The Gilded Age and Progressive Era
advertisement
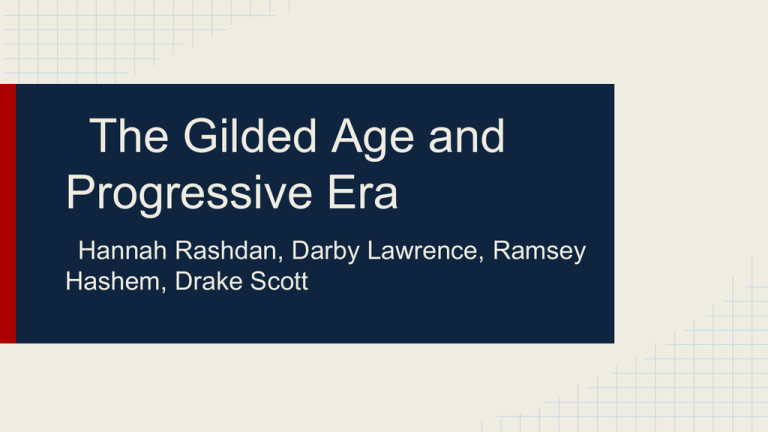
The Gilded Age and Progressive Era Hannah Rashdan, Darby Lawrence, Ramsey Hashem, Drake Scott “It is a time when one's spirit is subdued and sad, one knows not why; when the past seems a storm-swept desolation, life a vanity and a burden, and the future but a way to death.” -Mark Twain, 1873 The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • Ulysses S. Grant 1869-1877 18th President Republican Former Civil War commander for the Union War Heroics made him popular The Railroad takes hold • Transcontinental railroad commences building in 1865 o The Union Pacific Railroad began building in 1865 westward from Omaha, Nebraska when Indians protested, they were killed or pushed out of land many people lost lives from working on the rails o The Central Pacific Railroad eastward from Sacramento to Sierra, Nevada Many Chinese laborers worked relentlessly and lost their lives on the rails with minimalistic pay o The Northern Pacific Railroad New Orleans to San Francisco The Railroad takes hold • Cornelius Vanderbilt o Welded together and expanded the older eastern networks o offered superior railway service at lower rates amassed a fortune of $100 million o Popularized the steel rail replaced the old iron tracks of the New York Central with tougher metal safer and more economical The Railroad takes hold Benefits Stimulated growth of other industries (steel, iron, coal, lumber, glass) Helped cities grow Helped increase westward expansion of America Standard time zones were created to get everyone on correct time Welded the West Coast more firmly to the union Facilitated a flourishing trade with Asia Corruption Exercised more direct control over the lifes of more people than did the president Absolute disregard for the public interest Bribed judges and legislatures for their own benefits Charged much higher rates to western farmers Credit Mobilier Scandal 1868 o Union Pacific o Bribed members of Congress Represented corruption of period • • • • • • • • • • • • The Railroad takes hold Effects on the American lifestyle For the first time, a sprawling nation became united in a physical sense Created and enormous domestic market for American raw materials and manufactured goods o beckoned to foreign and domestic investors Spurred the amazing industrialization of the post- Civil War years o opened up fresh markets for manufactured goods and sped raw materials to factories Stimulated mining and agriculture, especially in the West Played a leading role in the great cityward movement of the last decades of the 1800s The maker of millionaires o a raw new aristocracy replaced the old southern “lords of the lash” • • • • • • Corruption leads to depression • • Credit mobilier scandal (1872) o the Union Pacific Railroad formed the Credit mobilier construction company and hired themselves at inflated prices o distributed shares to key congressmen o hurt President Grant because of his association with it Panic of 1873: o Overreaching promoters created too many businesses that the existing markets could bear o Bankers made too many imprudent loans to finance Monopolists Emerge • John D Rockefeller: o Founded the Standard Oil Co. 1870 o gained a monopoly in the oil industry by buying rival refineries and developing companies for distributing and marketing its products around the globe o had little mercy for competitors used whatever means necessary to beat competition o Used trusts Monopolists Emerge • Andrew Carnegie: o Founded the Carnegie Steel Company as steel became crucial in the developing technologies (Railroads, factories, etc) o Monopolized the steel industry o Carnegie built plants around the country,using technology and methods that made manufacturing steel easier,faster and more productive o later became a philanthropist and donated much of his money to museums and libraries Monopolists Emerge • JP Morgan: o an American financier, banker, philanthropist and art collector who dominated corporate finance and industrial consolidation o 1892 Morgan arranged the merger of Edison General Electric and Thomson-Houston Electric Company to form General Electric. After financing the creation of the Federal Steel Company, he merged in 1901 with the Carnegie Steel Company Monopolists Emerge • Vertical Integration o A process in which a company combines all phases of manufacturing into one organization. (Ex. coal and iron mines, ore freighters, rr lines) • o Pioneered by Andrew Carnegie Horizontal Consolidation o A process in which a company buys out or merges with all competing companies (JP Morgan bought out Carnegie steel and other companies) Monopolists Emerge • Trusts o A group of separate companies placed under the control of a single managing board • Critics called these practices unfair and the business leaders “Robber Barons” The Era of Good Stealings • • Black Friday (September 24, 1869) o Two corrupt industrialists, Fisk and Gould, bid the price of gold skyward until businesspeople became bankrupt o Grant worked with