. 507 Read pp. 506 and 514516 Sections 17.1 & 17.2 Read pp 507-509 Read pp 507-513 And PP 12 & 13 on p. 513 Read pp 507-513 Do PP 3 & 4 on p. 510 Sections 13.1, 13.4, 17.3 For gases Read pp. 385-389 For liquids Read pp.390-393 For solids Read pp. 396 What are plasma and Bose-Einstein condensates? 3. 4. Describe the role that energy plays in phase changes. a) Sections 3.2, 13.1, 17.1 & 17.2 What are the terms associated with specific phase changes? (evaporation, boiling, condensation, melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition) How is energy involved in phase changes? What happens to the motion of molecules as energy is added –or removed – from a system? What information can be obtained from a phase diagram? (i.e. triple point) What happens to the temperature of a substance (like ice) as it is heated? (What would a graph of this process look like? Why does the graph have flat regions? Given data (heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, mass of substance undergoing phase change), calculate the heat involved in a phase change. Date of Self-Assessments Sections 13.1, 13.2, 13.3, 13.4, 17.3 For evaporation & boiling Read pp. 391-394 For sublimation, Read pp. 401-403 Read pp. 402-403 Read pp. 520-524 See graph on p. 523 Read pp. 520-524 Do PP 21 & 22 on p. 521 Do PP 23 & 24 on p. 524 Check 1: __________ Check 2: __________ Check 3: _________ Check 4: _________