China and Japan During the Imperial Period (text only)
advertisement

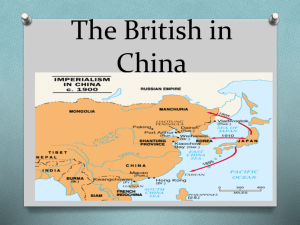
China and Japan in the Imperial Period China and the West: Tea-Opium Connection • Largely self-sufficient – Agriculture • Quick growing rice • Spanish and Portuguese traders brought maize, sweet potatoes, and peanuts from the Americas – Extensive mining and manufacturing industries • Salt, tin, silver, and iron – Trading goods • Silk, cottons, porcelain – Not much interest in Western goods • Only allowed to trade at the port of Guangzhou Opium Wars • Found one good the Chinese would trade for – opium – By 1835, 12 million people were addicted – British refused to stop trading it • Lead to Opium Wars – Mostly fought at sea – Chinese lost because of outdated ships – Forced to sign the Treaty of Nanjing » Gave the British Hong Kong » Foreigners were not subject to Chinese law at Guangzhou and other Chinese ports Taiping Rebellion • Under the Qing Dynasty, population doubled in 60 years but the food production did not – Lead to widespread hunger and anger – Chinese people began to rebel • Taiping Rebellion – Led by Hong Xiuquan – Wanted to build “Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace” • All would share China’s wealth and no one would live in poverty – 1850s, Hong had a peasant army of almost 1,000,000 people • Took control of S. China • 1835 – captured Nanjing and made it his capital – Problems: constant feuding among leaders • British and French also attacked the army • 20,000,000 people (or more) died in the fighting Foreign Influence Grows • Dowager Empress Cixi – Supported the start to reforms • Updated education system, diplomatic service, and military • Sphere of Influence – Japan used the apparent weakness of China to gain a foothold • They needed this in order to gain extra land that wasn’t available in Japan – Open Door Policy • Championed by the US, it said that the “doors” should be open to merchants of all nations • Kept China from being controlled by any one nation Chinese Nationalism • Boxer Rebellion – Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists – Campaigning against the Dowager Empress’s rule and the foreign privilege seen in the country – Attacked Beijing shouting “Death to the Foreign Devils” • Multinational army marched on Beijing and defeated the Boxers – Consequence: Growth of nationalism • Needed to be more resistant to foreign intervention • Government must respond to the needs of the people End of the Tokugawa Shogun • 1600-1853 Japan was isolated • 1853 – Perry and the US – Angry over shipwrecked sailors • TREATY OF KANAGAWA – treaty signed on 31 March 1854, allowing US ships into the ports of Hakodate and Shimoda, where a US consul would also be accepted – First treaty Japan signed with a Western country Japan in the Imperial Period Samurai Rebellion against Western Influence • Sat-Cho (Satsuma – Choshu) Alliance – Defeated by the US – Japan need to militarize to survive • Sat – Cho coup over Tokugawa Shogunate Meiji Restoration • Sat-Cho emperor replaced shogun • Modernize and Westernize – Politics – prefects replace daimyos • Prime Minister and Parliament govern w/ Emperor – Military – based on the Prussian model • Iwakara Mission: Took ideas from other countries: – – – – France – Law Prussia (soon to be Germany) – Military, steel, medicine Britain – navy US – mechanized agriculture Imperial Japan • In short amount of time, Japan modernized and became the greatest military power in Asia – As Japanese power grew, they became more imperialistic – Wanted to show the world they were a powerful nation • Sino-Japanese War – China and Japan saw Korea as an important trading power and military post • Both countries signed a hands-off agreement, saying neither would send armies into Korea – China lied • To help with rebellions, China sent troops into Korea • Japan protested and send its troops in to fight China • Japan easily defeated the Chinese, drove them out of Korea, and gained a foothold in Manchuria • Peace treaty gave Japan Taiwan and the Pescadores Islands Russo-Japanese War • Russia and Japan ended up as major powers after China was defeated – Went to war over Manchuria • Japan launched a surprise attack on Russian ships off the coast of Manchuria • Drove the Russians out of Korea and captured the Russian fleet • 1905 Russia and Japan started peace negotiations – Signed the Treaty of Portsmouth » Gave Japan the captured territories » Forced Russia to withdraw from Manchuria and stay out of Korea