the two "Boss" Tweed o Used bribery, graft, and fraudulent elections to earn money and power The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • • Rutherford B. Hayes 1877-1881 19th President Republican Ended reconstruction in the first year of office by withdrawing federal troops from the South Marked the beginning of the Gilded Age Labor Unions • • • The purpose of a labor union was “strength in numbers.” Attempted to gain better working conditions and pay individual workers were powerless to battle single-handedly against giant industries mostly by laborers and NOT the middle class o the middle class grew deaf to the outcry of the worker as they got annoyed Labor Unions • The National Labor Union (1866) o included skilled, unskilled, and farmers o excluded Chinese and nominal effort to include women and blacks o won 8 hour workday for government workers Colored National Labor Union o organized by black workers Racism prevented unions from working together • • The Knights of Labor (1869) o Was the first union to accept workers of all races and gender, skilled and unskilled workers o Campaigned for economic and social reform o Pushed for 8 hour workday, equal pay for women Haymarket Square (1886) Chicago police kill/injur several dozen strikers The Knights of Labor began to be associated with anarchists Labor Unions • • The American Federation of Labor (1886) o lead by Samuel Gompers o composed of skilled craftsmen By 1900 attitudes toward labor began to change o the public began to concede the right of workers to organize, to bargain collectively, and to strike Labor Strikes The Great Strike (1877) in 1873, companies had reduced the pay of railroad workers by ten percent. In 1877 they announced another ten percent reduction in the workers' pay, and also that railroad employees would be required to use company hotels when away from home, which meant a further reduction in real wages. On top of this, they decided to reduce the work-force - which meant unemployment for some and intensified labor for those remaining. • • The Haymarket Riot (1886) Knights of Labor strike in support of the eight-hour day at McCormick Reaper Manufacturing Company it was assumed that an anarchist threw the bomb and raids were conducted on all known radical groups, including trade union leaders- sentenced to execution • • Labor Strikes Homestead Strike (1892) 5,000 steelworkers struck Andrew Carnegie's steel plant near Pittsburg PA. A pitched battle erupted between the strikers and Pinkertons hired by plant manager Henry Clay Frick who had been hired to protect the strikebreakers. 7,000 state troopers were sent in by Governor Pattison; the steel mill was reopened by strikebreakers • • • Pullman Strike (1894) Eugene Debs , leader of the American Railway Union , led the strike by refusing to handle railroads using Pullman cars, encouraging other unions to join. The strike was ended by a court injunction, based on the Sherman Anti-Trust Act, after which President Cleveland sent in 10,000 federal troops (because of "interference" with the US mail), who along with 2,000 state troops smashed the ARU • • Labor Strikes & the Supreme Court Major supreme court decision: In re Debs (1895) o Debs’ writ of habeas corpus to the Supreme Court was denied on the basis of a broad interpretation of the commerce clause and the federal government’s obligation to deliver the mail • The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • James Garfield March 1881-September 1881 20th President Republican Assassinated after less than 4 months American lifestyles • America move to the city o cities grew up and out-skyscrapers o Americans were becoming commuters- needed transportation to and fro work o Americans created a huge mass of waste o Criminals flourish o cities represented “the best and the worst combined” o Sums: filthy, especially after the perfection of the “dumbbell” tenement architectural plan that minimized the amount of air and light o those in cities generally live together by ethnicity • American lifestyle Women • • • • group most profoundly affected by new industrial age worked “women jobs”; began working into industry by recent inventions o typewriter, telephone switchboard o earned less than men working for middle-class women meant delayed marriages and smaller families o most women worked because of economic necessity Accentuated class divisions Lifestyles in the Factories • • • The concept of time was revolutionized as now people follow the works hours, not the clock of nature long, hard, arduous hours many died from the terrible conditions of the factories The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • • Chester A. Arthur 1881-1885 21st President Republican Took office after Garfield’s assassination Pushed for intervention in Latin America Civil Service Reform Hurts • Pendleton Act of 1883: o "the Magna Carta of civil service reform" o made compulsory campaign contributions from federal employees illegal o Established the Civil Service Commission Make appointments to federal jobs on basis of