Ch-14 Blood
advertisement

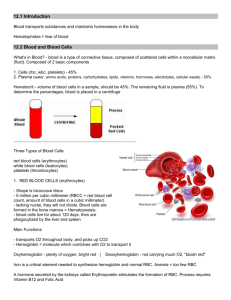
Ch-14 Blood Blood is a connective tissue formed primarily in the bone marrow. Functions: • Transport nutrients, oxygen, waste and hormones. • Distributes heat. • Promotes homeostasis. An average adult has about 5 liters of blood in the body. It accounts for 8% body weight. Blood Composition • • • • Plasma Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets 1. Plasma • Composition: 92% water, wastes, salts and proteins. Proteins: • Albumins- maintain osmotic blood pressure. • Globulins- transports lipids and fat soluble vitamins. • Fibrogens- aids in blood coagulation. 2. Platelets • Cell fragments that help with blood clotting, or thrombus. • Hemostasis- coagulation of blood. • Proteins repair the holes in the vessels. • Lack of platelets = hemophilia • Life span = 12 days Hemostasis= stoppage of blood Blood vessel spasms and contracts. 5. Blood clot forms and surface forms a scab. 3. Red Blood Cells (erythrocytes) • Carry oxygen to the lungs and tissues via hemoglobin. (O2 = scarlet red color.) • Constantly produced within red bone marrow. • Life span ~120days • Lack nuclei • Flexible to fit through capillaries. • Lack of rbc’s = anemia. 4. White Blood Cells (leukocytes) • Primary cells of the immune system that produce antibodies. • Normal count 5,000 – 10,000 (mL) • leukopenia • low WBC count • flu, measles, chicken pox, & AIDS • leukocytosis • high WBC count • acute infections, vigorous exercise, great loss of body fluids and leukemia (cancer of white blood cells.) Types of WBC’s 1. Neutrophils: (54%-62% of all leukocytes) • General phagocytosis; acute bacterial infections. • First to arrive at infections 2. Basophils: (less than 1% of leukocytes) • Cause inflammatory reactions: - release histamine (inflammation) -Heparin- natural anticoagulant to keep blood flowing. 3. Eosinophils: (1-3% of all leukocytes) • moderate allergic reactions • defend against parasitic worm infestations 4. Monocytes: (3-9% of all leukocytes) • leave bloodstream to become macrophages, which digest bacteria and dead cells. • elevated in typhoid fever, malaria, tuberculosis 5. Lymphocytes: (25-33% of all leukocytes) • Important in immunity due to T and B Cells. • Produce antibodies • Decreased T Cells in AIDS patients. Diapadesis • How leukocytes squeeze through capillary walls to leave the blood vessels and enter infected tissues. Blood Typing • Proteins called antigens coat the outside of the red blood cells. • 4 Types: A B AB O= no coating O= universal donor AB = universal recipient O+ most common blood type AB- most rare blood type Blood Typing Game Blood Typing con’t • Rh Blood Group – discovered in rhesus monkeys. - agglutinogen D protein coating = (+) - NO agglutinogen D coating = (-) - causes concern for transplants and transfusions and some pregnancies. Example: An Rh- mother pregnant with a Rh+ baby leads to miscarriage or erythroblastosis fetalis if not treated with a Rhogam serum. The end! Blood Doping Blood Doping • http://on.aol.com/vide o/the-problem-ofblood-doping517653049 Stop at nothing https://www.youtube.com /watch?v=DKscASTSN5U