rheumatic heart disease
advertisement

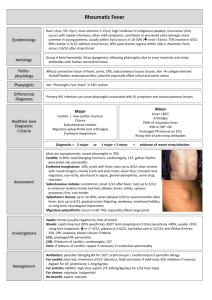
RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE D. HANA OMER OBJECTIVES • To know definition, symptoms, signs, diagnosis of Rheumatic fever. • To know the treatment of Rheumatic fever. • Rheumatic fever is an acute, multisystem inflammatory disease that follows a group A (β-hemolytic) streptococcal (GAS) throat infection. • It is a disease of school-aged children. • The incidence between 5 and 15 years of age. • The most serious aspect of rheumatic fever is :1. chronic valvular disorders . 2. heart failure . PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute stage • The acute stage of rheumatic fever includes a history of an initiating streptococcal infection and subsequent involvement of the connective tissue of the heart, blood vessels, joints, and subcutaneous tissues. • It is characterized by present of lesion called the Aschoff body ( which is a localized area of tissue necrosis surrounded by immune cells in the heart valve) . the Aschoff body the Aschoff body recurrent phase • The recurrent phase usually involves extension of the cardiac effects of the disease. chronic phase • The chronic phase of rheumatic fever is characterized by permanent deformity of the heart valves and is a common cause of mitral valve stenosis . • Chronic rheumatic heart disease usually does not appear until at least 10 years after the initial attack . Clinical features • • • • • • • • Symptoms before the onset of rheumatic fever :Sore throat . headache. Fever . abdominal pain . nausea. vomiting . swollen glands (usually at the angle of the jaw). Clinical features • Clinical features associated with an acute episode of rheumatic fever :• Carditis . • Migratory polyarthritis of the large joints . • Erythema marginatum . • Subcutaneous nodules . • Sydenham’s chorea. Carditis. • The carditis can affect the pericardium, myocardium, or endocardium, and all of these layers of the heart usually are involved. • The involvement of the endocardium and valvular structures produces the permanent and disabling effects of rheumatic fever. • Although any of the four valves can be involved, the mitral and aortic valves are affected most often. • During the acute inflammatory stage of the disease, the valvular structures become red and swollen; small vegetative lesions develop on the valve leaflets . • small vegetative lesions develop on the valve leaflets . • development of fibrous scar tissue . • deformity of the valve leaflets and shortening of the chordae tendineae. • 1. 2. 3. 4. The manifestations of acute rheumatic carditis include :heart murmur . Cardiomegaly . friction rub . congestive heart failure . Carditis . Arthritis • The arthritis involves the larger joints, particularly the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists . • It is almost always is migratory, affecting one joint and then moving to another. • It is usually response (usually within 48 hours) to salicylates. migratory polyarthritis of the large joints Erythema marginatum • lesions are maplike, macular areas most commonly seen on the trunk or inner aspects of the upper arm and thigh. • they are transitory and disappear during the course of the disease. erythema marginatum subcutaneous nodules • The subcutaneous nodules are 1 to 4 cm in diameter. • They are hard, painless, and freely movable and usually overlie the extensor muscles of the wrist, elbow, ankle, and knee joints. subcutaneous nodules . Sydenham’s chorea • Is the major central nervous system manifestation. • It is seen most frequently in girls. • The choreic movements are spontaneous, rapid, purposeless, jerking movements that interfere with voluntary activities. • The chorea is self-limited, usually running its course within a matter of weeks or months. Sydenham’s chorea. Diagnosis Treament • 1. 2. 3. The treatment is based on :Antibiotics . Anti-inflammatory drugs . selective restriction of physical activities are prescribed. • Penicillin also is the antibiotic of choice for treating the acute illness. • Salicylates and corticosteroids are used as apain killer and disease control . • Penicillin is the treatment of choice for secondary prophylaxis, but sulfadiazine or erythromycin may be used in penicillinallergic individuals . • The duration of prophylaxis could extend to 10 years . THANK YOU