competitive exams This hurt because: A new breed of "boss" emerged, although less skilled Drove politicians into "marriages" with big businesses, instead of temporary contracts • • Old Immigrants • • Immigrants before 1880 Mainly from the British Isles and Western Europe (Germany, scandinavia, etc) o Fair skinned, anglo saxon o protestant o high literacy o fit easily into representative government because of their previous governments New Immigrants • Immigrants after 1880 o Mainly from southern and eastern Europe o orthodox/Jewish; faced religious persecution o previous country of origin had little history of a democracy • • Italians, Croats, Slovaks, Greeks, Poles people had lived in despotism o illiterate o moved mainly to cities o high birth rate; brought culture with them “America fever” captures Europe o the population of the old world increased exponentially with the introduction of the potato. o America was seen as the land of opprotunity and freedom for religion savage persecution of Jews in Europe Once in the United States, many immigrants lived and worked in the most strenuous jobs o especially in “sweatshops” New Immigrants Chinese Major influx of chinese immigrants, esp from 1870-1880 Viewed as cheap, efficient and expendable labor Lived in very inclusive communities, faced a lot of racism • • • • Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882: o prohibit further chinese immigrants o represents the racism the Americans viewed Chinese with and the growing fear of immigrants New Immigrants Italians Huge influx from 1880-1920 Came from the more poorer areas of Italy and intended to bring money back to Italy from America (half of them did) clustered in tight knit communities mainly Industrial laborers o remained in blue collar jobs • • • • Immigrant-phobia Nativism: (“Know-Nothings” revived) Became exceptionally profound in the 1880s Viewed the new immigrants as religiously exotic hordes and gave them rude receptions o seen as “inferior”- racism a major player Blamed immigrants for the degradation of urban government Created the American Protective Association 1887 (APA)- urged voting against roman catholic candidates Congress passes first restrictions against inpouring immigrants o 1882, prevented paupers, criminals, and convicts from entering o expanded later to include the “undesirables” (prostitutes, polygamists, alcoholics, etc) • • • • • The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • • Grover Cleveland 1885-1889 22nd President Democrat Stood for hard work and civil service Opposed high tariffs and free silver Railroads influence • • • President Cleaveland in 1887 allowed for land grants to the railroads o Huge criticism as it was seen as “giveaway” of a birthright to greed corporations o government received big benefits long term preferntial rates for postal service and military traffic granting land was a “cheap” way to subsidize a transportation system (avoided new taxes for direct cash grants) Americans were initially slow to combat the economic injustice o dedicated to free enterprise and the principle that competition is the soul of trade, they cherished the tradition o “American Dream”- anyone can become a millionaire Depression of 1870s force farmers to protest against railroads Railroads influence Stopping the railroad corruption: Major supreme court decision: Wabash Case (1886) o The decision of the Illinois Court was reversed and the decreed that individual states had no power to regulate interstate commerce act- only the federal government can regulate lead to the passage of the Interstate Commerce Act prohibited rebates and pools and required the railroads to publish their rates openly forbade unfair discrimination against shippers set up the Interstate Commerce Commission o made to administer and enforce this new legislation ***First large-scale attempt by Washington to regulate business in the interest of society at large*** • • • • • Prevailing ideologies • • Many during this time believed in the “survival-of-the-fittest” theories of Charles Darwin o this concluded that “millionaires are a product of natural selection” invoked contempt for the poor, hence those who stayed poor must be lazy and lacking in enterprise The Gospel of Wealth o written by Andrew Carnegie in 1889 o he stated that the wealthy, entrusted with society’s riches, had to prove themselves morally responsible The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • • Benjamin Harrison 1889-1893 23rd President Grandson of William Henry Harrison Republican President during first billion dollar congress Graft Continues • The Billion Dollar Congress: o Lead by Thomas Reed, HOR speaker o Passed the McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent, an act designed to protect domestic industries from foreign competition helped big industrialists, not the people Attempts to stop monopoly • Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890 o Law outlawing a combination of companies that restrained interstate trade or commerce; important to prevent monopolies; forbade trusts o Did not make any distinction between “good” trusts and “bad” trusts bigness not badness, was the sin o Not initially enforced properly. o Proved highly ineffective too many legal loopholes and no “teeth” Major supreme court decision US v. EC Knight Co. (1895) • o The E.C. Knight Company was a combination controlling over 98 percent of the sugar-refining business o The court found the Sherman Anti trust act constitutional but said it did not apply to manufacturing. o The effect of this decision was to seriously impair enforcement of the anti-trust laws and put most monopolies beyond the reach of federal control. The Forgettable Presidents • • • • • • • • Grover Cleveland (again!) 