Landmark Supreme Court Cases
advertisement

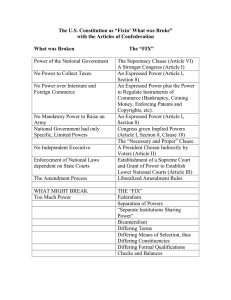
Landmark Supreme Court Cases Year 1793 1803 1819 1824 1831 1832 1841 1857 1873 1877 1895 Case Chisolm v. Georgia Marbury v. Madison McCulloch v. Maryland Gibbons v. Ogden Cherokee Nation v. Georgia Worcester v. Georgia US v. The Amistad Dred Scott v. Sanford Bradwell v. Illinois Munn v. Illinois US v. E.C. Knight Co. Ruling Holding: The Court repealed the States’ sovereign immunity and granted federal courts the power to hear disputes between private citizens and States. Chief Justice John Jay (1st Chief Justice) Holding: Established the doctrine of judicial review. Holding: The Constitution gives the federal government certain implied powers. Holding: The commerce clause of the Constitution grants the federal government the power to determine how interstate commerce is conducted. John Marshall (4th Chief Justice) Holding: The Supreme Court does not have original jurisdiction to hear a suit brought by the Cherokee Nation, which is not a "foreign State" within the meaning of Article III Holding: States have no criminal jurisdiction in Indian Country. Holding: Africans are free, are not property, kidnapped, and are ordered to be released. The President is not required to return the Africans to Spain since they had no intention of being slaves. Holding: 1. Persons of African descent cannot be, nor were ever intended to be, citizens under the U.S. Constitution. Plaintiff is without standing to file a suit. 2. The Property Clause is only applicable to lands possessed at the time of ratification. Congress cannot ban slavery in the territories. Missouri Compromise is unconstitutional. 3. Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment prohibits the federal government from freeing slaves brought into federal territories. Roger Taney (5 Chief Justice) th Holding: Illinois constitutionally denied law licenses to women, because the right to practice law was not one of the privileges and immunities guaranteed by the Fourteenth Amendment. Salmon Chase (6th Chief Justice) Holding: The Fourteenth Amendment does not prevent the State of Illinois from regulating charges for use of a business' grain elevators. Morrison Waite (7th Chief Justice) Holding: Manufacturing is not considered an area that can be regulated by Congress pursuant to the commerce clause. Melville Fuller (8th Chief Justice) 1896 Plessy v. Ferguson 1904 Northern Securities Co. v. US 1905 1911 1919 1919 1935 1936 1944 1954 1958 1961 1962 Lochner v. New York Standard Oil Co. v. US Abrams v. US Schenck v. US Schechter v. US US v. Butler Kormeatsu v. US Brown v. Board of Education Cooper v. Aaron Mapp v. Ohio Engel v. Vitale Holding: The "separate but equal" provision of private services mandated by state government is constitutional under the Equal Protection Clause. Holding: The federal government had the right to break up a corporation called the Northern Securities Company. Gave further strength to the Sherman Anti-Trust Act. Melville Fuller (8th Chief Justice) Holding: New York's regulation of the working hours of bakers was not a justifiable restriction of the right to contract freely under the 14th Amendment's guarantee of liberty. Holding: The Standard Oil Company conspired to restrain the trade and commerce in petroleum, and to monopolize the commerce in petroleum, in violation of the Sherman Act, and was split into many smaller companies. Several individuals, including John D. Rockefeller, were fined. Holding: Defendants' criticism of U.S. involvement in World War I was not protected by the First Amendment, because they advocated a strike in munitions production and the violent overthrow of the government. Holding: Defendant's criticism of the draft was not protected by the First Amendment, because it created a clear and present danger to the enlistment and recruiting practices of the U.S. armed forces during a state of war. Holding: Section 3 of the National Industrial Recovery Act was an unconstitutional delegation of legislative power to the Executive, and was not a valid exercise of congressional Commerce Clause power. Second Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed in part, reversed in part. Holding: The Agricultural Adjustment Act is an unconstitutional exercise of power. Holding: The exclusion order leading to Japanese American Internment was constitutional. Edward Douglass White (9th Chief Justice) Charles Evans Hughes (11th Chief Justice) Harlan Stone (12th Chief Justice) Holding: Separate schools are not equal. Overturns Plessy v. Ferguson Holding: States cannot nullify decisions of the federal courts. Holding: Illegally obtained material cannot be used in a criminal trial. Holding: School initiated-prayer in the public school system violates the First Amendment. Earl Warren (14th Chief Justice) 1963 1964 1965 1966 1971 1972 1973 1974 1978 1989 2012 2013 Gideon v. Wainwright Escobedo v. Illinois Griswold v. Connecticut Miranda v. Arizona New York Times v. US Furman v. Georgia Roe v. Wade US v. Nixon University of California v.Bakke Texas v. Johnson National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius Shelby County v. Holder Holding: Indigent defendants must be provided representation without charge. Holding: Where a police investigation begins to focus on a particular suspect who has been refused counsel, his statements to police are excluded. Holding: A Connecticut law criminalizing the use of contraceptives violated the right to marital privacy. Connecticut Supreme Court reversed. Earl Warren (14th Chief Justice) Holding: Police must inform suspects of their rights before questioning. Holding: In order to exercise prior restraint, the Government must show sufficient evidence that the publication would cause a “grave and irreparable” danger. Holding: The arbitrary and inconsistent imposition of the death penalty violates the Eighth and Fourteenth Amendments, and constitutes cruel and unusual punishment. Holding: Texas law making it a crime to assist a woman to get an abortion violated her due process rights. Warren Burger (15th Chief Justice) Holding: The President is not above the law. Holding: The Court held that while affirmative action systems are constitutional, a quota system based on race is unconstitutional. Holding: Even offensive speech such as flag burning is protected by the First Amendment. Holding: Upheld the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act on the basis that Congress has the right to regulate Interstate Commerce. Holding: Overturns section 4 of the Voting Rights Act, 1965. Regions of the nation who needed pre-clearance from the federal government to change polling places no longer need to seek permission. William Rehnquist (16th Chief Justice)