1893-1897 24th President Democrat Only president to serve two non-consecutive terms Very Noble and Honest Intervened with Pullman Strike to keep railroads moving Hawaii Issues • • • • • • • Many farmers from the United States moved to Hawaii to plant sugar January 17, 1893- US sugar planters revolt, overthrow Queen Liliuokalani in coup d’etat, led by Sanford Dole At the time, US had Pearl Harbor Naval Base, also had high sugar imports from Hawaii Grover Cleveland sent a US minister to Hawaii to restore the Queen under Hawaii’s 1887 constitution but Dole refused to give up seat William McKinley negotiated a treaty with Republic of Hawaii in 1897 Pearl Harbor played a big part in the Spanish American War Hawaii was annexed in 1898, Hawaiians got US citizenship The Gilded Age Presidents • • • • • • • • • William McKinley 1897-1901 25th President Republican Ensured Gold Standard President during Spanish-American War Assassinated, Teddy Roosevelt took over Death marked end of the Gilded Age The Spanish- American War ● Started in Cuban struggle for independence in Spain, 1895 ● Yellow Journalism played a big role in generating US sympathy for Cuban rebels ● Maine Explosion on Feb 15, 1898- US suspected Spain of doing it, caused tension ● US demanded Cuba’s independence, withdrawal of Spain and US wasn’t interested in annexation ● Spain declared war on April 24, US declared war on 25th ● George Dewey led US navy into Manila Bay in Philippines, destroyed Spanish fleet ● US “rough riders” including Teddy Roosevelt fought ● Santiago, Cuba surrendered on July 17th ● Treaty of Paris signed on December 10, 1898: Spain had no claim to Cuba, US got Guam, Puerto Rico, and Philippines all for $20 million ● Ended expansionism of Spain ● US became a world power, led to arguments over what to do with Philippines and debate over expansionism Postwar Conflicts • • • • • • • • In 1899, Aguinaldo led a Filipino rebellion against the United States 600,000 Filipinos died US broke up rebellion in 1901 US appeared to be no less oppressive than Spanish Spanish-American War: 10 weeks, 400 deaths. PhilippineAmerican War: 3 years, 4,000 Americans died A lot of anti-imperialist views, US was meant to be freeing Cuba, not controlling it General public supported McKinley’s expansionism though Platt Amendment in 1901- US troops out of Cuba by 1902 Boxer Rebellion • ● ● ● ● China was occupied by several different nations, “spheres of influence” Sec. of State John Hay suggested Open Door Policy Chinese nationalists attacked Western Occupants in China in 1900, known as the “Boxers” Rebels were subdued, China was forced to pay $330 million to the US Marked the first time US invaded without goals of getting territory The Progressive Presidents • • • • • • • • • • Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 26th President Republican Part of Rough Riders during Spanish-American War Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty in 1903- US got control of Panama Canal from Panama Roosevelt Corollary- Extended Monroe Doctrine, US would be police of Western Hemisphere, would intervene in Latin America in the event of wrongdoing Won Nobel Prize in 1906 for negotiating end to Russo-Japanese War Sent Great White Fleet around world in 1907 to show power President Roosevelt Roosevelt Corollary -Germany and Britain sent ships to blockade Venezuela - roosevelt felt that they were offensive and we needed to help defend Venezuela - made the us the police of Latin America the great white fleet -believed that a strong navy was crucial for a strong defence -convinced congress to add battleships and in 1907 he proposed sending them out and in 1909 they traveled around the world to show their power. Russo- Japanese War ● War broke out in 1904, Russia and Japan fought over Manchuria and Korea ● Teddy Roosevelt offered to mediate peace process ● Two sides met with TR at Portsmouth, NH, Treaty of Portsmouth was arranged, Manchuria returned to China ● Roosevelt got Nobel Peace Prize for efforts- first president to win it ● Russia unhappy, felt like the US robbed them of victory ● Japan felt it hadn’t been awarded enough, led to anti-US sentiment in Japan ● Caused tense relations with Japan, Japan was a new world power ● ○ Japanese immigrants faced with discrimination ○ Gentleman’s agreement of 1907- US would end separate schooling if Japan stopped immigration ○ Roosevelt sent Great White Fleet to show power ○ 1908- Root-Takahira agreement- respect between US and Japan US lost all isolationist appearances Darwinism • Charles Darwin On the Origin of Species, generated high controversy on its publication o set forth the “survival of the fittest” o cast doubt on the Bible conservatives condemned the Darwinians modernists refuse to accept the Bible in its entirety Halting Industrialists’ Powers Major Supreme Court decision: Northern Securities Company v. United States (1904) o The Supreme Court ruled that a holding company formed solely to eliminate competition between the 2 railroads was in violation of the anti-trust laws because it unreasonably restrained commerce. o The federal government now had the authority to regulate any conspiracy which sought to eliminate competition between otherwise competitive railroads. o The government’s policy of trust busting helped restore competition in the American economy Muller v. Oregon (1908) o Protective legislation limiting the hours women could work o Later became a NEGATIVE when it was used to discriminate against women in the workplace • • The Progressive Presidents • • • • • • • • William Howard Taft 1909-1913 27th President Republican Prominent Trust Buster Used Dollar Diplomacy- invest money in Latin America and East Asia to boost US political interests abroad Became Chief Justice after Presidency The Progressive Presidents • • • • • • • • Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 28th President Democrat Passed Federal Reserve Act Passed Clayton Antitrust Act President during WWI Minorities • • African-Americans faced unemployment, eviction, and physical harm when they tried to assert their rights, esp. in Democratic South Jim Crow Laws (1890's) o Systematic state-level legal codes of segregation o Enacted literacy requirements, voter registration and poll taxes Minorities Major supreme court decisions: Plessy v Ferguson (1896) o "separate but equal" was constitutional under the 14th amendment of 'equal protection' U.S. v Wong Kim Ark (1898) o Guarantee citizenship to all persons born in the U.S. o "Birthright Citizenship", specifically helped Chinese • • Platt Amendment The Platt Amendment made the conditions for the withdrawal of United States troops remaining in Cuba at the end of the Spanish-American war and defined the terms of Cuban-U.S relations. Terms of Amendment Cuba could not make a treaty with other countries Cuba had to allow the U.S the ability to lease naval stations and ports Cuba’s depts had to stay low U.S had the right to intervene and protect Cuba • • • • 16th Amendment The 16th amendment is an important amendment that allows the federal United States government to collect an income tax from all Americans.These taxes then went to being spent on the military, building roads and bridges, and enforcing our laws. 17th Amendment The 17th amendment declared that 2 U.S senators will be provided by each state by popular vote and that each senator would serve a term of 6 years. The Jungle The Jungle was written by Upton Sinclair and was published February 26, 1906. The novel portrayed the lives of immigrants in the U.S in Chicago and similar industrialized cities. The book was most known for its exposure of health violations and unsanitary practices in the American meatpacking industry. The Influence of Sea Power Upon History The Influence of Sea Power was written by Alfred Thayer Mahan and published sometime in the year of 1890. The book concentrated highly on the history of naval warfare and its role during the 17th and 18th centuries. It also discusses the factors needed to support and achieve sea power dominance with emphasis on having the largest and most powerful fleet. Yellow Journalism • • Yellow journalism or the yellow press is a type of journalism that presents little or no legitimate well-researched news and instead uses eye-catching headlines to sell more newspapers. The techniques used may include exaggerations of news events or sensationalism. The term originated during the American Gilded Age of the late nineteenth century with the circulation battles between Joseph Pulitzer's New York World and William Randolph Hearst's New York Journal. The battle peaked from 1895 to about 1898. Both papers were accused by critics of sensationalizing the news in order to drive up circulation, although the newspapers did serious reporting as well. Thomas Edison Thomas Edison was the inventor of many things during this period including the photograph and the light bulb. He invented the photograph December 6th in 1877 when he was 30 years old. The light bulb was invented October 21st in 1879. He later then worked towards making electricity available to the general public and even started his own electricity company. Telephone 29 year old Alexander Graham Bell patents the telephone February 14th in 1876. The telephone presented a way of communicating to others over thousands of miles away and the opportunity of connecting with others worldwide and a cheaper way to send messages.